| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 25g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
Endogenous Metabolite
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
LPS (1 μg/mL) 与 ATP (5 mM) 共处理一小时对 HGF 的 NLRP3 炎性体激活具有积极影响 [3]。 IL-1β、KC 和 MIP-2 都是 ATP 依赖 caspase-1 激活诱导 BMDM 死亡率所必需的(2 mM;0.5-24 小时)[4]。在体外,ATP 刺激中性粒细胞趋化性 [4]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
ATP(50 mg/kg;腹腔注射)可保护外壳免受细菌感染 [4]。 ATP 涵盖外周的 IL-1β、KC 和 MIP-2 以及中性粒细胞募集 [4]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
人类健康不断受到各种危险的威胁,包括自我和非自我。免疫系统负责保护宿主免受这种危险,以保护人类健康。为此,免疫系统配备了一系列不同的细胞和非细胞效应器,这些效应器相互持续通信。天然存在的核苷酸5’-三磷酸腺苷(ATP)及其代谢产物腺苷(Ado)可能通过其同源受体的嘌呤能信号传导构成这种广泛免疫网络的内在组成部分,嘌呤能信号在全身广泛表达。这篇综述全面概述了ATP和Ado对主要免疫细胞类型的影响。压倒性的证据表明,ATP和Ado是免疫和炎症中重要的内源性信号分子。尽管ATP和Ado在体内炎症和免疫反应过程中的作用似乎极其复杂,但我们认为它们的免疫作用是相互依存和多方面的,这意味着它们的作用性质可能从免疫刺激转变为免疫调节,反之亦然,这取决于细胞外浓度以及嘌呤能受体和胞外酶的表达模式。因此,嘌呤能信号有助于炎症和免疫反应的微调,从而有效消除对宿主的危险,对健康组织的损害最小[2]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
体外研究表明,细胞外核苷酸和核苷可能是炎症和免疫反应的重要调节因子。大多数关于5’-三磷酸腺苷(ATP)的研究都是在远离人类环境的细胞系中进行的。本研究的目的是确定ATP对刺激全血中TNF-α、IL-6和IL-10释放的影响。从健康志愿者中抽取血样,并与ATP和脂多糖(LPS)+植物血凝素(PHA)一起孵育24小时。与预期相反,100μM和300μM的ATP分别诱导TNF-α分泌减少32+/-8%(平均+/-SEM)和65+/-4%。此外,这些ATP浓度诱导全血中IL-10分泌增加48+/-5%和62+/-7%。ATP类似物5’-O-(3-硫代三磷酸)腺苷(ATP-gamma-S)和5’-二磷酸腺苷(ADP)也抑制TNF-α的释放,但只有ADP对IL-10有刺激作用。腺苷脱氨酶联合治疗不能逆转ATP对TNF-α和IL-10的作用。这些结果首次表明,ATP抑制受刺激全血中的炎症反应,如抑制TNF-α和刺激IL-10释放所示,并且这种作用主要由ATP而非腺苷介导[1]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Fourweeks old Kunming mice (18-22 g) [4]
Doses: 50 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection before bacterial (E. coli) challenge Experimental Results: Protect mice from bacterial infection. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Metabolism / Metabolites
Metabolism of organophosphates occurs principally by oxidation, by hydrolysis via esterases and by reaction with glutathione. Demethylation and glucuronidation may also occur. Oxidation of organophosphorus pesticides may result in moderately toxic products. In general, phosphorothioates are not directly toxic but require oxidative metabolism to the proximal toxin. The glutathione transferase reactions produce products that are, in most cases, of low toxicity. Paraoxonase (PON1) is a key enzyme in the metabolism of organophosphates. PON1 can inactivate some organophosphates through hydrolysis. PON1 hydrolyzes the active metabolites in several organophosphates insecticides as well as, nerve agents such as soman, sarin, and VX. The presence of PON1 polymorphisms causes there to be different enzyme levels and catalytic efficiency of this esterase, which in turn suggests that different individuals may be more susceptible to the toxic effect of organophosphate exposure. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. ATP can be produced by various cellular processes, most typically in mitochondria by oxidative phosphorylation under the catalytic influence of ATP synthase. The total quantity of ATP in the human body is about 0.1 mole. The energy used by human cells requires the hydrolysis of 200 to 300 moles of ATP daily. This means that each ATP molecule is recycled 2000 to 3000 times during a single day. ATP cannot be stored, hence its consumption must closely follow its synthesis. Toxicity Data Oral LD50 in rats is > 2 g/kg. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
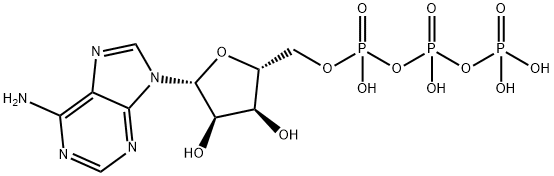
ATP is an adenosine 5'-phosphate in which the 5'-phosphate is a triphosphate group. It is involved in the transportation of chemical energy during metabolic pathways. It has a role as a nutraceutical, a micronutrient, a fundamental metabolite and a cofactor. It is an adenosine 5'-phosphate and a purine ribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate. It is a conjugate acid of an ATP(3-).
