| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Endogenous Metabolite; synthetic form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
人血清和羊水中的常见成分是硫酸甲状腺素(T4S)。它主要由外周甲状腺素产生,并在胎儿 I 型 5-单碘化活性较低或被碘酸盐等药物抑制时积聚[1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
硫酸甲状腺素 (T4S) 在胎羊血清、胆汁、胎便、羊水和尿囊液中含量很高。妊娠十八 (19) 周和十五 (15) 周时女性羊水中的 T4S 浓度(分别为 25.5 ng/dL 和 14.3 ng/dL)。甲状腺功能亢进症患者在摄入1克碘酸一天后,血浆T4S显着升高[1]。前列腺素在体内被大量硫酸化;如果阻止 I 型心肌作用,T4S 的胆汁排泄就会增加 [2]。危重病期间心肌 D1 的心肌作用下降似乎在血清 T4S 水平升高中发挥了作用,该水平明显高于健康受试者。函数[3]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
最近,我们在胎羊血清、胎粪、胆汁、羊水和尿囊液中发现了大量的硫酸甲状腺素(T4S)。然而,人们对甲状腺素在人体内的硫酸盐结合知之甚少。在这项研究中,我们采用了一种新颖、灵敏的T4S RIA来解决这个问题。兔抗血清具有很强的特异性;T4、T3、rT3和3,3'-T2的交叉反应性小于0.002%。其他类似物的交叉反应小于0.0001%。只有rT3S和T3S交叉反应显著(分别为9.9%和2.0%)。甲状腺功能正常者的平均血清T4S浓度(ng/dL)为8.6,甲状腺功能亢进者为14.4,甲状腺功能减退者为5.0,妊娠期为5.9,非甲状腺疾病患者为4.5。妊娠18-19周的女性羊水中T4S浓度(25.5 ng/dL)高于妊娠14-15周的女性(14.3 ng/dL)。甲状腺功能亢进症患者在摄入1克ipodate后1天,血清T4S显著升高。这些数据表明,T4S是人类血清和羊水中的正常成分,主要来源于T4外周,当胎儿I型5'-单脱碘活性低或被药物(如ipodate)抑制时会积聚[1]。
|
| 动物实验 |
A total of 64 blood samples and 65 liver biopsies were obtained within minutes after death from 79 intensive care patients, randomized for intensive or conventional insulin treatment. Serum T4S and the activities of hepatic D1 and 3,3'-diiodothyronine (T2)-SULT and estrogen-SULT were determined.
Results: No differences in T4S or hepatic SULT activities were found between patients treated with intensive or with conventional insulin therapy. T4S levels were significantly elevated compared with healthy references. Furthermore, hepatic D1, but not SULT activity, showed a strong correlation with serum T4S (R = -0.53; P < 0.001) and T4S/T4 ratio (R = -0.62; P < 0.001). Cause of death was significantly correlated with hepatic T2- and estrogen-SULT activities (P < 0.01), with SULT activities being highest in the patients who died of severe brain damage and lowest in the patients who died of a cardiovascular collapse. A longer period of intensive care was associated with higher levels of T4S (P = 0.005), and high levels of bilirubin were associated with low T2-SULT (P = 0.04) activities and high levels of T4S (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Serum T4S levels were clearly elevated compared with healthy references, and the decreased deiodination by liver D1 during critical illness appears to play a role in this increase in serum T4S levels.[3]
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
The liver metabolizes T4 by deiodination and conjugation to T4 glucuronide (T4G), but little information exists about the formation of T4 sulfate (T4S) in vivo. We have examined the excretion of T4G, T4S, T3 and rT3 glucuronide (T3G and rT3G) in bile, collected under pentobarbital anesthesia 0-8 h or 17-18 h after iv [125I]T4 injection to control and 6-propyl-2-thiouracil (PTU)-treated rats. Radioactivity in bile, plasma, feces, and urine was analyzed by Sephadex LH-20 chromatography and HPLC. PTU induced a 2-fold increase in the biliary excretion of total radioactivity (26.6% vs. 15.0% dose between 0-8 h; 2.0% vs. 1.0% dose between 17-18 h). Biliary metabolites, 17-18 h after T4 injection, in control vs. PTU rats amounted to (percent dose): T4G, 0.44 vs. 0.75; T3G, 0.19 vs. 0.07; rT3G, 0.02 vs. 0.15; and T4S, 0.06 