| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
mAChR; Muscarinic receptors (M1-M5):Competitive antagonist with varying affinities. Ki values for M1-M5 receptors: 1.3 nM (M1), 0.8 nM (M2), 0.14 nM (M3), 2.4 nM (M4), 0.7 nM (M5). [2]
- Voltage-dependent K+ channels (Kv):Inhibits Kv channels in coronary arterial smooth muscle cells with an IC50 of approximately 2.5 μM. [1] Central muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (M1-M5), Ki values: M1 (1.2 nM), M2 (3.4 nM), M3 (0.8 nM), M4 (2.1 nM), M5 (2.7 nM) [2] - Voltage-dependent K+ channels (Kv channels) in coronary arterial smooth muscle cells [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
- 毒蕈碱受体结合:奥昔布宁对M3受体亲和力最高(Ki = 0.14 nM),对M2和M5受体亲和力中等(Ki分别为0.8 nM和0.7 nM),对M1和M4受体亲和力较低(Ki分别为1.3 nM和2.4 nM)。[2]
- Kv通道抑制:在冠状动脉平滑肌细胞的膜片钳实验中,奥昔布宁以浓度依赖方式可逆性抑制Kv电流,IC50为2.5 μM。这种抑制导致膜去极化和钙内流增加。[1] 在冠状动脉平滑肌细胞中,奥昔布宁(0.1、0.3、1、3、10、30、100 μM;200 ms)以浓度依赖性方式抑制血管Kv通道,而不影响抗胆碱能作用[1]。 在分离的冠状动脉平滑肌细胞中,奥昔布宁(1 μM、10 μM、100 μM)呈浓度依赖性抑制电压依赖性钾通道电流。100 μM浓度时,Kv通道峰值电流幅度较对照组下降68%,且对通道的稳态激活和失活曲线无显著影响 [1] - 在中枢毒蕈碱受体结合实验中,奥昔布宁对M3受体亲和力最高(Ki=0.8 nM),对其他毒蕈碱亚型(M1、M2、M4、M5)呈中等亲和力。它可竞争性置换放射性标记毒蕈碱激动剂与受体的结合,总毒蕈碱受体结合的IC50值为1.5 nM [2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
中枢毒蕈碱受体占有率:在小鼠中,奥昔布宁以0.3、1、3和10 mg/kg的剂量腹腔注射给药。30分钟后取脑,通过[3H]-NMS结合实验测量受体占有率。10 mg/kg剂量下,奥昔布宁对中枢毒蕈碱受体的占有率为71%,显著高于同剂量的托特罗定(35%)和达非那新(15%)。[2]
当 0.5 和 2 小时后发生特异性 [3H]N-甲基东莨菪碱结合时,奥昔布宁(27.2 mg/kg;口服;单次)显着结合小鼠脑部毒蕈碱受体,使 Kd 值增加约两倍[2]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
本研究证明了抗胆碱能药物奥昔布宁对兔冠状动脉平滑肌细胞电压依赖性K+(Kv)通道的抑制作用。奥昔布宁以浓度依赖的方式抑制血管Kv通道,IC50值为11.51±0.38μmol/L,Hill系数(n)为2.25±0.12。奥昔布宁的应用使活化曲线向右移动,失活曲线向左移动。Kv1.5亚型抑制剂DPO-1和Kv2.1亚型抑制剂广西毒素预处理抑制了奥昔布宁诱导的Kv电流抑制。然而,应用Kv7亚型抑制剂利诺哌啶不会影响奥昔布宁对Kv电流的抑制。抗胆碱能药物阿托品既不抑制Kv电流,也不影响奥昔布宁诱导的Kv电流抑制。根据这些结果,我们得出结论,奥昔布宁通过影响稳态激活和失活曲线,以浓度依赖的方式抑制血管Kv电流,而与其抗胆碱能作用无关[1]。
中枢毒蕈碱受体结合实验:从大鼠脑组织中制备富含M1-M5受体的膜组分,将其与系列浓度的奥昔布宁在氚标记毒蕈碱激动剂存在下共同孵育。25°C孵育90分钟后,通过玻璃纤维滤膜过滤去除未结合配体,采用液体闪烁计数器检测结合组分的放射性,通过非线性回归分析计算各毒蕈碱亚型的Ki值 [2] - 电压依赖性钾通道活性实验:通过酶解法分离冠状动脉平滑肌细胞,将其置于记录槽中。采用膜片钳技术(全细胞模式)记录Kv通道电流,在细胞外液中加入1 μM、10 μM、100 μM浓度的奥昔布宁,记录给药前后阶梯去极化(从-80 mV至+60 mV)诱发的电流反应,评估抑制效果 [1] |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[1]
细胞类型:冠状动脉平滑肌细胞(来自雄性新西兰白兔) 测试浓度: 10 μM 孵育时间: 200 ms 实验结果: 2分钟内快速抑制Kv电流,+60 Mv时Kv电流降低44%。通过改变 Kv 通道的门控特性来抑制 Kv 电流。 细胞活力测定[1] 细胞类型:冠状动脉平滑肌细胞(来自雄性新西兰白兔) 测试浓度: > 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10, 30, 100 μM 孵育时间: 200 ms 实验结果: 降低 Kv 电流幅度浓度依赖性,IC50值为11.51 μM。 毒蕈碱受体结合实验:将表达毒蕈碱受体的组织膜制剂与放射性标记配体(如[3H]-NMS)在不同浓度的奥昔布宁存在下共同孵育。分离结合态和游离态配体,测量放射性以确定结合亲和力。[2] - 膜片钳电生理实验:分离冠状动脉平滑肌细胞,采用全细胞模式进行电压钳制。细胞外施加奥昔布宁,记录Kv电流变化。绘制浓度-反应曲线以计算IC50。[1] 冠状动脉平滑肌细胞分离及Kv通道实验:从实验动物体内分离冠状动脉,通过酶解法获得平滑肌细胞,将细胞接种于盖玻片上,静置2-4小时使其贴壁。在浴液中加入奥昔布宁,使用膜片钳放大器记录全细胞Kv电流,绘制电流-电压关系曲线和浓度-反应曲线,分析奥昔布宁的抑制作用 [1] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male ddY strain mice (9 to 13weeks old)[2].
Doses: 27.2 mg/kg (76.1 µmol/kg) Route of Administration: Oral administration; single. Experimental Results: Significant increased Kd values for specific [3H]NMS binding in Significant increased Kd values for specific [3H]NMS binding in mouse cerebral cortex with values of 120% and 71.2% when at 0.5 and 2 hrs (hours), respectively. Central muscarinic receptor binding study:Mice are randomly assigned to groups receiving oxybutynin (0.3, 1, 3, 10 mg/kg), tolterodine, darifenacin, or vehicle (intraperitoneal injection). Thirty minutes after administration, mice are euthanized, and brains are rapidly removed. Brain membranes are prepared and incubated with [3H]-NMS to measure specific binding. The percentage of receptor occupancy by oxybutynin is calculated by comparing binding in drug-treated vs. vehicle-treated mice. [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Oxybutynin should be swallowed whole with the help of liquids. A pharmacokinetic study revealed that oxybutynin was rapidly absorbed, and peak concentrations were reached within about 1 hour of administration, measured at 