| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Calmodulin (CaM): Ki = 0.8 μM (competitive binding with calcium-calmodulin complex) [1]
- L-type Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel (LTCC) (focus on autophagy induction via LTCC inhibition) [2] - L-type Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel (LTCC): IC50 = 12 nM (inhibits calcium influx in cardiac myocytes); no activity against N-type calcium channels (IC50 > 1000 nM) [3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
松弛猪冠状动脉最有效的药物是非洛地平,一种二氢吡啶钙拮抗剂(IC50=0.15 nM)[1]。 L 型钙通道阻滞剂非洛地平可促进自噬并清除许多与神经系统疾病相关且易于聚集的蛋白质 [2]。非洛地平的 IC50 为 1.45 nM,以 Ca2+ 依赖性方式抑制毒蕈碱受体(卡巴胆碱)介导的豚鼠回肠纵向平滑肌 (GPILSM) 的收缩 [3]。
舒张离体猪冠脉动脉段:1 μM Felodipine(CGH869)可使氯化钾(KCl)预收缩的冠脉段舒张75%;10 μM可实现完全舒张(EC50 = 0.3 μM)[1] - 诱导小鼠神经母细胞瘤N2a细胞自噬:500 nM Felodipine处理24小时,LC3-II/LC3-I比值升高3.2倍;自噬体数量增加4.5倍(免疫荧光检测)[2] - 抑制L型钙通道活性:100 nM Felodipine可使大鼠心室肌细胞钙内流减少88%;1 μM对N型钙通道无影响[3] - 具有抗惊厥活性:在小鼠皮层神经元培养中,1 μM Felodipine可使戊四氮(PTZ)诱导的惊厥样活性降低65%[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
口服非洛地平可显着降低 5/6 肾消融大鼠的平均血压 (BP),但会对已经受损的肾脏自动调节造成额外损害。服用非洛地平可通过阻断 NF-κB 激活,显着降低收缩压 (SBP)、血清胰岛素、细胞间粘附分子-1 (ICAM-1) 和血管细胞粘附分子-1 (VCAM-1),并减少主动脉中的巨噬细胞壁,导致血管炎症反应的调节。
C57BL/6小鼠(自噬研究):口服Felodipine(10 mg/kg/天)持续7天,海马神经元中LC3斑点数量增加3.8倍;脑/血浆浓度比=0.62[2] - ICR小鼠(抗惊厥研究):腹腔注射Felodipine(20 mg/kg),30分钟后给予PTZ,惊厥严重程度评分从溶剂组4.2降至1.8;ED50 = 15 mg/kg[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
钙调素结合实验:纯化牛脑钙调素(2 μg/孔)与Felodipine(0.1-10 μM)、0.1 μM [³H]-钙调素在结合缓冲液(25 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4,1 mM CaCl2,100 mM NaCl)中于37°C孵育60分钟。通过离心(12,000×g,10分钟)分离结合的[³H]-钙调素,液体闪烁计数法检测放射性,计算Ki值[1]
- L型钙通道活性实验:大鼠心室肌细胞用5 μM fura-2 AM(钙荧光探针)负载30分钟。加入Felodipine(0.01-1 μM),用60 mM KCl诱导钙内流。记录荧光强度(激发光340/380 nm,发射光510 nm),计算钙内流抑制率以确定IC50[3] |
| 细胞实验 |
自噬检测实验(N2a细胞):细胞接种于6孔板(2×10⁵个细胞/孔),用Felodipine(100-1000 nM)处理24小时。用RIPA缓冲液(含蛋白酶抑制剂)裂解细胞,通过Western blot检测LC3-I/LC3-II水平(每泳道30 μg蛋白,12% SDS-PAGE)。免疫荧光检测时,细胞用4%多聚甲醛固定,抗LC3抗体染色,共聚焦显微镜下计数自噬体[2]
- 抗惊厥细胞实验(小鼠皮层神经元):神经元接种于96孔板(1×10⁴个细胞/孔),用Felodipine(0.1-10 μM)处理1小时。加入500 μM PTZ,通过钙成像(fura-2 AM荧光)监测30分钟,记录惊厥样活性[3] |
| 动物实验 |
Oral
Rats Mouse brain autophagy model (C57BL/6 mice): 8-week-old male mice were randomized to vehicle (0.5% methylcellulose + 0.2% Tween 80) or Felodipine groups (10 mg/kg/day, oral gavage) for 7 days. Mice were euthanized, and hippocampi were dissected for Western blot (LC3 detection) and immunofluorescence (LC3 puncta counting) [2] - Mouse pharmacokinetic study (C57BL/6 mice): Mice received Felodipine (10 mg/kg, oral gavage or intraperitoneal injection). Blood and brain samples were collected at 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8 hours post-administration. Drug concentration was measured via LC-MS/MS to calculate brain/plasma ratio and half-life [2] - Mouse anticonvulsant model (ICR mice): 6-week-old female mice received Felodipine (5-30 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection) 30 minutes before 85 mg/kg PTZ (intraperitoneal). Seizure severity was scored (0-5 scale) for 30 minutes; ED50 was calculated via probit analysis [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Is completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract; however, extensive first-pass metabolism through the portal circulation results in a low systemic availability of 15%. Bioavailability is unaffected by food. Although higher concentrations of the metabolites are present in the plasma due to decreased urinary excretion, these are inactive. Animal studies have demonstrated that felodipine crosses the blood-brain barrier and the placenta. 10 L/kg 0.8 L/min [Young healthy subjects] Metabolism / Metabolites Hepatic metabolism primarily via cytochrome P450 3A4. Six metabolites with no appreciable vasodilatory effects have been identified. Biological Half-Life 17.5-31.5 hours in hypertensive patients; 19.1-35.9 hours in elderly hypertensive patients; 8.5-19.7 in healthy volunteers. In C57BL/6 mice: Oral bioavailability of Felodipine = 42% (10 mg/kg dose); plasma half-life (t1/2) = 2.8 hours; brain/plasma concentration ratio = 0.62 at 1 hour post-oral administration [2] - In C57BL/6 mice (intraperitoneal): t1/2 = 1.9 hours; clearance rate = 18 mL/min/kg; volume of distribution at steady state (Vss) = 1.2 L/kg [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because no information is available on the use of felodipine during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding 99%, primarily to the albumin fraction. In 7-day mouse autophagy study (10 mg/kg/day, oral): No significant weight loss (>8%); serum ALT = 26 ± 4 U/L, AST = 48 ± 6 U/L, BUN = 17 ± 3 mg/dL (within normal ranges) [2] - In acute toxicity study (ICR mice): Intraperitoneal LD50 of Felodipine = 120 mg/kg; no histopathological changes in liver/kidney at doses ≤30 mg/kg [3] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