vs. 0.32. Similar results were obtained for control rats when bile was collected between 7-8 h after iv T4. The excretion rate of T3G was lower and that of rT3G higher when bile was continuously collected for 8 h immediately after T4 administration, probably due to prolonged experimental stress. However, regardless of the period of bile collection, PTU induced a more than 24-fold decrease in the T3G/rT3G ratio and a 5-fold increase in T4S excretion. In the animals killed 18 h after T4 injection, PTU treatment increased plasma T4 retention by 50%, reduced urinary I- excretion by 74%, and increased fecal radioactivity by 47%. No conjugates were detected in feces, and the distribution of fecal T4:T3:rT3 was 70:18:2 in control and 68:7:6 in PTU-treated rats. The results indicate that 1) the glucuronidative clearance of T4 is not affected by PTU; 2) the T3G/rT3G ratio in bile is a sensitive indicator of type I deiodinase inhibition; 3) T4 undergoes significant sulfation in rats in vivo, and 4) biliary excretion of T4S is enhanced if its type I deiodination is inhibited.[2]
|
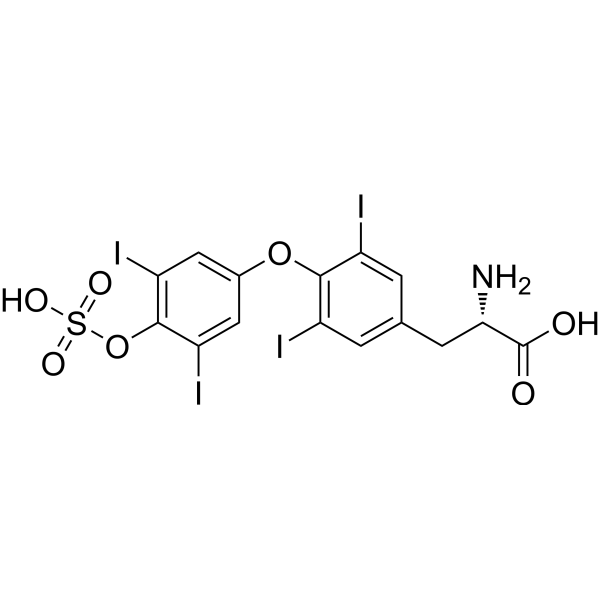
| 分子式 |
C15H11I4NO7S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
856.93
|
| 精确质量 |
856.644
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 21.02; H, 1.29; I, 59.24; N, 1.63; O, 13.07; S, 3.74
|
| CAS号 |
77074-49-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
L-Thyroxine;51-48-9;L-Thyroxine sodium salt pentahydrate;6106-07-6
|
| PubChem CID |
131742
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
5.814
|
| tPSA |
144.53
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
28
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
625
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
C1=C(C=C(C(=C1I)OC2=CC(=C(C(=C2)I)OS(=O)(=O)O)I)I)C[C@@H](C(=O)O)N
|
| InChi Key |
QYXIJUZWSSQICT-LBPRGKRZSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H11I4NO7S/c16-8-1-6(3-12(20)15(21)22)2-9(17)13(8)26-7-4-10(18)14(11(19)5-7)27-28(23,24)25/h1-2,4-5,12H,3,20H2,(H,21,22)(H,23,24,25)/t12-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2S)-2-amino-3-[4-(3,5-diiodo-4-sulfooxyphenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]propanoic acid
|
| 别名 |
T4 Sulfate; Thyroxine sulphate; L-Tyrosine,O-[3,5-diiodo-4-(sulfooxy)phenyl]-3,5-diiodo-; Thyroxine-4-sulfate; T4 Sulfate; Thyroxine 4'-O-Sulfate; (2S)-2-amino-3-[4-(3,5-diiodo-4-sulfooxyphenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]propanoic acid; Thyroxine sulfate
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~140 mg/mL (~163.37 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 5.75 mg/mL (6.71 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 57.5 mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 5.75 mg/mL (6.71 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 57.5 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入900 μL 玉米油中,混合均匀。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.58 mg/mL (3.01 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.1670 mL | 5.8348 mL | 11.6696 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2334 mL | 1.1670 mL | 2.3339 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1167 mL | 0.5835 mL | 1.1670 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。