| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
PDE5 (IC50 = 0.7 nM); PDE6 (IC50 = 11 nM); PDE1 (IC50 = 180 nM); PDE3 (IC50 >1000 nM); PDE4 (IC50 >1000 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
伐地那非的 IC50 为 0.7 nM,可选择性防止 PDE5 水解 cGMP[1]。伐地那非通过提高阴茎海绵体组织中的细胞内 cGMP 水平,导致人体的鼻窦和血流扩张[3]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
给予海绵体神经损伤的大鼠给予伐地那非(IV;0.03 mg/kg)时显示出促进作用[4]。伐地那非(静脉注射;0.17 mg/kg,每日一次;7 天)可降低肝组织中 NF-κB 和 iNOS 的表达,并保护肝脏免受 Con A 诱导的肝炎[5]。在 ZDF 心脏中,伐地那非(PO;10 mg/kg,每日一次;25 周)可抑制 3-NT 生成的增加和组织 cGMP 水平的降低[6]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
在这项研究中,研究人员调查了伐地那非对磷酸二酯酶(PDE)酶的效力和选择性,其改变cGMP代谢和引起阴茎平滑肌放松的能力,以及在外源性一氧化氮(NO)刺激条件下对体内勃起的影响。PDE同工酶从人血小板(PDE5)或牛来源(PDE 1、2、3、4和6)中提取和纯化。测定了伐地那非对这些PDE和人重组PDE的抑制作用。在体外测量了增强NO介导的松弛和影响人海绵体条中cGMP水平的能力,并在口服和静脉注射硝普钠(SNP)后,在清醒的兔子身上证明了勃起诱导活性。将伐地那非的效果与公认的PDE5抑制剂西地那非的效果进行了比较(括号内为西地那菲的值)。伐地那非特异性抑制PDE5对cGMP的水解,IC50为0.7 nM(6.6 nM)。相比之下,伐地那非对PDE1的IC50为180 nM;对PDE6的IC50为11 nM;对于PDE2、PDE3和PDE4的IC50超过1000 nM。相对于PDE5,PDE1的IC50比率为257(60),PDE6为16(7.4)。在3 nM(10 nM)的浓度下,伐地那非显著增强了SNP诱导的人小梁平滑肌松弛。伐地那非还显著增强了ACh诱导和透壁电刺激诱导的小梁平滑肌松弛。显著增强SNP诱导的cGMP积累的伐地那非最低浓度为3 nM(30 nM)[1]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male rat (9weeks old) underwent surgery for laparotomy or bilateral cavernous nerve (CN) crush injury[4]
Doses: 0.03 mg/kg Route of Administration: intravenous (iv) injection Experimental Results: Restored normal erectile responses with a combind administration of BAY 60- 4552 (0.03, 0.3 mg/kg). Animal/Disease Models: Liver injury induced by Con A in male Swiss albino mice (20 ± 2 g)[5] Doses: 0.17 mg/kg Route of Administration: intravenous (iv) injection; one time/day, for 7 days ; as a pretreatment Experimental Results: decreased the levels of serum transaminases and alleviated Con A-induced hepatitis. Animal/Disease Models: Male 7weeks old Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats (preserved ejection fraction, HFpEF)[6] Doses: 10 mg /kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); one time/day, for 25 weeks Experimental Results: Improved myofilament function in diabetic rat hearts. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Over the recommended dose range, vardenafil has a dose-proportional pharmacokinetics profile. In healthy male volunteers given a single oral dose of 20 mg of vardenafil, maximum plasma concentrations were reached between 30 minutes and 2 hours (median 60 minutes) after oral dosing in the fasted state, and 0.00018% of the dose was detected in semen 1.5 hours after dosing. Vardenafil has a bioavailability of approximately 15%. High-fat meals cause a Cmax reduction of 18%-50%; however, no changes were detected in AUC or Tmax. Vardenafil is excreted as metabolites mainly through feces and urine. Approximately 91-95% of administered oral dose is found in feces, while 2-6% of administered oral dose is found in urine. Vardenafil has a steady-state volume of distribution of 208 L. Vardenafil has a total body clearance of 56 L/h. Protein binding: Very high: 95% bound to plasma proteins; reversible and independent of total drug concentrations Rapidly absorbed; absolute bioavailability is approximately 15%. Maximum observed plasma concentrations after a single 20 mg dose in healthy volunteers are usually reached between 30 minutes and 2 hours (median 60 minutes) after oral dosing in the fasted state. A high-fat meal causes a reduction in Cmax by 18% to 50%. Enhancement of nitric oxide (NO)-induced erections in rabbits by 0.1 mg/kg vardenafil is limited by its pharmacokinetic properties (Tmax=1 h; T1/2=1.2 h), although