| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 25g |
|
||
| 50g |
|
||
| 100g | |||
| 200g | |||
| Other Sizes |

| 靶点 |
Neural Stem Cell (NSC) proliferation and differentiation-related pathways ( Diclofenac Sodium (GP 45840) inhibited NSC proliferation at concentrations ≥10 μM and disrupted NSC differentiation at 20 μM) [3]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
双氯芬酸的 IC50 为 7±3 nM,可有效抑制 U937 细胞中 COX-1 介导的微粒体前列腺素合成[1]。当暴露于双氯芬酸钠(1–60 μM;1 天)时,神经干细胞 (NSC) 会发生浓度依赖性细胞凋亡 [3]。当暴露于双氯芬酸钠 (10–60 μM) 六小时时,克隆(激活)的 caspase-3 表达更多 [3]。
1. 抑制神经干细胞(NSC)增殖:对从胚胎14天(E14)大鼠大脑皮质分离的原代NSC进行双氯芬酸钠(Diclofenac Sodium, GP 45840) 处理。处理48小时后,10 μM的双氯芬酸钠使BrdU(5-溴-2'-脱氧尿苷,细胞增殖标志物)掺入量较对照组显著降低32.5±4.2%;20 μM时,BrdU掺入抑制率增至51.3±5.7%;浓度≤5 μM时未观察到显著增殖抑制作用[3] 2. 干扰NSC分化:当NSC在双氯芬酸钠存在下诱导分化时,分化7天后,20 μM的药物使神经元(用β-微管蛋白III标记)数量较对照组减少40.2±6.1%,使星形胶质细胞(用胶质纤维酸性蛋白GFAP标记)数量较对照组增加28.7±3.9%;浓度≤10 μM时对NSC分化无显著影响[3] 3. 对NSC活力的影响:MTT实验显示,处理48小时后,浓度≤15 μM的双氯芬酸钠对NSC活力无显著影响(活力≥对照组的90%);仅在20 μM时观察到轻微活力下降(为对照组的82.3±4.5%)[3] 4. 与其他非甾体抗炎药(NSAID)的比较:吲哚美辛(另一种NSAID)在浓度高达20 μM时仍不影响NSC增殖或分化,表明双氯芬酸钠对NSC的抑制作用并非NSAID的共同特性[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
双氯芬酸钠(3 mg/kg,bid)连续五天可大大增加大鼠粪便 51Cr 的排泄。在松鼠猴中也观察到了这种效果,松鼠猴每天两次服用 1 mg/kg,持续四天 [1]。在 Wistar 大鼠中,在炎症发生前口服双氯芬酸钠 (10 mg/kg) 可发挥抗炎作用 [1]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[3]
细胞类型:神经干细胞 (NSC) 测试浓度:1、3、10、30、60 μM 孵育时间: 1 天 实验结果:细胞死亡的诱导具有浓度依赖性,并且在浓度高达 60 μM 时效果不饱和。 蛋白质印迹分析[3] 细胞类型: 神经干细胞 (NSC) 测试浓度: 10、30 或 60 μM 孵育持续时间:6小时 实验结果:caspase-3的激活以浓度依赖性方式增加。 1. 原代神经干细胞(NSC)分离与培养:从E14 Sprague-Dawley大鼠胚胎中分离大脑皮质,用火焰抛光吸管将其机械解离为单细胞。细胞悬浮于NSC培养基(含杜氏改良 Eagle 培养基/F12、B27补充剂、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和表皮生长因子)中,以5×10⁴个细胞/cm²的密度接种。培养物在37°C、5% CO₂培养箱中维持,每2天更换一次培养基。培养5-7天后形成的神经球用于后续实验[3] 2. BrdU掺入实验(增殖检测):将神经球解离为单细胞,以1×10⁴个细胞/孔接种于96孔板。贴壁24小时后,加入双氯芬酸钠(Diclofenac Sodium, GP 45840)(0.1-20 μM),孵育48小时。孵育的最后16小时,向培养基中加入10 μM BrdU。细胞用4%多聚甲醛固定15分钟,0.2% Triton X-100透化10分钟,4°C下与抗BrdU一抗孵育过夜。洗涤后加入荧光标记二抗,用酶标仪检测荧光强度(激发波长488 nm,发射波长520 nm)。增殖率按(样品荧光强度/对照荧光强度)×100%计算[3] 3. MTT实验(活力检测):将NSC以1×10⁴个细胞/孔接种于96孔板,用双氯芬酸钠(0.1-20 μM)处理48小时。每孔加入20 μL MTT溶液(5 mg/mL),37°C继续孵育4小时。去除上清液,加入150 μL二甲基亚砜(DMSO)溶解甲臜结晶,用酶标仪检测570 nm处的吸光度。细胞活力按(样品吸光度/对照吸光度)×100%计算[3] 4. NSC分化实验:将神经球解离为单细胞,接种于多聚-L-赖氨酸包被的盖玻片上,密度为2×10⁴个细胞/cm²。通过从培养基中去除生长因子(碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和表皮生长因子)并加入双氯芬酸钠(0.1-20 μM)诱导分化。分化7天后,细胞用4%多聚甲醛固定,0.2% Triton X-100透化,4°C下与抗β-微管蛋白III(神经元标志物)和抗GFAP(星形胶质细胞标志物)一抗孵育过夜。加入荧光二抗后,在荧光显微镜下计数β-微管蛋白III阳性细胞和GFAP阳性细胞数量。分化率按(标志物阳性细胞数/总细胞数)×100%计算[3] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male SD (Sprague-Dawley) rats (150±200 g)[1]
