| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Bcr-Abl1 tyrosine kinase (IC50 = 7 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在表达 BCR-ABL1、BCR-ABL1L248V、BCR-ABL1Y253H 或 BCR-ABL1E255V 的 Ba/F3 细胞中,经沃多巴替尼 (K0706;0-2000 nM) 治疗后,BCR-ABL1 酪氨酸自磷酸化受到有效抑制 [1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
截至2020年7月15日,31名CP-CML患者接受了剂量为12至240毫克的沃他替尼治疗;波那替尼治疗(PT)队列中有16名患者(9名男性)[7名(44%)波那替尼是TKI的前一名患者],波那替尼初治(PN)队列中则有15名患者(7名男性)。基线人口统计和疾病史如表1所示。[2]
疗效:波那替尼治疗组和初治组的中位治疗时间分别为17.3(0.6-36)个月和14.8(0.5-42)个月;PT组有11名患者[深部分子反应(DMR)2名,MMR 3名;MCyR 5名(CCyR 2名,PCyR 3名);疾病稳定组有1名],PN组有10名患者(DMR 2名,MM 4名,CCyR 3名,疾病稳定组1名)仍在继续治疗。总体疗效结果见表2和表3。[2] 在16名PT患者中,2名(13%)患者(均为双突变)出现了疾病进展。在15名PN患者中,4名(26%)患者(基线突变T315I为48 mg,Y253H为66 mg,F317L和E255V为174 mg)出现进展。 |
| 酶活实验 |
BCR-ABL1激酶结构域的Sanger测序[1]
从表达Ba/F3 BCR-ABL1的裂解物中分离的DNA被用作扩增BCR-ABL 1激酶结构域的模板。使用两步PCR进行扩增(Phusion高保真DNA聚合酶),以排除内源性ABL1。PCR产物在1%琼脂糖凝胶上电泳以确认扩增、纯化和Sanger测序。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞增殖IC50测定[1]
用表达p210 BCR-ABL1(MSCV-IRES-GFP)的逆转录病毒感染在RPMI-1640完全培养基 中培养的IL-3依赖性小鼠Ba/F3细胞,该培养基补充了10%胎牛血清、1%青霉素/链霉素、1%L-谷氨酰胺和WEHI条件培养基中的IL-3。通过提取IL-3进行感染细胞的选择。使用定点突变(QuikChange II XL定点突变试剂盒)引入临床相关的BCR-ABL1点突变。使用磷酸钙转染293FT细胞并收获上清液产生逆转录病毒。Ba/F3 BCR-ABL1和BCR-ABL1-突变体被放置在96孔板(2x103个细胞/孔)中,并与指定的抑制剂一起孵育72小时。抑制剂浓度:K0706、尼罗替尼、达沙替尼、博舒替尼和波那替尼(0、4.9、9.8、19.5、39.1、78.1、156.3、315.5、625、1250、2500和5000 nmol/L);在(0、0.2、0.4、0.8、1.6、3.1、6.3、12.5、25、50、10和200 nmol/L)下重新测试原始筛选的敏感细胞系(IC50≤3)。使用基于甲硫磺酸(MTS)的存活率测定法(CellTiter 96 AQueous One Solution,Promega)测量增殖。IC50值为四次独立实验的平均值。 BCR-ABL1酪氨酸磷酸化免疫印迹分析[1] 将表达天然和突变BCR-ABL1的Ba/F3细胞铺在24孔板(2x106个细胞/孔)中,并在1 mL RPMI完全培养基中培养4小时,其中TKI的滴定浓度为(0、15.6、32.3、62.5、125、250、500、1000和2000 nmol/L)。用冷PBS洗涤细胞,并在冰上含有磷酸酶和蛋白酶抑制剂混合物的M-PER(哺乳动物蛋白质提取试剂)中裂解10分钟。样品在补充有2-巯基乙醇的SDS-Page加载缓冲液(2x Laemmli样品缓冲液)中以1:1稀释,并在95°C下煮沸10分钟变性。裂解物在4-20%Tris-Glycine(Mini-PROTEAN TGX)梯度凝胶上分离,转移并用抗c-Abl(Ab-3)小鼠单克隆抗体(24-21)、抗磷酸化c-Abl(Tyr204)(C42B5)兔单克隆抗体和抗β-肌动蛋白(D6A8)兔mAb进行免疫印迹。 基于细胞的耐药性测定[1] 用N-乙基-N-亚硝基脲(ENU,50μg/mL)处理天然表达BCR-ABL1的Ba/F3细胞过夜,造粒,重新悬浮在新鲜RPMI完全培养基中,并在96孔板(1.25x105个细胞/孔)中铺板,补充五倍的分级浓度K0706(400、800、1600和3200 nmol/L)。ENU用硫代硫酸钠(20%w/v)和氢氧化钠(100mmol/L)灭活过夜,并按照方案安全处置。在30天内,每两天使用显微镜目视监测井的生长情况。从每个处理组中随机选择50个生长菌落,并在含有与原始96孔板相同浓度K0706的24孔板中扩增。通过离心收集24孔板中的扩增细胞,并将其储存在-80°C下。 |
| 动物实验 |
Multiple escalating doses of vodobatinib (once daily) in 28-day cycles were evaluated in a 3+3 study design. The primary objective was determination of the maximal tolerated dose (MTD) or recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D) along with safety and a secondary objective was to evaluate anti-leukemic activity. Dose escalation involved dose doubling until 2 pts in a cohort experienced Grade 2 toxicity, or 1 pt experienced Grade 3 or 4 toxicity, after which dose escalation was reduced to 40% increments. Treatment continued until unacceptable toxicity, disease progression (PD), consent withdrawal, or death.[2]
|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In ponatinib treated pts, the most commonly reported treatment emergent adverse events (TEAEs), (all grades) included nausea (4, 25%) and diarrhea (3, 25%). Other commonly reported TEAEs included thrombocytopenia (3, 19%), rash (3, 19%), non-cardiac chest pain (3, 19%), increased amylase (3, 19%), and fall (3, 19%). Grade ≥ 3 TEAEs were reported in 10 (63%) pts included 1 pt each with anemia, lymphopenia, fall, skull fracture, spinal fracture, lipase increase, fluid overload, syncope, dyspnea, and hypertension. Vodobatinib related AEs included amylase increase, lipase increase, dyspnea, fluid overload, thrombocytopenia and neutropenia. Grade ≥ 3 TEAEs reported in more than one pt included neutropenia (2, 13%) amylase increase (2, 13%) and thrombocytopenia (2, 13%).[2]
