| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
mAChR3/muscarinic acetylcholine receptor
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
分别使用光学显微镜和 MTT 测定评估人角膜基质 (HCS) 细胞的形态和活力,以评估毛果芸香碱的细胞毒性。根据形态学数据,暴露于浓度在 0.625 至 20 g/L 之间的毛果芸香碱的 HCS 细胞表现出形态学异常,例如细胞收缩、细胞质空泡化、从培养基质脱离,最终死亡,以及剂量和时间依赖性增殖迟缓。观察。然而,对照组和暴露于低于 0.625 g/L 浓度的毛果芸香碱的对照组之间没有明显差异。 MTT法结果显示,浓度高于0.625 g/L的毛果芸香碱处理后,HCS细胞的细胞活力随着时间和浓度的增加而降低(P<0.01或0.05),而浓度低于0.625 g/L的毛果芸香碱处理的HCS细胞则随时间和浓度的增加而降低(P<0.01或0.05)。 g/L 与对照没有显着差异[2]。部分毒蕈碱激动剂毛果芸香碱的 EC50 为 2.4 mM,可在已用 Penylephrine(10 至 200 nM)收缩的离体大鼠尾动脉段中诱导浓度依赖性松弛[3]。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
检查的是运动大鼠(EX)和对照大鼠(CN)响应毛果芸香碱而分泌的唾液。毛果芸香碱在 EX 大鼠中诱导的唾液量显着高于 CN 大鼠(P<0.01)。另一方面,EX大鼠唾液中的Na+浓度明显低于CN大鼠(P<0.05)[1]。
|
||
| 细胞实验 |
用浓度为0.15625g/L至20.0g/L的毛果芸香碱处理HCS细胞后,通过光学显微镜和MTT法检测其形态和存活率。通过吖啶橙(AO)/溴化乙锭(EB)双重染色检测膜通透性、DNA断裂和超微结构。通过流式细胞术(FCM)测定DNA电泳和透射电子显微镜(TEM)、细胞周期、磷脂酰丝氨酸(PS)取向和线粒体跨膜电位(MTP)。ELISA检测胱天蛋白酶的激活[3]。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following oral administration of pilocarpine 5mg three times daily in healthy male subjects, peak plasma drug concentrations of 15μg/L were reached in 1.25 hours. At the dose of pilocarpine 10mg three times daily, peak plasma drug concentrations of 41μg/L were reached in 0.85 hours. The rate of absorption is increased when taken with food. Following ophthalmic administration in healthy subjects, the overall median Tmax was 2.2 hours. The mean (SD) Cmax and AUC0-t were 897.2 (287.2) pg/mL and 2699 (741.4) hr x pg/mL, respectively. In patients with presbyopia, the mean Cmax and AUC0-t,ss values were 1.95 ng/mL and 4.14 ng x hr/mL, respectively. The median Tmax was 0.3 hours postdose with a range from 0.2 to 0.5 hours post-dose. Pilocarpine and its degradation products are eliminated predominantly in the urine. There is no information available. There is no information available. LITTLE DEFINITIVE INFORMATION IS AVAIL ON FATE & ELIMINATION OF PILOCARPINE. IT IS PARTLY DESTROYED IN BODY, BUT LARGER FRACTION IS EXCRETED IN URINE IN COMBINED FORM. PILOCARPINE PENETRATES EYE WELL; AFTER TOPICAL INSTILLATION... POISONING HAS OCCURRED FROM CUTANEOUS ABSORPTION. Metabolism / Metabolites There is limited information available about the metabolism of pilocarpine in humans. Inactivation of pilocarpine can occur at neuronal synapses and probably in plasma. Pilocarpine is reported to undergo CYP2A6-mediated 3-hydroxylation to form stereoisomers of 3-hydroxypilocaripine. Pilocaripine also undergoes hydrolysis mediated by paraoxonase 1, a calcium-dependent esterase in plasma and the human liver. Pilocarpic acid is a possible metabolic product of hydrolysis. Pilocarpine metabolites are reported to possess negligible or no pharmacological activity. Pilocarpine has known human metabolites that include 3-hydroxypilocarpine. Possibly occurs at the neuronal synapses and in the plasma Half Life: 0.76 hours Biological Half-Life The elimination half-life was 0.76 and 1.35 hours following administration of a 5mg or lOmg dose 3 times daily, respectively. Following ophthalmic administration in healthy subjects, the half-life was 3.96 hours. |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In clinical trials of pilocarpine, serum enzyme elevations were uncommon and no more frequent than with placebo. Despite, wide scale use, there have been no published reports of acute liver injury attributable to pilocarpine. Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Limited information indicates that maternal use of ophthalmic pilocarpine did not adversely affect the breastfed infant. If ophthalmic pilocarpine is used during breastfeeding, monitor the infant for signs of cholinergic excess (diarrhea, lacrimation, and excessive salivation or urination), especially in younger, exclusively breastfed infants. To substantially diminish the amount of drug that reaches the breastmilk after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue. Because no information is available on the use of oral pilocarpine during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A woman with glaucoma used a pilocarpine insert (Ocusert; strength not specified) in one eye while nursing (extent not stated) her newborn infant for 9 weeks. No adverse reactions were noted in the infant.