Doses: 3 mg/kg Route of Administration: Oral administration, bid, for 5 days Experimental Results: Resulted in a significant increase in faecal 51Cr excretion. Animal/Disease Models: Wistar rats (150-175 g) bearing Formalin-induced rat foot paw edema model[2] Doses: 10 mg/kg Route of Administration: Administered via oral route just prior to induction of inflammation Experimental Results: demonstrated in vivo anti-inflammatory activity (% edema inhibition= 29.2, 1 h; 22.2, 3 h; 20, 6 h). |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Data on excretion of diclofenac into milk are poor, but the drug has a short half-life and little glucuronide metabolite formation. Levels in milk appear to be quite low. Most reviewers consider diclofenac to be acceptable during breastfeeding. Other agents having more published information may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. Maternal use of diclofenac topical gel or eye drops would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. To substantially diminish the amount of drug that reaches the breastmilk after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants In one study, 30 mothers undergoing elective cesarean section were allowed to use 25 mg diclofenac suppositories along with either spinal or spinal and epidural anesthesia with a local anesthetic after delivery. The spinal anesthetic group used an average of 56 mg of diclofenac on the day of delivery and 33 mg on the next day whereas the women receiving both spinal and epidural anesthesia used 21 and 18 mg. No mention was made of adverse effects on the breastfed infants. A breastfed infant developed urticaria on day 15 of life. Her mother had been taking diclofenac (dosage unspecified) for pain since her cesarean section delivery. Diclofenac is a possible cause of the urticaria; however, the infant had also received hepatitis B vaccination 7 days before and the authors thought that it was a more likely cause of the reaction. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk A randomized, double-blind study was performed in pregnant women scheduled for cesarean section under spinal anesthesia with bupivacaine and fentanyl. Patients received either 100 mg diclofenac (n = 100), 100 mg tramadol (n = 100) or placebo (glycerin suppositories) n = 100, all given as rectal suppositories every 8 hours for the first 24 hours after surgery. The time to initiate breastfeeding was significantly shorter among mothers who received diclofenac than a placebo, 1.5 vs 4.1 hours with breastfeeding support and 3.5 vs 6.2 hours without support. Diclofenac was slightly more effective than tramadol among mothers who received no support (3.5 vs 3.7 hours). In vitro cytotoxicity on NSCs: Diclofenac Sodium (GP 45840) showed minimal cytotoxicity on NSCs at concentrations ≤15 μM (cell viability ≥90% vs. control) after 48 h of treatment. Only at 20 μM did a slight decrease in cell viability occur (82.3 ± 4.5% vs. control), with no significant cell death observed [3] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
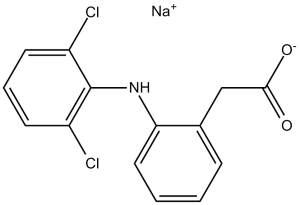
Diclofenac sodium is the sodium salt of diclofenac. It contains a diclofenac(1-).
