| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
地尔硫卓 (200 µM) 在适度数量的脉冲中会导致依赖于使用的阻塞 [1]。地尔硫卓通过加速动作电位期间的失活来降低 Ca2+ 流入,而使用依赖性阻塞是由于长时间保持关闭的通道数量增加引起的。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
地尔硫卓(100 mg/kg;口服;持续 4 周)以独立于血压的方式预防主动脉瘤形成[3]。地尔硫卓通过对单核细胞具有独立于血压的抗炎作用来抑制小鼠主动脉瘤的生长[3]。给予地尔硫卓(2 mg/kg;IV)的大鼠显示 T1/2 为 61.2 分钟,CLel 为 3.2 mL/min[4]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male ApoE−/− mice, angiotensin II induced aneurysms[3]
Doses: 100 mg/kg Route of Administration: Oral administration, in drinking water, for 4 weeks Experimental Results: Srongly decreased the vascular remodeling but also lowered the blood pressure. Animal/Disease Models: Rat (200-250 g)[4] Doses: 2 mg/kg ( pharmacokinetic/PK Analysis) Route of Administration: intravenous (iv) injection Experimental Results: T1/2 (61.2 min), CLel (3.2 mL/min) |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Diltiazem is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Minimum therapeutic plasma diltiazem concentrations appear to be in the range of 50 to 200 ng/mL. Following oral administration of extended formulations of 360 mg diltiazem, the drug in plasma was detectable within 3 to 4 hours and the peak plasma concentrations were reached between 11 and 18 hours post-dose. Diltiazem peak and systemic exposures were not affected by concurrent food intake. Due to hepatic first-pass metabolism, the absolute bioavailability following oral administration is about 40%, with the value ranging from 24 to 74% due to high interindividual variation in the first pass effect. The bioavailability may increase in patients with hepatic impairment. Due to its extensive metabolism, only 2% to 4% of the unchanged drug can be detected in the urine. The major urinary metabolite in healthy volunnteers was N-monodesmethyl diltiazem, followed by deacetyl N,O-didesmethyl diltiazem, deacetyl N-monodesmethyl diltiazem, and deacetyl diltiazem; however, there seems to be large inter-individual variability in the urinary excretion of DTZ and its metabolites. The apparent volume of distribution of diltiazem was approximately 305 L following a single intravenous injection in healthy male volunteers. Following a single intravenous injection in healthy male volunteers, the systemic clearance of diltiazem was approximately 65 L/h. After constant rate intravenous infusion, the systemic clearance decreased to 48 L/h. The protein binding of diltiazem is 80-90%, & the volume of distribution is approx 5.3 L/kg. Clearance of diltiazem after oral ingestion follows first-order kinetics, with a half-life of 5-10 hr, independent of the amount ingested. In sustained release preparations, however, the peak absorption time is delayed & the half-life may be very prolonged because of continued GI absorption. Although the absorption of ... agents /like diltiazem/ is nearly complete after oral admin, their bioavailability is reduced, in some cases markedly, because of first-pass hepatic metab. The effects of these drugs are evident within 30-60 min of an oral dose ... . During repeated oral admin, bioavailability and half-life may incr because of saturation of hepatic metabolism. A major metabolite of diltiazem is desacetyldiltiazem, which has about 1/2 of diltiazem's potency as a vasodilator. Diltiazem is excreted into human milk. The pharmacokinetic changes of diltiazem ... and its main metabolite, deacetyldiltiazem (DAD) were studied after oral admin of diltiazem to normal rabbits and mild and medium folate-induced renal failure rabbits. Diltiazem 10 mg/kg was given to the rabbits ... orally (n=6). Plasma concns of diltiazem and DAD were determined by a high performance liquid chromatography assay. The area under the plasma concn-time curves (AUC) and max plasma concn (Cmax) of diltiazem were significantly increased in mild and medium folate-induced renal failure rabbits. The metabolite ratio of the diltiazem to DAD were significantly decreased in mild and medium folate-induced renal failure rabbits. The volume of distribution (Vd) and total body clearance (CLt) of diltiazem were significantly decreased in mild and medium folate-induced renal failure rabbits. The elimination rate constant (beta) of diltiazem was significantly decreased in folate-induced renal failure rabbits, but that of DAD was significantly increased. These findings suggest that the hepatic metab of diltiazem was inhibited ... . The pharmacokinetics of diltiazem in rabbits after subconjunctival and topical admin was studied. Diltiazem successfully penetrated the aq humor of rabbit eyes. The peak aq concns were 3.8 +/- 0.4 ug/ml after topical application and 15.3 +/- 1.1 ug/ml after subconjunctival injection. The peak aq concn was achieved 1/2 hrs after admin in both cases. Metabolism / Metabolites Diltiazem is subject to extensive first-pass metabolism, which explains its relatively low absolute oral bioavailability. It undergoes N-demethylation primarily mediated by CYP3A4. CYP2D6 is responsible for O-demethylation and esterases mediate deacetylation. There was large inter-individual variability in the circulating plasma levels of metabolites in healthy volunteers. In healthy volunteers, the major circulating metabolites in the plasma are N-monodesmethyl diltilazem, deacetyl diltiazem, and deacetyl N-monodesmethyl diltiazem, which are all pharmacologically active. Deacetyl diltiazem retains about 25-50% of the pharmacological activity to that of the parent compound. Deacetyl diltiazem can be further transformed into deacetyl diltiazem N-oxide or deacetyl O-desmethyl diltiazem. N-monodesmethyl diltilazem can be further metabolized to N,O-didesmethyl diltiazem. Deacetyl N-monodesmethyl diltiazem