In PN pts, the most commonly reported TEAEs (all grades) included myalgia (5, 33%) and back pain (4, 27%). Other commonly reported TEAEs were thrombocytopenia (4, 27%), and nasopharyngitis (3, 20%). Grade ≥ 3 TEAEs were reported in 7 (47%) pts (1 pt with anemia, 1 pt with pneumonia, 1 pt with neutropenia, 1 pt with gout, hypokalemia, thrombocytopenia, 1 pt with increased liver and pancreatic enzymes and 1 pt each with dementia and amnesia. Vodobatinib related AEs included alanine aminotransferase increase, blood bilirubin increased, amnesia, neutropenia and thrombocytopenia. No grade ≥ 3 event was reported in more than 1 pt.[2] Overall, three cardiovascular TEAEs were reported, in 2 pts (1 each in PT and PN), all deemed unrelated to vodobatinib. Three pts died on study: 1 due to disease progression in the PT group; 1 due to pneumonia (suspected COVID-19) and 1 due to intracranial hemorrhage in the PN group. The intracranial hemorrhage event (Grade 5 AE) was considered possibly related and was confounded by disease progression to blast phase that included extra-medullary sites. At the highest dose of 240 mg, two dose limiting toxicities were reported. The next lower dose level of 204 mg was established as MTD with a favorable safety profile in heavily pre-treated CP-CML pts.[2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Vodobatinib is an orally bioavailable, Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon administration, vodobatinib selectively targets and binds to the Bcr-Abl fusion oncoprotein, including various Bcr-Abl mutant forms, such as those with the 'gatekeeper' resistance mutation T315I. This inhibits proliferation of Bcr-Abl-expressing tumor cells. The Bcr-Abl fusion protein is an aberrantly activated tyrosine kinase produced by certain leukemia cells. T315I, an amino acid substitution where threonine (T) has been mutated to isoleucine (I) at position 315 in the tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 portion of the Bcr-Abl fusion protein, plays a key role in resistance to certain chemotherapeutic agents and its expression is associated with poor prognosis.
|
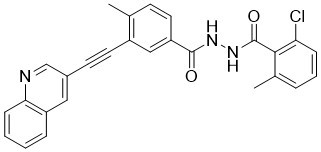
| 分子式 |
C27H20CLN3O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
453.919605255127
|
| 精确质量 |
453.124
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 71.44; H, 4.44; Cl, 7.81; N, 9.26; O, 7.05
|
| CAS号 |
1388803-90-4
|
| PubChem CID |
89884852
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
748.6±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
406.5±32.9 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.5 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.701
|
| LogP |
5.73
|
| tPSA |
71.1
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
774
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
ClC1=CC=CC(C)=C1C(NNC(C1C=CC(C)=C(C#CC2=CN=C3C=CC=CC3=C2)C=1)=O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
ZQOBVMHBVWNVBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C27H20ClN3O2/c1-17-10-12-22(26(32)30-31-27(33)25-18(2)6-5-8-23(25)28)15-20(17)13-11-19-14-21-7-3-4-9-24(21)29-16-19/h3-10,12,14-16H,1-2H3,(H,30,32)(H,31,33)
|
| 化学名 |
2-chloro-6-methyl-N'-[4-methyl-3-(2-quinolin-3-ylethynyl)benzoyl]benzohydrazide
|
| 别名 |
Vodobatinib; K-0706; K0706; SCO-088; K0706; Vodobatinib [USAN]; K-0706; N8Q12KU2SW; 2-Chloro-6-methyl-N'-(4-methyl-3-(quinolin-3-ylethynyl)benzoyl)benzohydrazide; K0706;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~125 mg/mL (~275.38 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.08 mg/mL (4.58 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.58 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2030 mL | 11.0152 mL | 22.0303 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4406 mL | 2.2030 mL | 4.4061 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2203 mL | 1.1015 mL | 2.2030 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。