| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Chk1 (Ki = 0.9 nM); Chk1 (IC50 <1 nM); Chk2 (IC50 = 8 nM)
Checkpoint Kinase 1 (CHK1) (IC50 = 0.9 nM for recombinant human CHK1 kinase activity; Ki = 0.3 nM; >100-fold selectivity over CHK2, CDK1, and 50+ other kinases) [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Prexasertib(也称为 LY2606368)是一种新型、有效、选择性和 ATP 竞争性 CHK1(检查点激酶 1)蛋白激酶抑制剂,对 CHK1 和 CHK2 的 IC50 值分别<1 nM 和 8 nM。 CHK1 是一种多功能蛋白激酶,对于细胞对 DNA 损伤的反应和活性复制叉数量的控制都是不可或缺的。由于 CHK1 在细胞周期中建立 DNA 损伤检查点方面的作用,CHK1 抑制剂目前正在作为化学增效剂进行研究。 Prexasertib 作为单一药物会导致双链 DNA 断裂,同时消除 DNA 损伤检查点的保护。 Prexasertib 的作用取决于 CHK1 的抑制以及 CDK2 CDC25A 激活的相应增加,这增加了复制叉的数量,同时降低了其稳定性。用 Prexasertib 处理细胞会导致 S 期细胞群中快速出现 TUNEL 和 pH2AX 阳性双链 DNA 断裂。 Prexasertib 在异种移植肿瘤模型中显示出类似的活性,从而导致显着的肿瘤生长抑制。总之,Prexasertib 是一类通过复制灾难来治疗癌症的新型药物的有力代表。激酶测定:Prexasertib (LY2606368) 有效且选择性地抑制 CHK1,IC50 小于 1 nM,并且还抑制 CHK2,IC50 为 8 nM。 LY2606368 通过丝氨酸 296 自磷酸化对 CHK1 活性的 EC50 为 1 nM,对 HT-29 CHK2 自磷酸化 (S516) 的 EC50 <31 nM。 LY2606368 可有效消除 p53 缺陷型 HeLa 细胞中阿霉素激活的 G2-M 检查点,EC50 为 9 nM。然而,100 nM LY2606368 不会抑制 PMA 刺激的 RSK,而是微弱地刺激丝氨酸 235/236 上 S6 的磷酸化。 LY2606368 对 U-2 OS、Calu-6、HT-29、HeLa 和 NCI-H460 细胞系具有广泛的抗增殖作用,IC50 分别为 3 nM、3 nM、10 nM、37 nM 和 68 nM。 LY2606368 (4 nM) 导致细胞周期群体从 G1 和 G2-M 向 S 期发生大幅转变,同时诱导 U-2 OS 细胞中的 H2AX 磷酸化。 LY2606368 (25 μM) 对 AGS 和 MKN1 细胞的增殖具有抑制活性。 LY2606368 (20 nM) 抑制 DR-GFP 细胞的 HR 修复能力。 LY2606368 (5 nM) 与 PARP 抑制剂 BMN673 组合,在胃癌细胞中显示出协同抗癌作用。细胞检测:采用MTS细胞增殖比色检测试剂盒检测BMN673和LY2606368的CHK1消融的增殖抑制作用、IR敏感性、抗癌作用。将细胞接种到96孔细胞培养板中,按照规定的实验条件处理,然后向每孔中加入20 μL MTS试剂,孵育2小时后,在酶标仪上以490 nM的波长检测每孔的细胞活力。
Prexasertib (LY2606368)(0.01-10 nM)剂量依赖性抑制重组CHK1激酶活性,5 nM浓度下抑制率达95%;10 nM时在HCT116细胞中阻断CHK1介导的CDC25C(Ser216)磷酸化,抑制率80% [1] - Prexasertib (LY2606368) 抑制多种人类癌细胞系增殖:72小时后,HCT116结直肠癌GI50 = 0.3 μM,A549肺癌GI50 = 0.5 μM,MDA-MB-231乳腺癌GI50 = 0.4 μM,PC-3前列腺癌GI50 = 0.6 μM [1] - Prexasertib (LY2606368)(0.5 μM)诱导HCT116细胞复制灾难:免疫荧光和DNA纤维实验显示,DNA损伤标志物γ-H2AX表达增加3.2倍,DNA纤维长度较对照组减少65% [1] - Prexasertib (LY2606368)(0.2 μM)与PARP抑制剂BMN673(0.1 μM)在胃癌细胞系(MGC803、BGC823)中产生协同效应:联合指数(CI)<1,细胞活力降低70%(Prexasertib单药组30%,BMN673单药组25%)[2] - Prexasertib (LY2606368)(0.3 μM)+ BMN673(0.15 μM)处理MGC803细胞48小时,凋亡率从单药组的12%升至48%;Western blot显示剪切型caspase-3(增加3.5倍)和PARP(增加2.8倍)表达升高 [2] - Prexasertib (LY2606368)(≤1 μM)对正常人胃上皮细胞(GES-1)毒性低,CC50 = 25 μM,对MGC803细胞的治疗指数>50 [2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Prexasertib (LY2606368) 作为单一疗法或与其他药物联合使用时,可抑制癌症异种移植物中的肿瘤生长。在原位 SKOV3 卵巢癌模型中,LY2606368 抑制原发肿瘤的生长,并显着降低转移和腹水积聚的发生率。 LY2606368 还在 SW1990 原位胰腺癌模型中表现出功效,可抑制原发肿瘤生长 92%,并消除淋巴结、脾脏和肠道的转移
