| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
DPP-4 (IC50 = 4 nM)
The target of Trelagliptin (SYR-472, Zafatek) is dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). For human recombinant DPP-4, the inhibition constant (Ki) of Trelagliptin was determined to be 0.4 nM. The compound showed high selectivity for DPP-4, with negligible inhibitory activity against other DPP family enzymes including DPP-8 (Ki > 10,000 nM) and DPP-9 (Ki > 10,000 nM), as well as prolyl endopeptidase (PEP, Ki > 10,000 nM) [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
曲格列汀(也称为 SYR-472)是武田正在开发的一种有效、高选择性、长效的 DPP-4(二肽基肽酶-4)抑制剂,用于治疗 2 型糖尿病 (T2D)。 -每周曲格列汀治疗对 2 型糖尿病患者的血糖控制产生了临床和统计学上的显着改善。它具有良好的耐受性,可能成为这种疾病患者的一种新的治疗选择。曲格列汀在日本被批准用于治疗 2 型糖尿病 (T2DM)。
1. DPP-4抑制活性:曲格列汀对人重组DPP-4具有强效且浓度依赖性的抑制活性。在1 nM浓度下,其对DPP-4活性的抑制率超过90%;即使在低至0.1 nM的浓度下,抑制率仍可达约50%。对人DPP-4的半数抑制浓度(IC50)为0.6 nM。此外,曲格列汀对其他物种的DPP-4也具有有效抑制作用,如对小鼠DPP-4的IC50为0.8 nM,对大鼠DPP-4的IC50为0.7 nM [2] 2. 对DPP家族酶的选择性:针对与DPP-4同源性较高且抑制后可能引发毒性的DPP-8和DPP-9,曲格列汀即使在10,000 nM的高浓度下,也未表现出显著的抑制作用;对脯氨酰特异性肽酶PEP,在相同高浓度下同样无抑制活性,表明其对DPP-4具有高选择性 [2] 3. 体外对GLP-1和GIP水平的影响:在肠道上皮细胞体外实验中,曲格列汀(10 nM)处理可显著提高细胞分泌的活性胰高血糖素样肽-1(active glucagon-like peptide-1,active GLP-1)和活性葡萄糖依赖性促胰岛素多肽(active glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide,active GIP)水平。与对照组相比,活性GLP-1浓度升高约2.5倍,活性GIP浓度升高约2.0倍 [2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Trelagliptin/曲格列汀(口服灌胃;7 mg/kg;单次剂量)在狗体内抑制DPP-4活性的时间超过80%,即使在24小时后也是如此,这表明了持续的帕金森病效应[1]。
与赋形剂组相比,Trelagliptin(口服灌胃;3 mg/kg;单次剂量;口服葡萄糖前60分钟)使ob/ob小鼠的AUC0-120min降低了19.3%,大大提高了葡萄糖耐量[3]。 Trelagliptin(口服灌胃;10mg/kg;每周一次;8周)显著降低了空腹血糖(FBG)水平;在治疗期间,平均下降幅度比对照组低16.8%。此外,它提高了胰岛素水平,在ob/ob小鼠中,AUC0-120min[3]的胰岛素水平提高了1.7倍。 1. 对db/db小鼠(2型糖尿病模型)的降糖 efficacy: - 单剂量研究:给db/db小鼠口服曲格列汀(0.3、1、3、10 mg/kg)后,空腹血糖(fasting blood glucose,FBG)呈剂量依赖性降低。给药后24小时,10 mg/kg剂量组的FBG较溶媒对照组降低40%;降糖效果可持续长达7天,给药后第7天,10 mg/kg剂量组的FBG仍较对照组低25% [2] - 多剂量研究(每周一次给药):以1、3、10 mg/kg剂量给db/db小鼠每周口服一次曲格列汀,连续4周后,10 mg/kg剂量组的糖化血红蛋白(glycated hemoglobin,HbA1c)较基线显著降低1.2%,而溶媒对照组在同期HbA1c升高0.5%。此外,治疗组在第4周时血浆活性GLP-1水平升高1.8倍、活性GIP水平升高1.5倍,且在葡萄糖耐量试验中血浆胰岛素浓度升高30% [2] 2. 与西格列汀(每日一次DPP-4抑制剂)的对比:在db/db小鼠中,曲格列汀(3 mg/kg,每周一次)与西格列汀(10 mg/kg,每日一次)在4周内的降糖效果(以FBG和HbA1c降低衡量)相当。但曲格列汀对活性GLP-1水平的维持作用更持久,在7天给药间隔内始终保持较高浓度,而西格列汀在每日给药后24小时内GLP-1水平即出现下降 [2] 3. 对ob/ob小鼠(饮食诱导肥胖糖尿病模型)的 efficacy:给ob/ob小鼠每周口服一次曲格列汀(10 mg/kg),连续3周后,FBG降低35%,葡萄糖耐量改善,葡萄糖曲线下面积(area under the glucose curve,AUCglucose)较溶媒对照组减少28% [2] |
| 酶活实验 |
酶抑制试验[2]
这些研究中使用的人DPP-4酶来自几个来源。如前所述,使用从ATCC(ATCC编号HTB-37;www.ATCC.org)购买的Caco-2细胞部分纯化的人DPP-4来确认trelagliptin抑制剂的效力。为了比较DPP-4抑制剂,trelagliptin、阿格列汀和西格列汀,使用市售重组人DPP-4(台湾Abnova)。为了进行详细的动力学研究,如前所述克隆、表达和纯化重组人DPP-4。此外,使用人、狗和大鼠的血浆样本测定了血浆DPP-4活性的抑制作用。根据之前报道的方法,DPP-4相关蛋白酶,二肽基肽酶-2(DPP-2)和脯氨酰内肽酶(PEP)分别从大鼠肾脏和脑中制备。通过亲和层析从表达每种FLAG标记蛋白的293-F细胞中纯化人二肽基肽酶-8(DPP-8)、二肽基多肽酶-9(DPP-9)和成纤维细胞活化蛋白α(FAPα)。[2] 为了进行详细的动力学研究,使用GP pNA作为底物,并在室温下在pH 7.4的缓冲液中进行测定,该缓冲液含有20 mmol/L HEPES、20 mmol/L MgCl2、0.1 mg/ml牛血清白蛋白和1%(v/v)DMSO。在大多数情况下,最后加入DPP-4酶(终浓度为1 nmol/L)以启动酶反应,但在测量预先形成的DPP-4抑制剂复合物中DPP-4酶活性的恢复时除外,在这种情况下,酶首先与trelagliptin预孵育70分钟,然后通过稀释50倍到含有大量过量(2 mmol/L,约17xKm)GP pNA底物的反应缓冲液中来启动反应。所有测定均以96孔格式重复进行,总测定体积为200uL,每10秒测量405nm处的吸光度,以确定反应时间过程。在大多数情况下,整个反应过程曲线如下所述进行分析。然而,对于通过trelagliptin建立GP pNA底物竞争性抑制的初始速率研究,仅使用了前40秒的吸光度测量值。 