[1] A mother who was taking pilocarpine eye drops (concentration not stated) twice daily as well as 2 drops of timolol 0.5% eye drops daily and acetazolamide 250 mg orally twice daily and delivered a preterm infant at 36 weeks of gestation. The infant began 5 months of exclusive breastfeeding at 6 hours after birth. On day 2, the infant developed electrolyte abnormalities consisting of hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, and metabolic acidosis. The infant was treated with oral calcium gluconate and a single dose of intramuscular magnesium sulfate. Despite continued breastfeeding and maternal drug therapy, the infant's mild metabolic acidosis disappeared on day 4 of life and the infant was gaining weight normally at 1, 3 and 8 months, but had mild hypotonicity. The authors considered the metabolic effects to be caused by transplacental passage of acetazolamide that resolved despite the infant being breastfed. The infant gained weight adequately during breastfeeding, but had some mild, residual hypertonicity of the lower limbs requiring physical therapy.[2] ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information in nursing mothers was not found as of the revision date. In animals, cholinergic drugs increase oxytocin release,[3] and have variable effects on serum prolactin.[4] Other centrally acting cholinergic drugs increase serum prolactin in humans.[5][6] The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. Protein Binding Pilocarpine does not bind to human or rat plasma proteins over a concentration range of 5 to 25,000 ng/mL. The effect of pilocarpine on plasma protein binding of other drugs has not been evaluated. |
||
| 参考文献 |
|
||
| 其他信息 |
Pilocarpine hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt of (+)-pilocarpine, a medication used to treat increased pressure inside the eye and dry mouth. It contains a (+)-pilocarpine.
Pilocarpine Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt of a natural alkaloid extracted from plants of the genus Pilocarpus with cholinergic agonist activity. As a cholinergic parasympathomimetic agent, pilocarpine predominantly binds to muscarinic receptors, thereby inducing exocrine gland secretion and stimulating smooth muscle in the bronchi, urinary tract, biliary tract, and intestinal tract. When applied topically to the eye, this agent stimulates the sphincter pupillae to contract, resulting in miosis; stimulates the ciliary muscle to contract, resulting in spasm of accomodation; and may cause a transitory rise in intraocular pressure followed by a more persistent fall due to opening of the trabecular meshwork and an increase in the outflow of aqueous humor. A slowly hydrolyzed muscarinic agonist with no nicotinic effects. Pilocarpine is used as a miotic and in the treatment of glaucoma. See also: Pilocarpine (has active moiety); Betaxolol hydrochloride; pilocarpine hydrochloride (component of). (+)-pilocarpine is the (+)-enantiomer of pilocarpine. It has a role as an antiglaucoma drug. It is an enantiomer of a (-)-pilocarpine. A naturally occurring alkaloid derived from the Pilocarpus plants, pilocarpine is a muscarinic acetylcholine agonist. Pilocarpine is associated with parasympathomimetic effects by selectively working on muscarinic receptors. Pilocarpine is used to treat dry mouth and various ophthalmic conditions, including elevated intraocular pressure and glaucoma. The usage of glaucoma by pilocarpine dates back to 1875. Pilocarpine is a Cholinergic Receptor Agonist. The mechanism of action of pilocarpine is as a Cholinergic Agonist, and Cholinergic Muscarinic Agonist. Pilocarpine is an orally available cholinergic agonist that is used to treat symptoms of dry mouth in patients with keratoconjunctivitis sicca (Sjögren syndrome) or with xerostomia (dry mouth) due to local irradiation. Pilocarpine has not been linked to serum enzyme elevations during therapy or to instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Pilocarpine has been reported in Pilocarpus microphyllus, Pilocarpus racemosus, and other organisms with data available. Pilocarpine is a natural alkaloid extracted from plants of the genus Pilocarpus with cholinergic agonist activity. As a cholinergic parasympathomimetic agent, pilocarpine predominantly binds to muscarinic receptors, thereby inducing exocrine gland secretion and stimulating smooth muscle in the bronchi, urinary tract, biliary tract, and intestinal tract. When applied topically to eyes, this agent stimulates the sphincter pupillae to contract, resulting in miosis; stimulates the ciliary muscle to contract, resulting in spasm of accommodation; and may cause a transitory rise in intraocular pressure followed by a more persistent fall due to opening of the trabecular meshwork and an increase in the outflow of aqueous humor. Pilocarpine is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is a slowly hydrolyzed muscarinic agonist with no nicotinic effects. Pilocarpine