Adenosine triphosphate is a metabolite found in or produced by Escherichia coli (strain K12, MG1655). Adenosine-5'-triphosphate has been reported in Helianthus tuberosus, Arabidopsis thaliana, and other organisms with data available. Adenosine Triphosphate is an adenine nucleotide comprised of three phosphate groups esterified to the sugar moiety, found in all living cells. Adenosine triphosphate is involved in energy production for metabolic processes and RNA synthesis. In addition, this substance acts as a neurotransmitter. In cancer studies, adenosine triphosphate is synthesized to examine its use to decrease weight loss and improve muscle strength. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleotide consisting of a purine base (adenine) attached to the first carbon atom of ribose (a pentose sugar). Three phosphate groups are esterified at the fifth carbon atom of the ribose. ATP is incorporated into nucleic acids by polymerases in the processes of DNA replication and transcription. ATP contributes to cellular energy charge and participates in overall energy balance, maintaining cellular homeostasis. ATP can act as an extracellular signaling molecule via interactions with specific purinergic receptors to mediate a wide variety of processes as diverse as neurotransmission, inflammation, apoptosis, and bone remodelling. Extracellular ATP and its metabolite adenosine have also been shown to exert a variety of effects on nearly every cell type in human skin, and ATP seems to play a direct role in triggering skin inflammatory, regenerative, and fibrotic responses to mechanical injury, an indirect role in melanocyte proliferation and apoptosis, and a complex role in Langerhans cell-directed adaptive immunity. During exercise, intracellular homeostasis depends on the matching of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) supply and ATP demand. Metabolites play a useful role in communicating the extent of ATP demand to the metabolic supply pathways. Effects as different as proliferation or differentiation, chemotaxis, release of cytokines or lysosomal constituents, and generation of reactive oxygen or nitrogen species are elicited upon stimulation of blood cells with extracellular ATP. The increased concentration of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in erythrocytes from patients with chronic renal failure (CRF) has been observed in many studies but the mechanism leading to these abnormalities still is controversial. (A3367, A3368, A3369, A3370, A3371). Adenosine triphosphate is a metabolite found in or produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. An adenine nucleotide containing three phosphate groups esterified to the sugar moiety. In addition to its crucial roles in metabolism adenosine triphosphate is a neurotransmitter. |
| 分子式 |
C10H16N5O13P3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
507.1810
|
| 精确质量 |
506.995
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 23.68; H, 3.18; N, 13.81; O, 41.01; P, 18.32
|
| CAS号 |
56-65-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
ATP disodium salt;987-65-5;ATP disodium trihydrate;51963-61-2;ATP dimagnesium;74804-12-9;ATP-13C10,15N5 disodium;ATP disodium salt hydrate;34369-07-8;ATP dipotassium;42373-41-1;ATP ditromethamine;102047-34-7;ATP-13C10,15N5;752972-20-6
|
| PubChem CID |
5957
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
2.6±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
951.4±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
187 - 190ºC (Decomposes)
|
| 闪点 |
529.2±37.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.904
|
| LogP |
-4.18
|
| tPSA |
308.56
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
7
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
17
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
800
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
| SMILES |
C1=NC(=C2C(=N1)N(C=N2)[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O3)COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)O)O)O)N
|
| InChi Key |
ZKHQWZAMYRWXGA-KQYNXXCUSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C10H16N5O13P3/c11-8-5-9(13-2-12-8)15(3-14-5)10-7(17)6(16)4(26-10)1-25-30(21,22)28-31(23,24)27-29(18,19)20/h2-4,6-7,10,16-17H,1H2,(H,21,22)(H,23,24)(H2,11,12,13)(H2,18,19,20)/t4-,6-,7-,10-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
[[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl] phosphono hydrogen phosphate
|
| 别名 |
Adenosine triphosphate; Ara-ATP; Atipi; Triphosphaden; Triphosphoric acid adenosine ester; Adenosine 5'-triphosphate; ATP; adenosine-5'-triphosphate; Myotriphos; Striadyne; Triadenyl;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ≥ 100 mg/mL (~197.17 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 100 mg/mL (197.17 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。 (<60°C).
请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9717 mL | 9.8584 mL | 19.7169 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3943 mL | 1.9717 mL | 3.9434 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1972 mL | 0.9858 mL | 1.9717 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT02580253 | Withdrawn | Drug: Individualized Chemotherapy Drug: mFOLFOX6 |
Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Zhejiang University | November 1, 2017 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00014248 | Completed | Drug: adenosine triphosphate Procedure: quality-of-life assessment |
Cachexia Unspecified Adult Solid Tumor, Protocol Specific |
Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center | October 2000 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00565188 | Completed | Drug: Adenosine 5'-triphosphate | Cancer Palliative Care |
Maastricht University Medical Center | March 2002 | Phase 3 |
| NCT02279511 | Completed | Drug: ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE Drug: PLACEBO |
Alzheimer's Disease | Sara Varea | December 2014 | Phase 2 |