荷HCT116结直肠癌异种移植瘤的裸鼠(BALB/c-nu)接受Prexasertib (LY2606368)(10 mg/kg,腹腔注射,每3天1次,连续4周)处理。肿瘤生长抑制率达68%,中位生存期从35天延长至48天 [1] - 荷MGC803胃癌异种移植瘤的裸鼠中,Prexasertib (LY2606368)(8 mg/kg,腹腔注射,每3天1次×4周)联合BMN673(15 mg/kg,灌胃,每日1次×14天)的肿瘤生长抑制率达82%,显著高于Prexasertib单药组(45%)和BMN673单药组(50%)[2] - Prexasertib (LY2606368)(10 mg/kg,腹腔注射)处理HCT116异种移植瘤小鼠后,肿瘤组织中γ-H2AX和剪切型caspase-3表达分别增加2.5倍和3倍,证实复制灾难和凋亡诱导 [1] - 联合治疗使BGC823异种移植瘤小鼠的肺转移结节较BMN673单药组减少65% [2] |
| 酶活实验 |
Prexasertib (LY2606368)抑制 CHK1 和 CHK2,IC50 值分别小于 1 nM 和 8 nM,具有很强的特异性效力。对于通过丝氨酸 296 自磷酸化的 CHK1 活性,LY2606368 的 EC50 为 1 nM,对于 HT-29 CHK2 自磷酸化,其 EC50 <31 nM (S516)。 LY2606368 的 EC50 为 9 nM,可有效抑制多柔比星在 p53 缺陷型 HeLa 细胞中激活的 G2-M 检查点。尽管如此,100 nM LY2606368 并未微弱抑制 PMA 刺激的 RSK,而是略微增加了丝氨酸 235/236 上 S6 的磷酸化。 LY2606368 对 U-2 OS、Calu-6、HT-29、HeLa 和 NCI-H460 细胞系表现出广泛的抗增殖活性,IC50 值分别为 3 nM、3 nM、10 nM、37 nM 和 68 nM。 LY2606368 (4 nM) 在 U-2 OS 细胞中诱导 H2AX 磷酸化以及细胞周期群体从 G1 和 G2-M 向 S 期的显着转变。 LY2606368 (25 μM) 证明了 AGS 和 MKN1 细胞的抗增殖特性。 DR-GFP 细胞中的 HR 修复能力受到 LY2606368 (20 nM) 的抑制。当与 PARP 抑制剂 BMN673 联合使用时,LY2606368 (5 nM) 在胃癌细胞中表现出协同抗癌作用。
siRNA knockdown[1] 用sirna转染U-2 OS细胞遵循Lipofectamine RNAiMAX反转染方案。48小时后,用Prexasertib (LY2606368)或DMSO处理细胞。作为对照的siRNA是ON-TARGETplus非靶向池,而CDK2 和CDC25A靶向sirna。每次转染siRNA的最终浓度为20 nmol/L。 重组人CHK1与ATP(5 μM)和合成CDC25C衍生肽(底物)在反应缓冲液(pH 7.4)中孵育。加入系列浓度的Prexasertib (LY2606368)(0.001-50 nM),30°C孵育60分钟。时间分辨荧光共振能量转移(TR-FRET)试剂盒检测磷酸化肽段,非线性回归分析计算IC50/Ki值 [1] - 激酶选择性面板实验:Prexasertib (LY2606368)(1 μM)针对50余种激酶(包括CHK2、CDK1/cyclin B、ATR、ATM)进行测试。使用激酶特异性底物和检测系统测定激酶活性,证实对CHK1的选择性>100倍 [1] |
| 细胞实验 |
MTS 细胞增殖比色检测试剂盒可测量 BMN673 和 LY2606368 的抗癌作用、CHK1 消融的增殖抑制作用以及 IR 敏感性。将细胞接种到96孔细胞培养板中后,根据指定的实验条件对每个孔进行处理。孵育两小时后,使用设置为检测 490 nM 波长的酶标仪测量每个孔的细胞活力。
抗增殖实验:HCT116、A549、MDA-MB-231、PC-3、MGC803和BGC823细胞分别在添加胎牛血清的RPMI 1640或DMEM培养基中培养,用Prexasertib (LY2606368)(0.01-10 μM)单药或联合BMN673(0.05-2 μM)处理72小时。MTT法检测细胞活力;从剂量-反应曲线推导GI50值和联合指数 [1][2] - 复制灾难实验:HCT116细胞用Prexasertib (LY2606368)(0.5 μM)处理24小时后固定,用抗γ-H2AX抗体和DAPI进行免疫染色,荧光显微镜量化γ-H2AX灶点;DNA纤维实验检测复制叉进展 [1] - 凋亡与Western blot实验:MGC803细胞用Prexasertib (LY2606368)(0.2 μM)+ BMN673(0.1 μM)处理48小时,Annexin V-FITC/PI染色流式细胞术检测凋亡;提取总蛋白,Western blot分析p-CHK1(Ser345)、γ-H2AX、剪切型caspase-3和GAPDH(内参)[2] - 克隆形成实验:BGC823细胞低密度接种于6孔板,Prexasertib (LY2606368)(0.1 μM)+ BMN673(0.05 μM)处理14天,甲醇固定,结晶紫染色,计数可见克隆 [2] |
| 动物实验 |
Female CD-1 nu-/nu- mice (26-28 g) with Calu-6 cells[1]
