| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
Muscarinic M3 receptor (Ki = 0.4 nM) [2][3]
- Muscarinic M1 receptor (Ki = 3.0 nM) [2][3] - Muscarinic M2 receptor (Ki = 49 nM) [2][3] - Muscarinic M4 receptor (Ki = 14 nM) [2][3] - Muscarinic M5 receptor (Ki = 1.2 nM) [2][3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Solifenacin Succinate (YM905) 是一种新型毒蕈碱受体拮抗剂。其 M1、M2 和 M3 受体的 pK 分别为 7.6±0.056、6.9±0.034 和 8.0±0.021。在小鼠颌下腺细胞中研究了奥昔布宁和 100 nM 琥珀酸索利那新对不同剂量卡巴胆碱 (CCh) 诱导的 Ca2+ 动员的拮抗作用。虽然奥昔布宁表现出牢不可破的拮抗相互作用,但琥珀酸索利那新不会以平行方式改变 CCh 剂量激活曲线。对于琥珀酸索利那新,pKb 值为 7.4±0.17,奥昔布宁为 8.8±0.21[1]。
Solifenacin succinate(YM905,琥珀酸索利那新) 对毒蕈碱M3受体具有高选择性,Ki值为0.4 nM,对M1(3.0 nM)、M4(14 nM)、M5(1.2 nM)和M2(49 nM)受体亲和力较低[2][3] - 在离体豚鼠膀胱平滑肌条中,Solifenacin succinate(0.1–100 nM)以剂量依赖性方式抑制乙酰胆碱(ACh)诱导的收缩,IC50为1.6 nM。其对膀胱的效价是回肠的30倍(回肠IC50 = 48 nM),体现膀胱选择性[2] - 在人膀胱平滑肌细胞中,该化合物(1–100 nM)抑制ACh诱导的细胞内钙动员,100 nM时最大抑制率达82%[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
210 nmol/kg (0.1 mg/kg) 时,琥珀酸索利那新 (YM905) 可使膀胱反射降低 40%,而 2100 nmol/kg (1 mg/kg) 时则完全消除膀胱反射。另一方面,在630 nmol/kg(0.3 mg/kg)时,其对唾液和心脏反应的抑制作用可以忽略不计,而在2100 nmol/kg(1 mg/kg)时,它们增加至66%和49%,分别。剂量为 63 和 210 nmol/kg(0.03 和 0.1 mg/kg)的琥珀酸索利那新会略微增加唾液分泌[1]。在 0.03 mg/kg 静脉注射或更高剂量时,琥珀酸索利那新(0.01 至 0.3 mg/kg 静脉注射)以剂量依赖性方式改善膀胱容量和排尿量;然而,在任何测试剂量下,残余容量和排尿压力均不受影响[2]。
在大鼠部分膀胱出口梗阻诱导的膀胱过度活动模型中,口服Solifenacin succinate(0.3、1、3 mg/kg)以剂量依赖性方式改善排尿参数。3 mg/kg剂量下,排尿次数减少45%,单次排尿量增加52%,残余尿量减少60%[2] - 在自发性高血压大鼠(SHR)冷应激诱导的逼尿肌过度活动模型中,Solifenacin succinate(1 mg/kg,口服)单独使用可减少38%的无排尿收缩;与β3肾上腺素能受体激动剂(10 mg/kg,口服)联合使用时,抑制率提升至65%,表现出协同效应[5] - 在韩国过度活跃膀胱患者的临床试验中,口服Solifenacin succinate(5 mg或10 mg,每日一次,连续12周)显著减少每日平均排尿次数(10 mg组从12.8次降至8.3次)和尿急发作次数(10 mg组从8.5次降至3.2次),24小时单次排尿量平均增加35%[4] |
| 酶活实验 |
在HEK293细胞中表达重组人毒蕈碱受体(M1–M5),制备细胞膜悬液。将系列稀释的Solifenacin succinate(0.01–1000 nM)与细胞膜悬液、[3H]-N-甲基东莨菪碱(非选择性毒蕈碱配体)在测定缓冲液中混合,25°C孵育60分钟。过滤去除未结合配体,液体闪烁计数器检测结合配体的放射性强度,采用Cheng-Prusoff方程计算Ki值[2][3]
|
| 细胞实验 |
人膀胱平滑肌细胞接种到96孔板,用荧光钙指示剂负载37°C孵育1小时。Solifenacin succinate(1–100 nM)预处理30分钟后,加入乙酰胆碱(10 μM)诱导钙动员,酶标仪连续60秒监测荧光强度,计算钙反应抑制率[2]
|
| 动物实验 |
0.01 to 0.3 mg/kg; i.v.