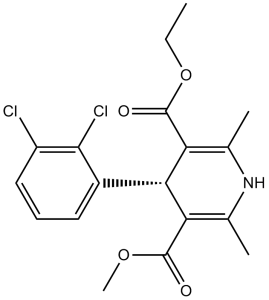
Felodipine is the mixed (methyl, ethyl) diester of 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid. A calcium-channel blocker, it lowers blood pressure by reducing peripheral vascular resistance through a highly selective action on smooth muscle in arteriolar resistance vessels. It is used in the management of hypertension and angina pectoris. It has a role as a calcium channel blocker, an antihypertensive agent, a vasodilator agent and an anti-arrhythmia drug. It is a dihydropyridine, a dichlorobenzene, an ethyl ester and a methyl ester.
Felodipine is a long-acting 1,4-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker (CCB)b. It acts primarily on vascular smooth muscle cells by stabilizing voltage-gated L-type calcium channels in their inactive conformation. By inhibiting the influx of calcium in smooth muscle cells, felodipine prevents calcium-dependent myocyte contraction and vasoconstriction. Felodipine is the most potent CCB in use and is unique in that it exhibits fluorescent activity. In addition to binding to L-type calcium channels, felodipine binds to a number of calcium-binding proteins, exhibits competitive antagonism of the mineralcorticoid receptor, inhibits the activity of calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase, and blocks calcium influx through voltage-gated T-type calcium channels. Felodipine is used to treat mild to moderate essential hypertension. Felodipine is a Dihydropyridine Calcium Channel Blocker. The mechanism of action of felodipine is as a Calcium Channel Antagonist. Felodipine is a second generation calcium channel blocker and commonly used antihypertensive agent. Felodipine therapy has been associated with a low rate of serum enzyme elevations, but has not been convincingly linked to instances of clinically apparent, acute liver injury. Felodipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocking agent. Felodipine inhibits the influx of extracellular calcium ions into myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cells, causing dilatation of the main coronary and systemic arteries and decreasing myocardial contractility. This agent also inhibits the drug efflux pump P-glycoprotein which is overexpressed in some multi-drug resistant tumors and may improve the efficacy of some antineoplastic agents. (NCI04) A dihydropyridine calcium antagonist with positive inotropic effects. It lowers blood pressure by reducing peripheral vascular resistance through a highly selective action on smooth muscle in arteriolar resistance vessels. See also: Enalapril maleate; felodipine (component of). Drug Indication For the treatment of mild to moderate essential hypertension. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Felodipine decreases arterial smooth muscle contractility and subsequent vasoconstriction by inhibiting the influx of calcium ions through voltage-gated L-type calcium channels. It reversibly competes against nitrendipine and other DHP CCBs for DHP binding sites in vascular smooth muscle and cultured rabbit atrial cells. Calcium ions entering the cell through these channels bind to calmodulin. Calcium-bound calmodulin then binds to and activates myosin light chain kinase (MLCK). Activated MLCK catalyzes the phosphorylation of the regulatory light chain subunit of myosin, a key step in muscle contraction. Signal amplification is achieved by calcium-induced calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum through ryanodine receptors. Inhibition of the initial influx of calcium decreases the contractile activity of arterial smooth muscle cells and results in vasodilation. The vasodilatory effects of felodipine result in an overall decrease in blood pressure. Felodipine may be used to treat mild to moderate essential hypertension. Pharmacodynamics Felodipine belongs to the dihydropyridine (DHP) class of calcium channel blockers (CCBs), the most widely used class of CCBs. There are at least five different types of calcium channels in Homo sapiens: L-, N-, P/Q-, R- and T-type. It was widely accepted that CCBs target L-type calcium channels, the major channel in muscle cells