erectile effects have been observed after 7 h. In humans, vardenafil is rapidly absorbed (Tmax approximately 40 min) and more slowly metabolized (T1/2 approximately 4 h), with an absolute bioavailability of 14.5% (vs 40% for sildenafil). Although the consumption of high-fat meals does not affect the drug's relative bioavailability, it retards intestinal absorption. Coadministration of CYP3A4 inhibitors such as ritonavir can affect hepatic metabolism. M1, an active metabolite of vardenafil, is a four-fold-less potent inhibitor of PDE5 than its parent compound, contributing approximately 7% to vardenafil's overall efficacy. Time to peak concentration: 30 minutes to 2 hours (oral dosing, fasted state) For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for VARDENAFIL (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Vardenafil is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4 in the liver, although CYP3A5 and CYP2C isoforms also contribute to its metabolism. The major circulating metabolite, M1 (N-desethylvardenafil), results from desethylation at the piperazine moiety of vardenafil, and has a plasma concentration of approximately 26% of that of the parent compound. M1 has a phosphodiesterase selectivity profile similar to that of vardenafil and an _in vitro_ inhibitory potency for PDE5 28% of that of vardenafil. Hepatic metabolism, via CYP3A4, with contribution from CYP3A5 and CYP2C isoforms. Major circulating metabolite, M1, results from desethylation at the piperazine moiety of vardenafil. M1 is subject to further metabolism. The plasma concentration of M1 is approximately 26% of the parent compound and accounts for 7% of total pharmacologic activity. This metabolite shows a phosphodiesterase selectivity profile similar to that of vardenafil and an in vitro inhibitory potency for PDE5 28% of that of vardenafil. Biological Half-Life Vardenafil and its primary metabolite (M1) have a terminal half-life of 4-5 hours. Terminal: 4 to 5 hours |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Despite fairly extensive use, vardenafil has not been associated with clinically apparent cases of liver injury and serum enzyme elevations during therapy are rare. The related PDE5 inhibitors, sildenafil and tadalafil have been linked to isolated, rare instances of acute liver injury and jaundice. The latency to onset ranged from a few days to 3 months and the pattern of injury was usually cholestatic. Autoimmune and immunoallergic features were not observed and all cases were self-limited without residual injury or acute liver failure. Whether vardenafil can cause a similar form of acute liver injury is unknown. Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No published information is available on the use of vardenafil during breastfeeding. An alternate agent may be preferred. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Approximately 95% of vardenafil and its major circulating metabolite is bound to plasma proteins. Their protein binding is reversible and independent of total drug concentrations. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
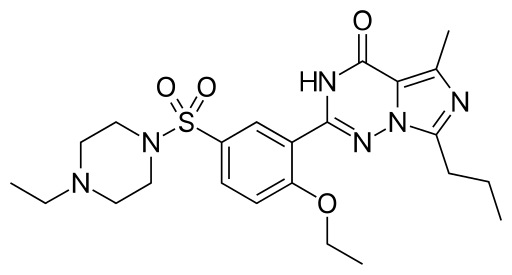
Vardenafil is the sulfonamide resulting from formal condensation of the sulfo group of 4-ethoxy-3-(5-methyl-7-propylimidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4(1H)-one-2-yl)benzenesulfonic acid and the secondary amino group of 4-ethylpiperazine. It has a role as a vasodilator agent and an EC 3.1.4.* (phosphoric diester hydrolase) inhibitor. It is a N-alkylpiperazine, an imidazotriazine and a N-sulfonylpiperazine.