is used as a miotic and in the treatment of glaucoma. [PubChem]Pilocarpine is a cholinergic parasympathomimetic agent. It increase secretion by the exocrine glands, and produces contraction of the iris sphincter muscle and ciliary muscle (when given topically to the eyes) by mainly stimulating muscarinic receptors. A slowly hydrolyzed muscarinic agonist with no nicotinic effects. Pilocarpine is used as a miotic and in the treatment of glaucoma. See also: Pilocarpine Hydrochloride (has salt form). Drug Indication Pilocarpine oral tablets are indicated for the treatment of dry mouth caused by Sjogren's Syndrome or radiotherapy for cancer of the head and neck. Pilocarpine ophthalmic formulations are used to treat presbyopia in adults, reduce elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension, manage acute angle-closure glaucoma, prevent postoperative elevated IOP associated with laser surgery, and induce miosis. Mechanism of Action The muscarinic M3 receptor is expressed in various endocrine and exocrine glands, including the gastric and salivary glands. It is also found in smooth muscle cells in pupillary sphincter and ciliary bodies. The M3 receptor is a Gq-protein-coupled receptor that activates phospholipase C and upregulates inositol trisphosphate and intracellular calcium. M3 receptor activation has been implicated in smooth muscle contraction and the stimulation of salivary glands. Pilocarpine is an agonist for M1 and M2 receptors, and is a full and partial agonist at the M3 receptor. ...ACT PRIMARILY @ MUSCARINIC RECEPTORS OF AUTONOMIC EFFECTOR CELLS, GANGLIONIC EFFECTS CAN ALSO BE OBSERVED. THIS IS PARTICULARLY TRUE OF PILOCARPINE, ALTHOUGH ITS GANGLIONIC ACTION ALSO INVOLVES STIMULATION OF MUSCARINIC RECEPTORS... ...AFTER TOPICAL INSTILLATION, MIOSIS BEGINS IN 15 TO 30 MIN & LASTS 4 TO 8 HR. REDUCTION OF INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE IS MAXIMAL IN 2 TO 4 HR, WHICH CORRELATES WITH MAX DECR IN OUTFLOW RESISTANCE. EFFECT ON INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE OUTLASTS EFFECT ON OUTFLOW FACILITY...PILOCARPINE...MAY DECR AQUEOUS PRODUCTION. ...PILOCARPINE /HAS AS/...PRINCIPAL ACTION STIMULATION OF SAME AUTONOMIC EFFECTOR CELLS AS THOSE ACTED UPON BY CHOLINERGIC POSTGANGLIONIC NERVE IMPULSES. ...PILOCARPINE...PRINCIPAL ACTION STIMULATION OF SAME AUTONOMIC EFFECTOR CELLS AS THOSE ACTED UPON BY CHOLINERGIC POSTGANGLIONIC NERVE IMPULSES. IN THIS RESPECT...RESEMBLE CHOLINE ESTERS... |
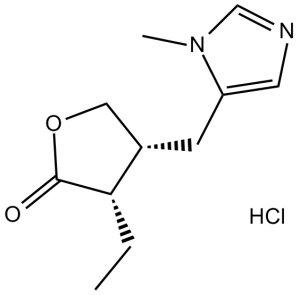
| 分子式 |
C11H16N2O2.HCL
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
244.72
|
|
| 精确质量 |
208.121
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 53.99; H, 7.00; Cl, 14.49; N, 11.45; O, 13.08
|
|
| CAS号 |
54-71-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Pilocarpine;92-13-7;Pilocarpine nitrate;148-72-1;Pilocarpine-d3 hydrochloride;1217838-88-4
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5909
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as white to off-white solids at room temperature
|
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
431.8±18.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
202-205 °C(lit.)
|
|
| 闪点 |
215.0±21.2 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.585
|
|
| LogP |
-0.09
|
|
| tPSA |
44.12
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
16
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
245
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
|
| SMILES |
Cl[H].O1C([C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])[C@]([H])(C1([H])[H])C([H])([H])C1=C([H])N=C([H])N1C([H])([H])[H])=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
RNAICSBVACLLGM-GNAZCLTHSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C11H16N2O2.ClH/c1-3-10-8(6-15-11(10)14)4-9-5-12-7-13(9)2;/h5,7-8,10H,3-4,6H2,1-2H3;1H/t8-,10-;/m0./s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
(3S,4R)-3-ethyl-4-[(3-methylimidazol-4-yl)methyl]oxolan-2-one;hydrochloride
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: (1). 该产品在溶液状态不稳定,请现配现用。 (2). 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (8.50 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (8.50 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (8.50 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 130 mg/mL (531.22 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0863 mL | 20.4315 mL | 40.8630 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8173 mL | 4.0863 mL | 8.1726 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4086 mL | 2.0432 mL | 4.0863 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。