that mediates contraction; however, some studies have shown that felodipine also binds to and inhibits T-type calcium channels. T-type calcium channels are most commonly found on neurons, cells with pacemaker activity and on osteocytes. The pharmacologic significance of T-type calcium channel blockade is unknown. Felodipine also binds to calmodulin and inhibits calmodulin-dependent calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The effect of this interaction appears to be minor. Another study demonstrated that felodipine attenuates the activity of calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (CaMPDE) by binding to the PDE-1B1 and PDE-1A2 enzyme subunits. CaMPDE is one of the key enzymes involved in cyclic nucleotides and calcium second messenger systems. Felodipine also acts as an antagonist to the mineralcorticoid receptor by competing with aldosterone for binding and blocking aldosterone-induced coactivator recruitment of the mineralcorticoid receptor. Felodipine is able to bind to skeletal and cardiac muscle isoforms of troponin C, one of the key regulatory proteins in muscle contraction. Though felodipine exhibits binding to many endogenous molecules, its vasodilatory effects are still thought to be brought about primarily through inhibition of voltage-gated L-type calcium channels. Similar to other DHP CCBs, felodipine binds directly to inactive calcium channels stabilizing their inactive conformation. Since arterial smooth muscle depolarizations are longer in duration than cardiac muscle depolarizations, inactive channels are more prevalent in smooth muscle cells. Alternative splicing of the alpha-1 subunit of the channel gives felodipine additional arterial selectivity. At therapeutic sub-toxic concentrations, felodipine has little effect on cardiac myocytes and conduction cells. Felodipine is a dihydropyridine-class L-type calcium channel blocker, originally developed for hypertension and angina pectoris via inhibiting calcium influx in vascular smooth muscle [3] - It binds to calmodulin competitively, enhancing calcium-calmodulin complex dissociation to relax coronary arteries [1] - In the brain, Felodipine crosses the blood-brain barrier and induces autophagy, suggesting potential for neurodegenerative disease treatment [2] - Its anticonvulsant activity is mediated via L-type calcium channel inhibition in cortical neurons, supporting repurposing for epilepsy [3] |
| 分子式 |
C18H19CL2NO4
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
384.25
|
|
| 精确质量 |
383.069
|
|
| CAS号 |
72509-76-3
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Felodipine-d3;1219795-30-8;Felodipine-d5;1242281-38-4
|
|
| PubChem CID |
3333
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
471.5±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
142-145°C
|
|
| 闪点 |
239.0±28.7 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.550
|
|
| LogP |
4.83
|
|
| tPSA |
64.63
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
25
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
614
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
RZTAMFZIAATZDJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H19Cl2NO4/c1-5-25-18(23)14-10(3)21-9(2)13(17(22)24-4)15(14)11-7-6-8-12(19)16(11)20/h6-8,15,21H,5H2,1-4H3
|
|
| 化学名 |
(RS)-3-ethyl 5-methyl 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.51 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.51 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6025 mL | 13.0124 mL | 26.0247 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5205 mL | 2.6025 mL | 5.2049 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2602 mL | 1.3012 mL | 2.6025 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05614037 | Active, not recruiting | Drug: Felodipine sustained release tablets (trade name: plendil®) |
Hypertension | Overseas Pharmaceuticals, Ltd. | October 28, 2022 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01238705 | Unknown | Drug: Felodipine add Irbesartan | Hypertension Sexual Dysfunction |
LanZhou University | April 2008 | Phase 4 |
| NCT00742066 | Unknown | Drug: Felodipine Drug: Irbesartan |
Hypertension Insulin Resistance |
Maastricht University Medical Center |
March 2008 | Not Applicable |
| NCT05258448 | Recruiting | Other: Chemoradiotherapy | Cardiac Toxicity Lung Cancer Stage III |
Odense University Hospital | August 2015 | |
| NCT05788159 | Not yet recruiting | Drug: Lacosamide Tablets | Epilepsy | Overseas Pharmaceuticals, Ltd. | April 1, 2023 | Phase 1 |
|
|
|