8.2 ngml-1 and AUC was 16 ngml-1. The biovailability of oxybutynin is about 6%, and the plasma concentration of the active metabolite, desethyloxybutynin is 5 to 12 times greater than that of oxybutynin. Bioavailability is increased in the elderly. Food has been shown to increase the exposure to controlled-release oxybutynin. Oxybutynin is heavily cleared by the liver. Under 0.1% of an administered dose is found as unchanged drug in the urine. Less than 0.1% of a single dose of oxybutynin is excreted as desethyloxybutynin. Oxybutynin has a wide volume of distribution of 193 L. In rats, oxybutynin penetrates the central nervous system. Metabolism / Metabolites Oxybutynin is heavily metabolized by the CYP3A4 enzyme system in both the liver and the wall of the intestine. It undergoes first-pass metabolism, and its resulting primary active metabolite, N-desethyloxybutynin circulates. It is active at the muscarinic receptors in both the bladder and the salivary gland. Hepatic biotransformation also produces its major inactive metabolite, phenylcyclohexylglycolic acid. Biological Half-Life The plasma elimination half-life is about 2 hours. In the elderly, the elimination half-life is prolonged up to 5 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In multiple, large clinical trials of oxybutynin therapy for overactive bladder syndrome, serum enzyme elevations were rare and no more frequent than with placebo, and there were no episodes of clinically apparent liver injury. Since its approval and widespread use for more than four decades, there has been only a single published case of suspected liver injury attributed to oxybutynin – a report of transient serum enzyme elevations without jaundice or apparent symptoms in a patient with a severe ischemic stroke arising within weeks of starting oxybutynin. Thus, clinically apparent liver injury from oxybutynin is very rare if it occurs at all. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of oxybutynin during breastfeeding. Long-term use of oxybutynin might reduce milk production or milk letdown, but a single dose is not likely to interfere with breastfeeding. During long-term use, observe for signs of decreased lactation (e.g., insatiety, poor weight gain). ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Anticholinergics can inhibit lactation in animals, apparently by inhibiting growth hormone and oxytocin secretion. Anticholinergic drugs can also reduce serum prolactin in nonnursing women. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. The manufacturer reports that cases of lactation suppression have been reported with some oxybutynin (immediate-release) formulations in postmarketing surveillance. Protein Binding Oxybutynin enantiomers are more than 97% bound to plasma proteins, primarily to alpha-1 acid glycoprotein. Toxicity Summary If an overdose of oxybutynin is suspected, a medical professional should be sought for immediate care. Symptoms of oxybutynin overdose may include central nervous system overactivity, fever, cardiac arrhythmias, vomiting, respiratory failure, paralysis, and coma. The treatment for oxybutynin overdose typically involves supportive care from healthcare providers. In some cases, medical professionals may consider administering activated charcoal to patients to help absorb the excess medication in their digestive system. Alternatively, a cathartic agent might be used to promote bowel movements in patients to facilitate the elimination of the drug from the body. There have been 2 reported cases of drug overdose due to the consumption of 100 mg of oxybutynin: 1 case involved a 13-year-old boy, and the other case involved a 34-year-old woman. In addition, there was another report of simultaneous alcohol ingestion with the medication. In another case, a 4-year-old boy experienced a drug overdose and central anticholinergic syndrome after taking 17 mg of oxybutynin over 12 hours. Patients in all the above cases completely recovered after receiving supportive care from healthcare professionals. The controlled-release formulation of oxybutynin contains insoluble contents, which may result in the formation of bezoars. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Oxybutynin is a racemate comprising equimolar amounts of (R)-oxybutynin and esoxybutynin. An antispasmodic used for the treatment of overactive bladder. It has a role as a muscarinic antagonist, a muscle relaxant, an antispasmodic drug, a parasympatholytic, a calcium channel blocker and a local anaesthetic. It is a tertiary amino compound and a racemate. It contains an esoxybutynin and a (R)-oxybutynin.
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a common condition negatively impacting the lives of millions of patients worldwide. Due to its urinary symptoms that include nocturia, urgency, and frequency, this condition causes social embarrassment and a poor quality of life. Oxybutynin, also marketed as Ditropan XL, is an anticholinergic medication used for the relief of overactive bladder symptoms that has been optimized for high levels of safety and efficacy since initial FDA approval in 1975. This drug relieves undesirable urinary symptoms, increasing the quality of life for patients affected by OAB. It is often used as first-line therapy for OAB. Oxybutynin is a Cholinergic Muscarinic Antagonist. The mechanism of action of oxybutynin is as a Cholinergic Muscarinic Antagonist. Oxybutynin is a synthetic anticholinergic agent that is used for treatment of urinary incontinence and overactive bladder syndrome. Oxybutynin has not been implicated in causing liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent acute liver injury. Oxybutynin is a tertiary amine possessing antimuscarinic and antispasmodic properties. Oxybutynin blocks muscarinic receptors in smooth muscle, hence inhibiting acetylcholine binding and subsequent reduction of involuntary muscle contractions. Oxybutynin is used to reduce bladder contractions by relaxing bladder smooth muscle. See also: Oxybutynin Chloride (has salt form). Drug Indication Oxybutynin is indicated for the symptomatic treatment of overactive bladder, which causes urge urinary incontinence and frequency, and urgency. Oxybutynin may also be used for children aged 6 and above for the symptomatic management of detrusor muscle overactivity which has been found to be related to a neurological condition. Spina bifida is an example of a neurological condition in which oxybutynin may be used to control urinary symptoms. On occasion, oxybutynin may be used off-label to relieve bladder spasms associated with ureteral stents or urinary catheters. Symptomatic treatment of urge incontinence and/or increased urinary frequency and urgency as may occur in adult patients with unstable bladder. Mechanism of Action Oxybutynin acts to relax the bladder by inhibiting the muscarinic action of acetylcholine on smooth muscle, and not skeletal muscle. The active of oxybutynin is metabolite is N-desethyloxybutynin. It competitively inhibits the postganglionic type 1, 2 and 3 muscarinic receptors. The above actions lead to increased urine capacity in the bladder, decreasing urinary urgency and frequency. In addition, oxybutynin delays the initial desire to void. RESULTS OF CYSTOMETRIC STUDIES SHOWED THAT THE DRUG INCR BLADDER CAPACITY @ ONSET OF FIRST CONTRACTION & FIRST DESIRE TO VOID, AS WELL AS @ END OF CYSTOMETRY. /CHLORIDE/ - Mechanism of action:Oxybutynin exerts its anticholinergic effects by competitively blocking muscarinic receptors, particularly M3 receptors in the bladder, reducing detrusor muscle contractions. Its higher central muscarinic receptor occupancy compared to tolterodine and darifenacin may contribute to central nervous system-related side effects. [2] - Clinical use:Approved for the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome, alleviating symptoms such