can be further metabolized to deacetyl N,O-didesmethyl diltiazem, which can be glucuronidated or sulphated. Diltiazem can be O-demethylated by CYP2D6 to form O-desmethyl diltiazem. A major metabolite of diltiazem is desacetyldiltiazem, which has about 1/2 of diltiazem's potency as a vasodilator. Diltiazem undergoes extensive metabolism in hepatic and extrahepatic tissues. Deacetyldiltiazem (M1) and N-demethyldiltiazem (MA) are 2 of the main basic metabolites of diltiazem that retain pharmacological activity. This drug impairs its own metab after chronic admin in the adult patient. Diltiazem has known human metabolites that include O-Demethyldiltiazem and N-Demethyldiltiazem. Diltiazem is metabolized by and acts as an inhibitor of the CYP3A4 enzyme. Half Life: 3.0 - 4.5 hours Biological Half-Life The plasma elimination half-life is approximately 3.0 to 4.5 hours following single and multiple oral doses. The half-life may slightly increase with dose and the extent of hepatic impairment. The apparent elimination half-life for diltiazem as extended-release tablets after single or multiple dosing is 6 to 9 hours. The plasma elimination half-life is approximately 3.4 hours following administration of a single intravenous injection. The elimination half-lives of pharmacologically active metabolites are longer than that of diltiazem. Clearance of diltiazem after oral ingestion follows first-order kinetics, with a half-life of 5-10 hr ... . |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Possibly by deforming the channel, inhibiting ion-control gating mechanisms, and/or interfering with the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, diltiazem, like verapamil, inhibits the influx of extracellular calcium across both the myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes. The resultant inhibition of the contractile processes of the myocardial smooth muscle cells leads to dilation of the coronary and systemic arteries and improved oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue. Hepatotoxicity Diltiazem therapy is associated with a low rate of mild and transient elevations in serum aminotransferase levels which are usually asymptomatic and often resolve even with continuation of therapy. Clinically apparent, acute liver injury with jaundice due to diltiazem is rare and only isolated case reports have been published. In large case series of drug induced liver injury, calcium channel blockers are rarely mentioned. Most cases attributed to diltiazem have been marked by a short latency period (3 to 14 days) and features of hypersensitivity with fever, rash and eosinophilia. The pattern of liver injury was ranged from cholestatic to hepatocellular. Jaundice is often absent and usually mild. Autoantibody formation has not been described. Thus, liver injury from diltiazem is likely to be idiosyncratic in nature and is typically mild and self-limited with resolution within 4 to 8 weeks of stopping. Acute hepatic injury is listened as a possible adverse event in the diltiazem product label. Likelihood score: C (probable but rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Based on limited data, amounts of diltiazem ingested by the infant are small and would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Diltiazem is about 70-80% bound to plasma proteins, according to _in vitro_ binding studies. About 40% of the drug is thought to bind to alpha-1-glycoprotein at clinically significant concentrations while about 30% of the drug is bound to albumin. Toxicity Data LD50=740mg/kg (orally in mice) Interactions Diltiazem interacts with Propranolol reducing oral clearance with increased concns of propanolol by inhibition of first-pass metab. Propanolol dose may need to be reduced. /from table/ Diltiazem interacts with cyclosporine increasing cyclosporine concns. Reduce cyclosporine dose after starting... diltiazem; monitor cyclosporine concns. /from table/ Diltiazem interacts with disopyramide, flecainide /causing/ cardiac failure by additive depression of myocardial contractility. Avoid use if possible, particularly in patients with impaired myocardial function. /from table/ Diltiazem interacts with Amiodarone, flecainide /causing/ sinus arrest, heart block by additive depression of sinus node function & AV nodal conduction. Use combination with extreme caution. /from table/ For more Interactions (Complete) data for DILTIAZEM (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Diltiazem ... may reduce the incidence of reinfarction in patients with a first non-Q-wave infarction who are not candidates for a beta-adrenergic receptor antagonist. ... Diltiazem ... /has/ been shown to provide symptomatic relief in Raynaud's disease. Diltiazem ... /is/ indicated, alone or in combination with other agents, for treatment of hypertension. /Included in US product labeling/ ... Parenteral diltiazem /is/ indicated in the treatment of supraventricular tachyarrhythmias. Diltiazem ... produces rapid conversion to sinus rhythm of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (including those associated with accessory bypass tracts, such as Wolff-Parkinson-White [W-P-W] or Lown-Ganong-Levine [L-G-L] syndrome) in patients who do not respond to vagal maneuvers {161} when the atrioventricular (AV) node is required for reentry to sustain tachycardia {125}. Parenteral diltiazem ... also produces temporary control of rapid ventricular rate in atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation. ... /Included in US product labeling/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for DILTIAZEM (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings The toxic effects of sustained-release