Male rats Rat partial bladder outlet obstruction model: Male SD rats underwent partial ligation of the bladder neck to induce overactive bladder. Two weeks post-surgery, rats were randomly divided into control (saline) and Solifenacin succinate groups (0.3, 1, 3 mg/kg, p.o., n=8 per group). Drugs were administered once daily for 7 days, and voiding parameters (voiding frequency, voided volume, residual urine) were measured using metabolic cages [2] - SHR cold stress-induced detrusor overactivity model: Spontaneously hypertensive rats were acclimated to metabolic cages, then exposed to cold stress (4°C) for 2 hours to induce detrusor overactivity. Rats were treated with Solifenacin succinate (1 mg/kg, p.o.), β3-agonist (10 mg/kg, p.o.), or their combination 1 hour before cold exposure. Voiding frequency and non-voiding contractions were recorded during the stress period [5] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
The oral bioavailability of Solifenacin succinate in humans is approximately 88% [3]
- After oral administration of 5 mg in humans, the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) is 32.3 ng/mL, achieved at 3–8 hours (Tmax), and the plasma half-life (t1/2) is about 50 hours [3] - The compound is widely distributed, with a volume of distribution of 600 L. It is highly bound to human plasma proteins (98%) [3] - Metabolism primarily occurs in the liver via cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) to inactive metabolites. Approximately 70% of the dose is excreted in urine (13% as unchanged drug) and 30% in feces [3] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because there is no published experience with solifenacin during breastfeeding and it has a long half-life averaging 55 hours, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. Long-term use of solifenacin might reduce milk production or milk letdown. During long-term use, observe the infant for signs of decreased milk production (e.g., insatiety, poor weight gain) and for anticholinergic symptoms (e.g., constipation, urinary retention, UTI, dry mouth). ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Anticholinergics can inhibit lactation in animals, apparently by inhibiting growth hormone and oxytocin secretion. Anticholinergic drugs can also reduce serum prolactin in nonnursing women. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. Common clinical adverse effects include dry mouth (23–30% of patients), constipation (10–15%), blurred vision (5–8%), and urinary retention (1–2%). These effects are mild to moderate and reversible [3][4] - No significant hepatotoxicity or nephrotoxicity was observed in clinical trials, with no consistent changes in serum ALT, AST, creatinine, or urea nitrogen levels [3][4] - Solifenacin succinate may interact with CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole), which can increase its plasma concentration by up to 2.5-fold [3] - The oral LD50 in rats is >2000 mg/kg, indicating low acute toxicity [3] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
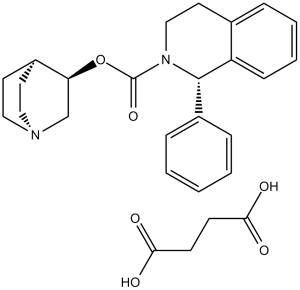
Solifenacin succinate is a member of isoquinolines.
A quinuclidine and tetrahydroisoquinoline derivative and selective M3 MUSCARINIC ANTAGONIST. It is used as a UROLOGIC AGENT in the treatment of URINARY INCONTINENCE. See also: Solifenacin (has active moiety). Drug Indication Treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity Solifenacin succinate (YM905) is a bladder-selective antimuscarinic agent, primarily indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms of urgency, frequency, and nocturia [2][3][4] - Its mechanism of action involves competitive antagonism of muscarinic M3 receptors in the bladder detrusor muscle, inhibiting acetylcholine-induced contraction and reducing bladder overactivity [2][3] - The high selectivity for bladder over other tissues (e.g., gastrointestinal tract) is attributed to its higher potency at bladder smooth muscle muscarinic receptors compared to intestinal smooth muscle [2] - Clinical doses range from 5 mg to 10 mg once daily, with no need for dose adjustment in elderly patients (≥65 years) or those with mild to moderate renal impairment [3][4] |
| 分子式 |
C23H26N2O.C4H6O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
480.55
|
| 精确质量 |
480.226
|
| CAS号 |
242478-38-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Solifenacin;242478-37-1;Solifenacin hydrochloride;180468-39-7;Solifenacin D5 hydrochloride;1426174-05-1;Solifenacin-d5 succinate
|
| PubChem CID |
216457
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.24g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
505.5ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
147 °C
|
| 闪点 |
259.5ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
2.41E-10mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.648
|
| LogP |
3.676
|
| tPSA |
107.38
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
35
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
617
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
C1CN2CCC1[C@H](C2)OC(=O)N3CCC4=CC=CC=C4[C@@H]3C5=CC=CC=C5.C(CC(=O)O)C(=O)O
|
| InChi Key |
RXZMMZZRUPYENV-VROPFNGYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H26N2O2.C4H6O4/c26-23(27-21-16-24-13-10-18(21)11-14-24)25-15-12-17-6-4-5-9-20(17)22(25)19-7-2-1-3-8-19;5-3(6)1-2-4(7)8/h1-9,18,21-22H,10-16H2;1-2H2,(H,5,6)(H,7,8)/t21-,22-;/m0./s1
|
| 化学名 |
[(3R)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-yl] (1S)-1-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinoline-2-carboxylate;butanedioic acid
|
| 别名 |
YM 905 succinate; Solifenacin succinate; YM-905; YM905; Trade name: Vesikur; Vesicare.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.20 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.20 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.20 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 50 mg/mL (104.05 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0809 mL | 10.4047 mL | 20.8095 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4162 mL | 2.0809 mL | 4.1619 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2081 mL | 1.0405 mL | 2.0809 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
A Clinical Study to Investigate How Solifenacin Fluid is Taken up, How Long it Stays in the Body and How Effective and Safe it is in Treating Children Aged From 6 Months to Less Than 5 Years With Symptoms of Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity (NDO)
CTID: NCT01981954
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Completed
Date: 2024-10-31