as urinary frequency, urgency, and incontinence. [2] Oxybutynin is an anticholinergic drug primarily used for the treatment of overactive bladder [2] - Its pharmacological effects are mediated by competitive antagonism of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (especially M3 subtype) and inhibition of voltage-dependent K+ channels in certain smooth muscle cells [1][2] - Compared to tolterodine and darifenacin, Oxybutynin exhibits higher affinity for central muscarinic receptors, which may be associated with its central nervous system-related side effects [2] - The inhibition of coronary arterial smooth muscle Kv channels by Oxybutynin may contribute to its potential cardiovascular effects [1] |
| 分子式 |
C22H31NO3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
357.49
|
| 精确质量 |
357.23
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 73.92; H, 8.74; N, 3.92; O, 13.43
|
| CAS号 |
5633-20-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Oxybutynin;5633-20-5;Oxybutynin chloride;1508-65-2;(R)-Oxybutynin hydrochloride;1207344-05-5;Oxybutynin-d11 chloride;1185151-95-4; Oxybutynin;5633-20-5;(R)-Oxybutynin hydrochloride;1207344-05-5;Oxybutynin-d11 chloride;1185151-95-4;(R)-Oxybutynin;119618-21-2; 5633-20-5 (racemate); 1508-65-2 (racemate HCl); 1207344-05-5 (R-isomer HCl); 119618-21-2 (R-isomer); 2738613-22-2 (R-isomer citrate); 119618-22-3 (S-isomer); 2862851-81-6 (R-isomer tartrate); 230949-16-3 (S-isomer HCl)
|
| PubChem CID |
4634
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as White to off-white solids at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
494.4±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
125 - 130ºC
|
| 闪点 |
252.8±28.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.546
|
| LogP |
5.19
|
| tPSA |
49.77
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
26
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
490
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
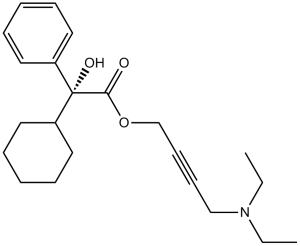
| SMILES |
O([H])C(C(=O)OC([H])([H])C#CC([H])([H])N(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])(C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=1[H])C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H]
|
| InChi Key |
XIQVNETUBQGFHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H31NO3/c1-3-23(4-2)17-11-12-18-26-21(24)22(25,19-13-7-5-8-14-19)20-15-9-6-10-16-20/h5,7-8,13-14,20,25H,3-4,6,9-10,15-18H2,1-2H3
|
| 化学名 |
4-(diethylamino)but-2-ynyl 2-cyclohexyl-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetate
|
| 别名 |
Ditropan, Lyrinel XL, Lenditro,Oxybutynin, Ditropan; 5633-20-5; Oxibutinina; Cystrin; Oxytrol; Oxibutyninum; kentera; Oxybutynine; Oxybutyninum; Uripan
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.08 mg/mL (5.82 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.82 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.82 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7973 mL | 13.9864 mL | 27.9728 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5595 mL | 2.7973 mL | 5.5946 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2797 mL | 1.3986 mL | 2.7973 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05637671 | Recruiting | Drug: oxybutynin ER Drug: Paroxetine CR |
Vasomotor Symptoms | Cairo University | February 10, 2022 | Phase 3 |
| NCT03952299 | Recruiting | Drug: Oxybutynin Transdermal Patch Drug: Oral Oxybutynin |
Overactive Bladder Syndrome Neuropathic Bladder |
University of California, Davis | September 1, 2021 | Phase 3 |
| NCT01855256 | Completed | Drug: Oxybutynin Drug: Placebo |
Hyperhidrosis | University Hospital, Brest | June 2013 | Phase 3 |
| NCT01310712 | Completed | Drug: Oxybutynin Drug: placebo |
Hyperhidrosis | University of Sao Paulo | December 2010 | Phase 4 |
| NCT02538302 | Completed | Drug: Minirin Drug: Oxybutynin |
Nocturnal Enuresis | Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences | July 2013 | Phase 3 |