SD大鼠的体外生物测定、晶体结构测定和药代动力学测定[3] 体外DPP-4抑制研究(至少三个独立实验)、使用表面等离子体共振的结合动力学研究、DPP-4与化合物5的共结晶以及结构测定,以及SD大鼠的药代动力学测定,都是使用我们之前工作中报告的相同操作方法进行的。 1. DPP-4活性测定: - 底物制备:将Gly-Pro-对硝基苯胺(Gly-Pro-pNA)溶解于pH 7.4的Tris-HCl-NaCl缓冲液中,制备终浓度为1 mM的显色底物溶液 [2] - 反应体系构建:反应体系总体积为200 μL,包含人重组DPP-4(0.1 μg/mL)、不同浓度的曲格列汀(0.01~1000 nM)及Gly-Pro-pNA底物。将反应体系在37°C下孵育30分钟 [2] - 检测与计算:使用酶标仪检测405 nm处的吸光度,以反映对硝基苯胺的释放量。根据处理组与溶媒对照组的吸光度差值计算曲格列汀对DPP-4的抑制率;采用非线性回归分析,将抑制数据拟合至米氏方程(Michaelis-Menten equation),计算Ki值 [2] 2. 对其他DPP家族酶的选择性测定: - 针对DPP-8和DPP-9:仍使用Gly-Pro-pNA作为底物,但将反应缓冲液pH调整为8.0,DPP-8和DPP-9的酶浓度均为0.2 μg/mL。曲格列汀的测试浓度最高达10,000 nM,反应体系在37°C下孵育60分钟后,检测405 nm吸光度并计算抑制率 [2] - 针对PEP:使用Z-Gly-Pro-7-氨基-4-甲基香豆素(Z-Gly-Pro-AMC)作为底物,反应体系在37°C下孵育45分钟后,检测荧光强度(激发波长360 nm,发射波长460 nm)。曲格列汀测试浓度为10,000 nM,根据荧光强度差值计算抑制率 [2] |
| 细胞实验 |
使用发色底物Gly-Pro-p-硝基苯胺(GP pNA)(终浓度为0.5 mmol/L)测定Caco-2细胞或血浆中的DPP-4活性,并在pH 7.5的缓冲液中进行,该缓冲液含有100 mmol/L Tris-HCl、1 mg/mL牛血清白蛋白和0.5 mg/mL CHAPS(3-[(3-甲酰氨基丙基)二甲基铵]-1-丙磺酸),在37°C(Caco-2电池的DPP-4组分)或30°C(血浆)下进行60分钟。测量405nm处的吸光度变化以确定反应速率。使用荧光底物Gly-Pro-7-氨基-4-甲基香豆素(GP-AMC)(终浓度90μmol/L)测定重组人DPP-4活性,并在含有25 mmol/L HEPES、140 mmol/L NaCl、1 mg/mL牛血清白蛋白的pH 7.8缓冲液中在37°C下进行15分钟。通过加入100μL 25%(v/v)乙酸停止反应,并使用Envision 2103 Multilabel Reader测量荧光(380 nm激发/460 nm发射)。表1中描述了测量DPP-2、DPP-8、DPP-9、PEP和FAPα活性的反应条件。测量405nm处的吸光度变化以确定反应速率[2]。
肠道上皮细胞GLP-1/GIP分泌实验: - 细胞培养:将人结肠腺癌细胞系(肠道上皮细胞模型)接种于含胎牛血清、青霉素和链霉素的培养基中,在37°C、5% CO2培养箱中培养。将细胞以5×104个/孔的密度接种于24孔板,培养至融合状态 [2] - 处理与刺激:更换培养基为含不同浓度曲格列汀(1、10、100 nM)或溶媒的无血清培养基,预孵育30分钟后,加入20 mM葡萄糖以刺激GLP-1和GIP分泌,继续在37°C下孵育2小时 [2] - 样本收集与检测:收集各孔上清液,1000×g离心10分钟去除细胞碎片。采用酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)试剂盒检测上清液中活性GLP-1和活性GIP的浓度;通过细胞计数试剂盒测定细胞数量,将分泌量归一化为每细胞的分泌量 [2] |
| 动物实验 |
ICR ob/ob mice[3]
10 mg/kg Oral gavage; 10 mg/kg; once a week; 8 weeks Effect on DPP-4 Activity in ob/ob Mice[3] Eight-week-old ob/ob mice (n = 10 in each group, 5 male and 5 female) were randomly assigned to treatment groups. After 2 h of fasting, baseline blood was collected into a tube containing EDTA. Mice were then treated orally with vehicle (0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, 10 mL/kg), compound 5 (0.3, 1, 3, 1, and 10 mg/kg), omarigliptin (3 mg/kg), or trelagliptin (3 mg/kg). Subsequently, blood per animal was collected at 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, 48, 72, 96, 120, 144, and 168 h. All samples were centrifuged at 10 000 rpm for 2 min, and the plasma was harvested. Aliquots of plasma samples were stored at −80 °C until analysis. The measurement of in vivo DPP-4 activity was the same as the method with ICR mice. Effect on OGTT in db/db Mice[3] To examine the effect of compound 5 on blood glucose after an oral glucose challenge in 6 week old db/db mice (n = 10 in each group, 5 male and 5 female), compound 5 (3 and 10 mg/kg), omarigliptin (10 mg/kg), trelagliptin (10 mg/kg), or vehicle (0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose) was orally administered to 6 h-fasted db/db mice 60 min prior to the oral glucose challenge (1.5 g/kg). Blood glucose was estimated using a glucometer at 60 min before the glucose load and 0, 15, 30, 60, 90, and 120 min post-glucose challenge. The AUC for the glucose tolerance test was calculated using the trapezoidal method. Long-Term Antidiabetic Effects in db/db Mice[3] Six-week-old db/db mice were divided into 5 groups (n = 10 in each group, 5 male and 5 female) based on nonfasting blood glucose and 6 h FBG, serum insulin levels, PBW (non-FBW), and 6 h FBW. Lean littermates were used as the lean control. Compound 5 (3 and 10 mg/kg), omarigliptin (10 mg/kg), trelagliptin (10 mg/kg), or vehicle (0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose) was orally administered once weekly for 8 weeks. Nonfasting glucose and FBG, PBW, and 6 h FBW were determined at 7 d intervals. After 7 weeks of treatment, the 6 h-fasted animal was challenged by 1.5 g/kg glucose. Blood glucose was estimated using a glucometer at 0, 15, 30, 60, 90, and 120 min post-glucose challenge. After 8 weeks of treatment, the 6 h-fasted animal was challenged by 1.5 g/kg glucose. Blood samples were collected at 0, 15, 30, and 60 min post-glucose challenge to test plasma insulin levels. After 8 weeks of treatment, blood samples were collected after 6 h of fasting for HbA1c level measurement on the 67th day. The detailed dosing regimen is provided in the Supporting Information (Figure S11). 1. db/db Mouse Antihyperglycemic Study (Single-Dose and Multiple-Dose): - Animal Preparation: Male db/db mice (8 weeks old, weighing 30-35 g) were acclimated for 1 week under standard conditions (12-hour light/dark cycle, 22±2°C, free access to food and water). Mice were randomly divided into 5 groups: vehicle control group, Trelagliptin 0.3 mg/kg group, Trelagliptin 1 mg/kg group, Trelagliptin 3 mg/kg group, and Trelagliptin 10 mg/kg group (n=6 per group) [2] - Drug Formulation and Administration: Trelagliptin was dissolved in a 0.5% methylcellulose solution to prepare the dosing formulations. The drug was administered orally using a gastric gavage needle. For the single-dose study, mice were dosed once, and blood samples were collected at 0, 2, 4, 8, 24, 48, 72, 96, 120, 144, and 168 hours post-administration. For the multiple-dose study, mice were dosed once weekly for 4 weeks, and blood samples were collected before each dose (to measure trough levels) and at the end of the study (week 4) [2] - Detection Indicators: Fasting blood glucose was measured using a glucose meter from tail vein blood samples. HbA1c was determined from whole blood samples using a HbA1c analyzer. Plasma levels of active GLP-1, active GIP, and insulin were measured using ELISA kits. At the end of the study, mice were euthanized, and pancreatic tissues were collected for histological analysis (hematoxylin-eosin staining) to evaluate islet morphology [2] 2. ob/ob Mouse Efficacy Study: - Animal Model: Male ob/ob mice (7 weeks old, weighing 25-30 g) were used. Mice were divided into 2 groups: vehicle control (0.5% methylcellulose) and Trelagliptin 10 mg/kg (n=5 per group) [2] - Dosing and Sampling: Trelagliptin was administered orally once weekly for 3 weeks. Fasting blood glucose was measured weekly. A glucose tolerance test (GTT) was performed at the end of the study: mice were fasted for 16 hours, and glucose (2 g/kg) was administered intraperitoneally. Blood glucose was measured at 0, 15, 30, 60, and 120 minutes after glucose administration to calculate the AUCglucose [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