1, 3.3, or 10 mg/kg SC; twice daily for 3 days, rest 4 days; for three cycles Prexasertib (LY2606368) was prepared as a 10 mmol/L stock in DMSO for in vitro use and in 20% Captisol, pH4, for in vivo use. In vivo biochemistry and tumor growth inhibition[1] Female CD-1 nu-/nu- mice (26–28 g) from Charles River Labs were used for this study. Tumor growth was initiated by subcutaneous injection of 1 × 106 Calu-6 cells in a 1:1 mixture of serum-free growth medium and Matrigel in the rear flank of each subject animal. When tumor volumes reached approximately 150 mm3 in size, the animals were randomized by tumor size and body weight, and placed into their respective treatment groups. Vehicle consisting of 20% Captisol pH4 or Prexasertib (LY2606368) was administered by subcutaneous injection in a volume of 200 μL. Four, eight, 12, 24, and 48 hours after drug administration, blood for plasma drug exposure was extracted via cardiac puncture and assayed on a Sciex API 4000 LC/MS-MS system. The xenograft tissue was promptly removed and prepared as previously described. Lysates were analyzed by immunoblot analysis for protein phosphorylation levels. Group means, SEs and P values were calculated using Kronos.[1] To measure xenograft tumor growth inhibition, tumors were implanted, established, and the animals randomized as above. Eight animals were used in each treatment group. Vehicle alone or Prexasertib (LY2606368) was administered BIDx3, followed by 4 days of rest and repeated for an additional two cycles. Tumor size and body weight were recorded biweekly and compared between vehicle- and drug-treated groups. Colorectal cancer xenograft model: 6-8 weeks old BALB/c-nu nude mice were subcutaneously injected with HCT116 cells (5×10⁶ cells/mouse). When tumors reached 100-150 mm³, mice were randomly divided into control (vehicle) and Prexasertib (LY2606368) groups (10 mg/kg). The drug was dissolved in DMSO and diluted with normal saline (final DMSO ≤5%) for intraperitoneal injection, administered once every 3 days for 4 weeks. Tumor volume was measured every 3 days; mice were monitored for survival, and tumor tissues were collected for immunohistochemical analysis [1] - Gastric cancer combination therapy model: BALB/c-nu nude mice bearing MGC803 or BGC823 xenografts were treated with Prexasertib (LY2606368) (8 mg/kg, ip, once every 3 days for 4 weeks) plus BMN673 (15 mg/kg, po, once daily for 14 days). Control groups