Diclofenac Sodium is the sodium salt form of diclofenac, a benzene acetic acid derivate and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory activity. Diclofenac sodium is a non-selective reversible and competitive inhibitor of cyclooxygenase (COX), subsequently blocking the conversion of arachidonic acid into prostaglandin precursors. This leads to an inhibition of the formation of prostaglandins that are involved in pain, inflammation and fever. A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent (NSAID) with antipyretic and analgesic actions. It is primarily available as the sodium salt. See also: Diclofenac (brandname of); Omeprazole (has active ingredient); Capsicum Oleoresin (has active ingredient) ... View More ... Drug Indication Treatment of inflammation, Treatment of pain 1. Diclofenac Sodium (GP 45840) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), but its inhibitory effect on NSC proliferation and differentiation is not mediated by cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibition. This conclusion is supported by the finding that indomethacin (a COX inhibitor with similar NSAID properties) had no effect on NSC proliferation or differentiation even at 20 μM [3] 2. The disruption of NSC differentiation by diclofenac sodium (20 μM) was characterized by a reduction in neuronal lineage cells and an increase in astrocyte lineage cells, suggesting that the drug may shift NSC fate toward glial differentiation [3] 3. The in vitro findings imply that diclofenac sodium may have potential effects on neural development or neurogenesis if administered during embryonic or postnatal periods when NSCs are active [3] |
| 分子式 |
C14H10CL2NNAO2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
318.13
|
|
| 精确质量 |
316.998
|
|
| CAS号 |
15307-79-6
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Diclofenac;15307-86-5;Diclofenac diethylamine;78213-16-8;Diclofenac-d4 sodium;154523-54-3;Diclofenac potassium;15307-81-0;Diclofenac-13C6 sodium heminonahydrate;Diclofenac-13C6 Sodium;1261393-73-0
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5018304
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 沸点 |
412ºC at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
288-290°C
|
|
| 闪点 |
203ºC
|
|
| LogP |
3.102
|
|
| tPSA |
52.16
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
20
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
310
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
KPHWPUGNDIVLNH-UHFFFAOYSA-M
|
|
| InChi Code |
1S/C14H11Cl2NO2.Na/c15-10-5-3-6-11(16)14(10)17-12-7-2-1-4-9(12)8-13(18)19;/h1-7,17H,8H2,(H,18,19);/q;+1/p-1
|
|
| 化学名 |
Benzeneacetic acid, 2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)-, monosodium salt
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 4.55 mg/mL (14.30 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。 (<60°C).
请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1434 mL | 15.7168 mL | 31.4337 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6287 mL | 3.1434 mL | 6.2867 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3143 mL | 1.5717 mL | 3.1434 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT02495831 | Completed Has Results |
Drug: Diclofenac sodium
Drug: Diclofenac sodium and safinamide |
Healthy | Zambon SpA | May 2015 | Phase 1 |
| NCT06111573 | Completed | Dietary Supplement: Vitamin D Drug: Diclofenac Sodium |
Myofascial Pain Dysfunction Syndrome,Temporomandibular Joint |
Yuzuncu Yıl University | June 1, 2022 | Phase 4 |
| NCT06342648 | Not yet recruiting | Drug: Sterile Water Injection Drug: Diclofenac Sodium injection |
Renal Colic | Suez Canal University | May 1, 2024 | Not Applicable |
| NCT06207253 | Recruiting | Drug: Diclofenac Sodium Drug: Calcium hydroxide |
Endodontic Disease Pulp Disease, Dental |
British University In Egypt | February 2024 | Phase 2 Phase 3 |
| NCT04341402 | Unknown † | Drug: Antifungal Nail Gel Study | Tinea Unguium, Onychomycosis |
William N Handelman | May 1, 2020 | Phase 2 |