1. Oral Absorption: In male Sprague-Dawley rats, oral administration of Trelagliptin (10 mg/kg) resulted in a peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of 125 ng/mL and an area under the plasma concentration-time curve from time 0 to infinity (AUC0-∞) of 1560 ng·h/mL. The oral bioavailability was calculated to be approximately 80% (compared to intravenous administration of 1 mg/kg) [2]
2. Distribution: In rats, the volume of distribution at steady state (Vdss) of Trelagliptin was 0.8 L/kg, indicating moderate distribution into tissues. The plasma protein binding rate was low, at approximately 15% (measured using ultrafiltration method with rat plasma) [2] 3. Metabolism: Trelagliptin showed minimal metabolism in vitro. When incubated with rat liver microsomes, less than 10% of the parent compound was metabolized after 2 hours. The main metabolite identified was a hydroxylated derivative, which accounted for less than 5% of the total drug-related material. In vivo, the metabolite concentration in rat plasma was less than 10% of the parent compound concentration [2] 4. Excretion: In rats, after oral administration of 10 mg/kg Trelagliptin, approximately 75% of the dose was excreted in urine and 15% in feces within 72 hours. The majority of the drug excreted in urine was the parent compound (about 65% of the dose), indicating that renal excretion is the main elimination pathway [2] 5. Half-Life: In rats, the elimination half-life (t1/2) of Trelagliptin was approximately 10 hours. In beagle dogs, oral administration of 5 mg/kg Trelagliptin resulted in a t1/2 of 18 hours, which supports the once-weekly dosing regimen [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. Acute Toxicity: In ICR mice, oral administration of Trelagliptin at doses up to 500 mg/kg did not cause any mortality or obvious toxic symptoms (such as weight loss, abnormal behavior, or organ damage) within 14 days of observation. The approximate lethal dose (LD50) was determined to be greater than 500 mg/kg [2]
2. Repeat-Dose Toxicity (28-Day Study in Rats): Male and female Sprague-Dawley rats were administered Trelagliptin orally at doses of 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg once daily for 28 days. No treatment-related deaths were observed. There were no significant changes in body weight, food intake, or hematological parameters (red blood cell count, white blood cell count, hemoglobin) in any dose group. Biochemical parameters (alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine) were also within the normal range, indicating no liver or kidney toxicity. Histopathological examination of major organs (liver, kidney, pancreas, heart, lung) showed no abnormal changes related to Trelagliptin treatment [2] 3. Plasma Protein Binding and Drug-Drug Interaction Potential: The plasma protein binding rate of Trelagliptin was low (15% in rat plasma, 20% in human plasma), which reduces the risk of drug-drug interactions mediated by plasma protein displacement. In vitro studies using human liver microsomes showed that Trelagliptin did not inhibit the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4) at concentrations up to 100 μM, indicating a low potential for metabolic drug-drug interactions [2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Trelagliptin is a member of benzenes and a nitrile.
