| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
GABA(A) receptor (EC50=60 μM)[1];
Small-conductance calcium-activated potassium (SK) channels[2]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
盐酸利鲁唑是一种抗惊厥药物,属于依赖使用的 Na+ 通道阻滞剂。它抑制 GABA 含量的 IC50 为 43 μM。盐酸利鲁唑持续延长 IPSC,但在 20 μM 时仅略微减少自体 IPSC。此外,使用盐酸利鲁唑观察到对 2 μM GABA 的反应显着、浓度依赖性且易于可逆地增加。在较高浓度(特别是 300 μM)持续共暴露后,GABA 电流对 2 μM GABA 和利鲁唑 HCl 表现出显着的脱敏。盐酸利鲁唑提高 GABA 反应性的 EC50 值约为 60 μM [1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
全身注射盐酸利鲁唑(8 mg/kg,腹膜内;n = 6 相应)是标准程序。在同一组中,超声诱导发声的持续时间总体上比载药试验更长(P<0.05),但一周不发声的时间较短。与制备前后相比,盐酸利鲁唑(8 mg/kg,腹腔注射;n = 19种成分)全身治疗显着降低了关节炎发声(P <0.05 ~ 0.001)。鱼引起的听力和超声发声持续时间盐酸利鲁唑可大大缩短刺激时间。
在大鼠海马脑片中,Riluzole (1–100 μM) 将 GABAA 受体介导的抑制性突触后电流(IPSCs)增强 40–60%(峰振幅 ↑),且不影响衰减动力学。该效应可被 GABAA 拮抗剂荷包牡丹碱阻断。 [1] 全细胞记录显示 Riluzole (10 μM) 使微型 IPSCs (mIPSCs) 频率增加 35% (p<0.01),表明其对 GABA 释放的突触前调控作用。 [1] |
| 酶活实验 |
电生理学表征:使用基于 CsCl 的内液填充微电极,在电压钳制神经元(Vhold = -70 mV)中评估 GABAA 受体功能。GABA (100 μM) 通过快速灌流系统给药。 [1]
|
| 动物实验 |
For neurophysiology: Rats received acute Riluzole (8 mg/kg i.p.) dissolved in 10% DMSO/saline 30 min before hippocampal slice preparation. [1]
For pain studies: Arthritic rats underwent stereotaxic implantation of amygdala cannulae. Riluzole (0.01–1 μg in 0.9% saline) or apamin was microinjected 15 min prior to behavioral testing. [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Riluzole is well-absorbed (approximately 90%), with average absolute oral bioavailability of about 60% (CV=30%). A high fat meal decreases absorption, reducing AUC by about 20% and peak blood levels by about 45%. Metabolism / Metabolites Riluzole is extensively metabolized to six major and a number of minor metabolites, which have not all been identified to date. Metabolism is mostly hepatic, consisting of cytochrome P450–dependent hydroxylation and glucuronidation. CYP1A2 is the primary isozyme involved in N-hydroxylation; CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP3A4, and CYP2E1 are considered unlikely to contribute significantly to riluzole metabolism in humans. Riluzole has known human metabolites that include 4-hydroxy-riluzole, 7-hydroxy-riluzole, 5-hydroxy-riluzole, and N-Hydroxyriluzole. Riluzole is extensively metabolized to six major and a number of minor metabolites, which have not all been identified to date. Metabolism is mostly hepatic, consisting of cytochrome P450–dependent hydroxylation and glucuronidation. CYP1A2 is the primary isozyme involved in N-hydroxylation; CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP3A4, and CYP2E1 are considered unlikely to contribute significantly to riluzole metabolism in humans. Half Life: The mean elimination half-life of riluzole is 12 hours (CV=35%) after repeated doses. Biological Half-Life The mean elimination half-life of riluzole is 12 hours (CV=35%) after repeated doses. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
The mode of action of riluzole is unknown. Its pharmacological properties include the following, some of which may be related to its effect: 1) an inhibitory effect on glutamate release (activation of glutamate reuptake), 2) inactivation of voltage-dependent sodium channels, and 3) ability to interfere with intracellular events that follow transmitter binding at excitatory amino acid receptors. Hepatotoxicity Serum aminotransferase elevations occur in approximately up to 12% of patients on long term riluzole therapy, but elevations above 3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) occur in less than 3% of patients. These elevations are usually mild-to-moderate in severity and are rarely associated with symptoms. Most elevations resolve spontaneously, but persistent or marked elevations require drug discontinuation or dose modification. Routine monitoring of serum aminotransferase levels is recommended for the first 6 months of therapy. Clinically apparent liver injury due to riluzole is rare, but several cases have been reported, arising after 1 to 12 months of therapy and characterized by a hepatocellular or mixed pattern of serum enzyme elevations. Immunoallergic and autoimmune features were uncommon. Most cases were mild to moderate in severity and recovery was rapid upon drug discontinuation, but evidently fatal cases have been reported to the sponsor. Likelihood score: C (probable rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Limited information indicates that maternal doses of riluzole up to 100 mg daily produce low levels in milk and would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants, especially if the infant is older than 2 months. Until more data are available, use riluzole with caution, particularly when breastfeeding a newborn. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding 96% bound to plasma proteins, mainly to albumin and lipoprotein over the clinical concentration range. Toxicity Data LD50: 85 mg/kg (p.o., mice) (L1859) LD50: 34.5 mg/kg (i.v, mice) (L1859) LD50: 45 mg/kg (p.o., rat) (L1859) LD50: 21 mg/kg (i.v, mice) (L1859) |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Riluzole, a member of the benzothiazole class, is indicated for the treatment of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Riluzole extends survival and/or time to tracheostomy. It is also neuroprotective in various in vivo experimental models of neuronal injury involving excitotoxic mechanisms. The etiology and pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) are not known, although a number of hypotheses have been advanced. One hypothesis is that motor neurons, made vulnerable through either genetic predisposition or environmental factors, are injured by glutamate. In some cases of familial ALS the enzyme superoxide dismutase has been found to be defective. BF-37 interferes directly with cellular processes of the immune system of the skin, thereby diminishing the inflammation that underlies the reddening and itching. Riluzole is FDA-approved for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Its neuroprotective effects involve dual modulation of GABAergic transmission and ion channels. [1][2] Black box warning: Risk of hepatotoxicity and neutropenia requires regular liver enzyme monitoring during clinical use. Riluzole is a member of benzothiazoles. A glutamate antagonist (receptors, glutamate) used as an anticonvulsant (anticonvulsants) and to prolong the survival of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Riluzole is marketed as Rilutek by Sanofi. BF-37 for the treatment of atopic dermatitis and/or psoriasis. The active ingredient in BF-37 is Riluzole, applied in a topical formulation, which is believed to correct the imbalances of the immune system that cause atopic dermatitis or psoriasis. Riluzole is a Benzothiazole. Riluzole is a neuroprotective agent used for therapy of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Riluzole is associated with a low rate of serum aminotransferase elevations during therapy and has been linked to rare instances of clinically apparent, acute liver injury. Riluzole is a benzothiazole derivative with neuroprotective and potential anti-depressant and anxiolytic activities. While the mechanism of action of riluzole is unknown, its pharmacological activities in motor neurons include the following, some of which may be related to its effect: 1) an inhibitory effect on glutamate release, 2) inactivation of voltage-dependent sodium channels, and 3) interference with intracellular events that follow transmitter binding at excitatory amino acid receptors. In animal models, this agent has been shown to exhibit myorelaxant and sedative activities, apparently due to the blockade of glutamatergic neurotransmission. RILUZOLE is a small molecule drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of IV (across all indications) that was first approved in 1995 and is indicated for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and has 22 investigational indications. Riluzole is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is a glutamate antagonist (receptors, glutamate) used as an anticonvulsant (anticonvulsants) and to prolong the survival of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. [PubChem]The mode of action of riluzole is unknown. Its pharmacological properties include the following, some of which may be related to its effect: 1) an inhibitory effect on glutamate release (activation of glutamate reuptake), 2) inactivation of voltage-dependent sodium channels, and 3) ability to interfere with intracellular events that follow transmitter binding at excitatory amino acid receptors. A glutamate antagonist (RECEPTORS, GLUTAMATE) used as an anticonvulsant (ANTICONVULSANTS) and to prolong the survival of patients with AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS. |
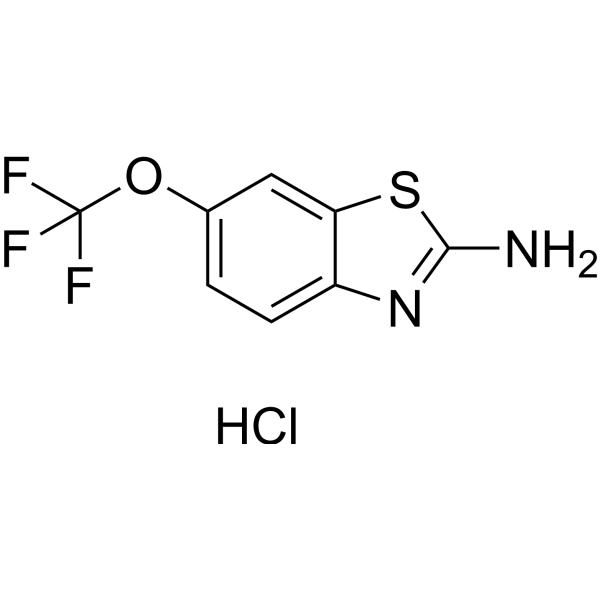
| 分子式 |
C8H6CLF3N2OS
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
270.659249782562
|
| 精确质量 |
269.984
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 35.50; H, 2.23; Cl, 13.10; F, 21.06; N, 10.35; O, 5.91; S, 11.85
|
| CAS号 |
850608-87-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Riluzole;1744-22-5
|
| PubChem CID |
6419992
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
4.16
|
| tPSA |
76.38
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
16
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
238
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
Cl.S1C(N)=NC2C=CC(=CC1=2)OC(F)(F)F
|
| InChi Key |
QEAOELIJQRYJJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C8H5F3N2OS.ClH/c9-8(10,11)14-4-1-2-5-6(3-4)15-7(12)13-5;/h1-3H,(H2,12,13);1H
|
| 化学名 |
6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amine;hydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
Riluzole hydrochloride; 850608-87-6; 2-Amino-6-trifluoromethoxybenzothiazole hydrochloride; 6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amine;hydrochloride; 6-(Trifluoromethoxy)benzo[d]thiazol-2-amine hydrochloride; SMR000449311; SR-01000002997; PK 26124;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~369.47 mM)
H2O : ~4.17 mg/mL (~15.41 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.24 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.24 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.24 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6947 mL | 18.4734 mL | 36.9467 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7389 mL | 3.6947 mL | 7.3893 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3695 mL | 1.8473 mL | 3.6947 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Riluzole and Sorafenib Tosylate in Treating Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors or Melanoma
CTID: NCT01303341
Phase: Phase 1 Status: Active, not recruiting
Date: 2024-09-19