received vehicle, single-agent Prexasertib (LY2606368), or BMN673 alone. Tumor growth and metastatic nodules were evaluated at endpoint [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Forty-five patients were treated; seven experienced dose-limiting toxicities (all hematologic). The maximum-tolerated doses (MTDs) were 40 mg/m(2) (schedule 1) and 105 mg/m(2) (schedule 2). The most common related grade 3 or 4 treatment-emergent adverse events were neutropenia, leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and fatigue. Grade 4 neutropenia occurred in 73.3% of patients and was transient (typically < 5 days). Febrile neutropenia incidence was low (7%). The LY2606368 exposure over the first 72 hours (area under the curve from 0 to 72 hours) at the MTD for each schedule coincided with the exposure in mouse xenografts that resulted in maximal tumor responses. Minor intra- and intercycle accumulation of LY2606368 was observed at the MTDs for both schedules. Two patients (4.4%) had a partial response; one had squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the anus and one had SCC of the head and neck. Fifteen patients (33.3%) had a best overall response of stable disease (range, 1.2 to 6.7 months), six of whom had SCC.
Conclusion: An LY2606368 dose of 105 mg/m(2) once every 14 days is being evaluated as the recommended phase II dose in dose-expansion cohorts for patients with SCC.
|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Prexasertib (LY2606368) (≤1 μM) showed low cytotoxicity to normal human gastric epithelial cells (GES-1) and fibroblasts (CCD-18Co), with cell viability >85% after 72 hours [2]
- Acute toxicity in mice: Single intraperitoneal injection of Prexasertib (LY2606368) up to 50 mg/kg did not cause mortality or significant weight loss (<5%) [1] - Subchronic toxicity study (28 days) in rats administered Prexasertib (LY2606368) (5, 10 mg/kg/day, ip) showed mild neutropenia (12% reduction at 10 mg/kg) and transient elevation of serum AST (10% above normal), with no significant hepatotoxicity or nephrotoxicity [1] - Prexasertib (LY2606368) (8 mg/kg, ip) combined with BMN673 (15 mg/kg, po) did not induce obvious organ pathological damage in nude mice [2] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Prexasertib has been used in trials studying the treatment and basic science of mCRPC, Leukemia, Neoplasm, breast cancer, and Ovarian Cancer, among others.