Vardenafil is a selective inhibitor of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) and an oral therapy for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. During sexual stimulation, nitric oxide (NO) is released from nerve endings and endothelial cells in the corpus cavernosum, activating the enzyme guanylate cyclase and increasing the synthesis of cGMP in the smooth muscle cells of the corpus cavernosum. PDE5 inhibitors, such as vardenafil, inhibit the degradation of cGMP and allow increased blood flow into the penis, resulting in an erection.. Compared to [sildenafil] and [tadalafil], vardenafil is a more potent inhibitor of PDE5; however, its selectivity for other PDE isoforms is lower than the one detected for tadalafil. The FDA approved the use of vardenafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in 2003. Although other PDE5 inhibitors such as [sildenafil] and [tadalafil] have been associated with rare cases of acute liver injury, the use of vardenafil has not been linked to hepatotoxic effects. The use of vardenafil as a monotherapy for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension has also been evaluated. Vardenafil is a Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of vardenafil is as a Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitor. Vardenafil is a selective inhibitor of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) and is used as therapy of erectile dysfunction. Vardenafil has not been associated with serum aminotransferase elevations nor with clinically apparent liver injury. Vardenafil is a benzenesulfonamide derivative and phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor with vasodilatory activity. Vardenafil selectively inhibits PDE5, thus inhibiting the degradation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) found in the smooth muscle of the corpus cavernosa and corpus spongiosum of the penis. The inhibition of cGMP degradation results in prolonged muscle relaxation, vasodilation, and blood engorgement of the corpus cavernosa, prolonging penile erection. A piperazine derivative, PHOSPHODIESTERASE 5 INHIBITOR and VASODILATOR AGENT that is used as a UROLOGICAL AGENT in the treatment of ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION. Drug Indication Vardenafil is indicated for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Treatment of erectile dysfunction in adult men. Erectile dysfunction is the inability to achieve or maintain a penile erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. In order for Levitra to be effective, sexual stimulation is required. Levitra is not indicated for use by women. Treatment of erectile dysfunction in adult men. Erectile dysfunction is the inability to achieve or maintain a penile erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. In order for Vivanza to be effective, sexual stimulation is required. Vivanza is not indicated for use by women. Mechanism of Action Vardenafil inhibits cyclic guanosine monophosphate (GMP) specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5), which is responsible for the degradation of cyclic GMP in the corpus cavernosum located around the penis. Penile erection during sexual stimulation is caused by increased penile blood flow resulting from the relaxation of penile arteries and corpus cavernosal smooth muscle. This response is mediated by the release of nitric oxide (NO) from nerve terminals and endothelial cells, which stimulates the synthesis of cyclic GMP in smooth muscle cells. Cyclic GMP causes smooth muscle relaxation and increased blood flow into the corpus cavernosum. The tissue concentration of cyclic GMP is regulated by both the rates of synthesis and degradation via phosphodiesterases (PDEs), and the most abundant PDE in the human corpus cavernosum is PDE5. Therefore, the inhibition of PDE5 by vardenafil enhances erectile function by increasing the amount of cyclic GMP. Penile erection is a hemodynamic process initiated by the relaxation of smooth muscle in corpus cavernosum and its associated arterioles. During sexual stimulation, nitric oxide is released from nerve endings and endothelial cells in the corpus cavernosum. Nitric oxide activates the enzyme guanylate cyclase resulting in increased synthesis of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) in the smooth muscle cells of the corpus cavernosum. The cGMP in turn triggers smooth muscle relaxation, allowing increased blood flow into the penis, resulting in erection. The tissue concentration of cGMP is regulated by both the rates of synthesis and degradation via phosphodiesterases (PDEs). The most abundant PDE in the human corpus cavernosum is the cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5); therefore, the inhibition of PDE5 enhances erectile function by increasing the amount of cGMP. Because sexual stimulation is required to initiate the local release of nitric oxide, the inhibition of PDE5 has no effect in the absence of sexual stimulation. In vitro studies have shown that vardenafil is a selective inhibitor of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5). The inhibitory effect of vardenafil is more selective on PDE5 than for other known phosphodiesterases (>15-fold relative to PDE6, >130-fold relative to PDE1, >300-fold relative to PDE11, and >1,000-fold relative to PDE2, 3, 4, 7, 8, 9, and 10). |
| 分子式 |
C23H32N6O4S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
488.6
|
| 精确质量 |
488.22
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 56.54; H, 6.60; N, 17.20; O, 13.10; S, 6.56
|
| CAS号 |
224785-90-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Vardenafil hydrochloride;224785-91-5;Vardenafil dihydrochloride;224789-15-5;Vardenafil-d5;1189685-70-8
|
| PubChem CID |
135400189
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
692.2ºC at 760mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
214-216ºC
|
| 闪点 |
372.5ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
5.17E-19mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.656
|
| LogP |
2.65
|
| tPSA |
121.28
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
34
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
854
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
UWRWYSQUBZFWPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H35N6O4S/c1-5-10-27-16-21-24-22(25-23(30)29(21,4)17-27)19-15-18(8-9-20(19)33-7-3)34(31,32)28-13-11-26(6-2)12-14-28/h8-9,15-16H,5-7,10-14,17H2,1-4H3,(H,24,25,30)
|
| 化学名 |
2-(2-ethoxy-5-((4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)sulfonyl)phenyl)-5-methyl-7-propyl-3,5,6,7-tetrahydro-4H-5l4-imidazo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazin-4-one
|
| 别名 |
BAY38-9456; BAY 38-9456; BAY-38-9456; Levitra; Vivanza; Vardenafil ODT; BAY38-9456; HSDB 7304; UNII-UCE6F4125H;BAY38-9456;trade names: Levitra; Staxyn; Vivanza;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.12 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.12 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.12 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0467 mL | 10.2333 mL | 20.4666 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4093 mL | 2.0467 mL | 4.0933 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2047 mL | 1.0233 mL | 2.0467 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
  |
|---|
  |
|