calcium channel blockers may be delayed more than 12 hr after ingestion. All patients with sustained-release calcium channel blocker overdose should be admitted to the hospital for observation, even if they are asymptomatic. /Calcium channel blockers/ Withdrawal of calcium channel blocking drugs from severely hypertensive patients, even in the absence of previous angina or myocardial infarction, may precipitate myocardial infarction. Worsening angina & myocardial infarction have been described after the withdrawal of calcium channel blocking agents in patients with normal coronary angiography who are being treated for ischemic chest pain. /Calcium channel blockers/ Patients with ventricular dysfunction, SA or AV nodal conduction disturbances, and systolic blood pressures below 90 mm Hg should not be treated with ... diltiazem, particularly iv. The most common adverse cardiovascular effect noted with IV diltiazem is symptomatic or asymptomatic hypotension, which occurred in 3.2 or 4.3%, respectively, of patients receiving the drug in clinical trials. Hypotension or postural hypotension also was noted in approximately 1% or less of patients receiving oral diltiazem. If symptomatic hypotension occurs, appropriate therapy (e.g., placement of the patients in the Trendelenburg's position, plasma volume expansion) should be initiated. Hypotension occurred secondary to the vasodilating action of diltiazem on vascular smooth muscle. Vasodilation or flushing occurred in 1.7% of patients receiving IV diltiazem and in approximately 1% or less of patients receiving oral diltiazem in clinical trials. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for DILTIAZEM (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Diltiazem is an antihypertensive and vasodilating agent that works by relaxing the vascular muscle and reducing blood pressure. This is related to the long-term therapeutic effects, as lowering the blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. Diltiazem inhibits the influx of extracellular calcium ions across the myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes during depolarization. Diltiazem is classified as a negative inotrope (decreased force) and negative chronotrope (decreased rate). It is also considered a rate-control drug as it reduces heart rate. Diltiazem is exerts hemodynamic actions by reducing blood pressure, systemic vascular resistance, the rate-pressure product, and coronary vascular resistance while increasing coronary blood flow. Diltiazem decreases sinoatrial and atrioventricular conduction in isolated tissues and has a negative inotropic effect in isolated preparations. In supraventricular tachycardia, diltiazem prolongs AV nodal refractories. As the magnitude of blood pressure reduction is related to the degree of hypertension, the antihypertensive effect of diltiazem is most pronounced in individuals with hypertension. In a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, dose-response study involving patients with essential hypertension, there was a reduction in the diastolic blood pressure by 1.9, 5.4, 6.1, and 8.6 mmHg in the patients receiving diltiazem at doses of 120, 240, 360, and 540 mg, respectively. In patients receiving placebo, there was a reduction in the diastolic blood pressure by 2.6 mmHg.In a randomized, double-blind study involving patients with chronic stable angina, variable doses of diltiazem administered at night all caused an increased exercise tolerance in the after 21 hours, compared to placebo. In the NORDIL study of patients with hypertension, the therapeutic effectiveness of diltiazem in reducing cardiovascular morbidity and mortality was assessed. When using the combined primary endpoint as fatal and non-fatal stroke, myocardial infarction, and other cardiovascular death, fatal and non-fatal stroke was shown to be reduced by 25% in the diltiazem group. Although the clinical significance to this effect remains unclear, it is suggested that diltiazem may exert a protective role against cerebral stroke in hypertensive patients. |
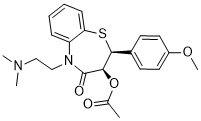
| 分子式 |
C22H26N2O4S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
414.52
|
| 精确质量 |
414.161
|
| CAS号 |
42399-41-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Diltiazem hydrochloride;33286-22-5;Diltiazem malate;144604-00-2;Diltiazem-d6;1242184-41-3
|
| PubChem CID |
39186
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
594.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
104-106°C (lit.)
|
| 闪点 |
313.3±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.621
|
| LogP |
3.63
|
| tPSA |
84.38
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
565
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
CC(=O)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](SC2=CC=CC=C2N(C1=O)CCN(C)C)C3=CC=C(C=C3)OC
|
| InChi Key |
HSUGRBWQSSZJOP-RTWAWAEBSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H26N2O4S/c1-15(25)28-20-21(16-9-11-17(27-4)12-10-16)29-19-8-6-5-7-18(19)24(22(20)26)14-13-23(2)3/h5-12,20-21H,13-14H2,1-4H3/t20-,21+/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2S,3S)-5-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b][1,4]thiazepin-3-yl acetate
|
| 别名 |
CRD 401 DiltiazemCRD-401 DilticardCRD401 Dilzen
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~241.24 mM)
H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.03 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4124 mL | 12.0621 mL | 24.1243 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4825 mL | 2.4124 mL | 4.8249 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2412 mL | 1.2062 mL | 2.4124 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。