Prexasertib is an inhibitor of checkpoint kinase 1 (chk1) with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon administration, prexasertib selectively binds to chk1, thereby preventing activity of chk1 and abrogating the repair of damaged DNA. This may lead to an accumulation of damaged DNA and may promote genomic instability and apoptosis. Prexasertib may potentiate the cytotoxicity of DNA-damaging agents and reverse tumor cell resistance to chemotherapeutic agents. Chk1, a serine/threonine kinase, mediates cell cycle checkpoint control and is essential for DNA repair and plays a key role in resistance to chemotherapeutic agents. \nCHK1 is a multifunctional protein kinase integral to both the cellular response to DNA damage and control of the number of active replication forks. CHK1 inhibitors are currently under investigation as chemopotentiating agents due to CHK1's role in establishing DNA damage checkpoints in the cell cycle. Here, we describe the characterization of a novel CHK1 inhibitor, LY2606368, which as a single agent causes double-stranded DNA breakage while simultaneously removing the protection of the DNA damage checkpoints. The action of LY2606368 is dependent upon inhibition of CHK1 and the corresponding increase in CDC25A activation of CDK2, which increases the number of replication forks while reducing their stability. Treatment of cells with LY2606368 results in the rapid appearance of TUNEL and pH2AX-positive double-stranded DNA breaks in the S-phase cell population. Loss of the CHK1-dependent DNA damage checkpoints permits cells with damaged DNA to proceed into early mitosis and die. The majority of treated mitotic nuclei consist of extensively fragmented chromosomes. Inhibition of apoptosis by the caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK had no effect on chromosome fragmentation, indicating that LY2606368 causes replication catastrophe. Changes in the ratio of RPA2 to phosphorylated H2AX following LY2606368 treatment further support replication catastrophe as the mechanism of DNA damage. LY2606368 shows similar activity in xenograft tumor models, which results in significant tumor growth inhibition. LY2606368 is a potent representative of a novel class of drugs for the treatment of cancer that acts through replication catastrophe.[2]\n \nCHEK1 encodes the serine/threonine kinase CHK1, a central component of the DNA damage response. CHK1 regulates cell cycle checkpoints following genotoxic stress to prevent the entry of cells with damaged DNA into mitosis and coordinates various aspects of DNA repair. Accordingly, CHK1 has become a target of considerable interest in oncology. CHK1 inhibitors potentiate the efficacy of DNA-damaging chemotherapeutics by abrogating CHK1-mediated cell cycle arrest and preventing repair of damaged DNA. In addition, CHK1 inhibitors interfere with the biological role of CHK1 as a principal regulator of the cell cycle that controls the initiation of DNA replication, stabilizes replication forks, and coordinates mitosis. Since these functions of CHK1 facilitate progression through an unperturbed cell cycle, CHK1 inhibitors are being developed not only as chemopotentiators, but also as single-agent therapies. This review is intended to provide information on the current progress of CHK1 inhibitors in pre-clinical and clinical development and will focus on mechanisms of single-agent activity and potential strategies for patient tailoring and combinations with non-genotoxic agents.[3]\n \nThe primary objective was to determine safety, toxicity, and a recommended phase II dose regimen of LY2606368, an inhibitor of checkpoint kinase 1, as monotherapy.\n\nPatients and methods: This phase I, nonrandomized, open-label, dose-escalation trial used a 3 + 3 dose-escalation scheme and included patients with advanced solid tumors. Intravenous LY2606368 was dose escalated from 10 to 50 mg/m(2) on schedule 1 (days 1 to 3 every 14 days) or from 40 to 130 mg/m(2) on schedule 2 (day 1 every 14 days). Safety measures and pharmacokinetics were assessed, and pharmacodynamics were measured in blood, hair follicles, and circulating tumor cells.\n\n\nConclusion: An LY2606368 dose of 105 mg/m(2) once every 14 days is being evaluated as the recommended phase II dose in dose-expansion cohorts for patients with SCC.[1] Prexasertib (LY2606368) is a potent, selective, and clinically advanced CHK1 inhibitor, designed to target DNA damage response pathways in cancer cells [1][2] - Its anti-tumor mechanism involves inhibiting CHK1-mediated cell cycle checkpoint activation, leading to replication catastrophe, DNA damage accumulation, and apoptotic cell death in cancer cells [1] - The drug exhibits synergistic anti-tumor activity with PARP inhibitors (BMN673) and chemotherapeutic agents in preclinical models of colorectal, lung, breast, and gastric cancer [1][2] - Prexasertib (LY2606368) has entered phase II clinical trials for the treatment of advanced solid tumors (e.g., triple-negative breast cancer, ovarian cancer) based on promising preclinical efficacy [1] - It shows favorable therapeutic index due to the dependency of cancer cells (vs. normal cells) on CHK1 for DNA damage repair and cell cycle progression [2] |