Trelagliptin is under investigation in clinical trial NCT03555591 (Specified Drug-Use Survey of Trelagliptin Tablets "Survey on Long-term Use in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus"). 1. Mechanism of Action: Trelagliptin inhibits DPP-4 via a non-covalent mechanism. Unlike some DPP-4 inhibitors that form covalent bonds with the active site serine residue of DPP-4, Trelagliptin binds to the active site through hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions, which contributes to its long-lasting inhibitory effect and favorable safety profile [2] 2. Therapeutic Advantage: As a once-weekly DPP-4 inhibitor, Trelagliptin offers improved patient compliance compared to daily DPP-4 inhibitors (such as sitagliptin, saxagliptin) for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Its long half-life and sustained DPP-4 inhibitory activity allow for weekly dosing while maintaining effective glycemic control [2] 3. Preclinical Development Status: Trelagliptin was identified as a novel preclinical candidate for type 2 diabetes based on its potent DPP-4 inhibitory activity, high selectivity, favorable pharmacokinetic profile (long half-life, high oral bioavailability), and good safety profile in preclinical toxicity studies [2] 4. Brief Mention in Literature [1]: Literature [1] (a 2014 review on DPP-4 inhibitors) mentioned that long-acting DPP-4 inhibitors are a promising direction in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, and Trelagliptin was cited as an example of a novel once-weekly DPP-4 inhibitor under development[1] |
| 分子式 |
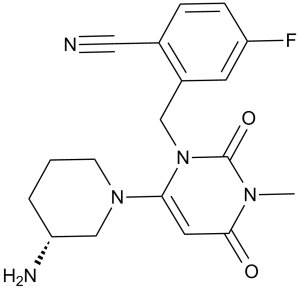
C18H20FN5O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
357.38
|
| 精确质量 |
357.16
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 60.49; H, 5.64; F, 5.32; N, 19.60; O, 8.95
|
| CAS号 |
865759-25-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Trelagliptin succinate;1029877-94-8
|
| PubChem CID |
15983988
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
519.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
267.7±32.9 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.646
|
| LogP |
1.88
|
| tPSA |
97.05
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
26
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
657
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
C(C1C=C(F)C=CC=1C#N)N1C(=O)N(C)C(=O)C=C1N1CCC[C@@H](N)C1
|
| InChi Key |
IWYJYHUNXVAVAA-OAHLLOKOSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H20FN5O2/c1-22-17(25)8-16(23-6-2-3-15(21)11-23)24(18(22)26)10-13-7-14(19)5-4-12(13)9-20/h4-5,7-8,15H,2-3,6,10-11,21H2,1H3/t15-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
2-[[6-[(3R)-3-aminopiperidin-1-yl]-3-methyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl]methyl]-4-fluorobenzonitrile
|
| 别名 |
SYR 472; Trelagliptin; SYR-472; TRELAGLIPTIN; 865759-25-7; Trelagliptin [USAN]; Trelagliptin [USAN:INN]; UNII-Q836OWG55H; Q836OWG55H; Trelagliptin (USAN); SYR472; trade name: Zafatek
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.00 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.00 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.00 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7981 mL | 13.9907 mL | 27.9814 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5596 mL | 2.7981 mL | 5.5963 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2798 mL | 1.3991 mL | 2.7981 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03555591 | Completed | Drug: Trelagliptin | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | Takeda | May 1, 2016 | |
| NCT02512068 | Completed | Drug: Trelagliptin 25 mg Drug: Placebo |
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | Takeda | August 7, 2015 | Phase 3 |
| NCT04285983 | Completed | Drug: Trelagliptin | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | Takeda | March 1, 2020 | |
| NCT03014479 | Completed | Drug: Trelagliptin Drug: Daily DPP-4 inhibitor |
Type 2 Diabetes | Takeda | February 18, 2017 | Phase 4 |
| NCT02771093 | Completed | Drug: Trelagliptin Drug: Alogliptin |
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | Takeda | September 8, 2016 | Phase 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|