| 分子式 |
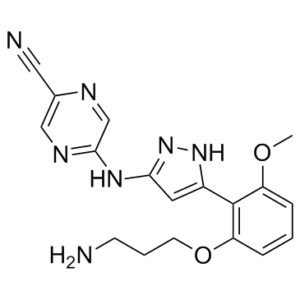
C18H19N7O2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
365.39
|
|
| 精确质量 |
365.16
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 59.17; H, 5.24; N, 26.83; O, 8.76
|
|
| CAS号 |
1234015-52-1
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Prexasertib dihydrochloride;1234015-54-3;Prexasertib dimesylate;1234015-58-7;Prexasertib Mesylate Hydrate;1234015-57-6;Prexasertib mesylate;1234015-55-4
|
|
| PubChem CID |
46700756
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to brown solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
608.5±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
321.8±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.655
|
|
| LogP |
2.03
|
|
| tPSA |
134.76
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
27
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
499
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
Cl[H].O(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N([H])[H])C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C(=C1C1=C([H])C(N([H])C2C([H])=NC(C#N)=C([H])N=2)=NN1[H])OC([H])([H])[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
DOTGPNHGTYJDEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H19N7O2/c1-26-14-4-2-5-15(27-7-3-6-19)18(14)13-8-16(25-24-13)23-17-11-21-12(9-20)10-22-17/h2,4-5,8,10-11H,3,6-7,19H2,1H3,(H2,22,23,24,25)
|
|
| 化学名 |
5-[[5-[2-(3-aminopropoxy)-6-methoxyphenyl]-1H-pyrazol-3-yl]amino]pyrazine-2-carbonitrile
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 1.67 mg/mL (4.57 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 +5% Tween-80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 16.7 mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80 +,混匀;然后加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7368 mL | 13.6840 mL | 27.3680 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5474 mL | 2.7368 mL | 5.4736 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2737 mL | 1.3684 mL | 2.7368 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04095221 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Prexasertib Drug: Irinotecan |
Desmoplastic Small Round Cell Tumor Rhabdomyosarcoma |
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center |
September 17, 2019 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT04023669 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Prexasertib Drug: Gemcitabine |
Brain Cancer CNS Cancer |
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital |
August 8, 2019 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02514603 | Completed | Drug: Prexasertib | Neoplasm | Eli Lilly and Company | October 2015 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02778126 | Completed | Drug: [¹⁴C]Prexasertib Drug: Prexasertib |
Advanced Cancer | Eli Lilly and Company | September 22, 2016 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03414047 | Completed | Drug: Prexasertib | Ovarian Cancer | Eli Lilly and Company | April 10, 2018 | Phase 2 |
 Exposure to LY2606368 results in DNA damage during S-phase.Mol Cancer Ther.2015 Sep;14(9):2004-13. |
|---|
 The DNA damage effects of LY2606368 are dependent upon CDC25A and CDK2.
LY2606368 causes chromosomal fragmentation.Mol Cancer Ther.2015 Sep;14(9):2004-13. |
LY2606368 causes DNA damage and growth inhibition in tumor xenografts.Mol Cancer Ther.2015 Sep;14(9):2004-13. |
 LY2606368 induces replication stress and depletes the pool of available RPA2 for binding to DNA.Mol Cancer Ther.2015 Sep;14(9):2004-13. |
|---|
 Chk1 inhibitor LY2606368 can induce DNA damage and apoptosis, and can suppress cell proliferation in gastric cancer cells.
LY2606368 can sensitize the anticancer effect of PARP inhibitor BMN673 in gastric cancer cells.Am J Cancer Res.2017 Mar 1;7(3):473-483. |
 Chk1 inhibitor LY2606368 can suppress HR repair capacity. Chk1 inhibitor LY2606368 can suppress HR repair capacity.
LY2606368 and BMN673 combination has synergistic anticancer effect in gastric cancer PDX model.Am J Cancer Res.2017 Mar 1;7(3):473-483. |