| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
apoptosis
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
与对照组相比,四水柠檬酸锂在 ARPE19 和 661W 细胞中表现出 HIF 抑制作用。在 ARPE19 细胞和 661W 细胞中,四水柠檬酸锂可以下调 Hif1a 及其下游基因。 CoCl2处理ARPE19和661W细胞可导致HIF-1α蛋白表达增强,而这种蛋白表达可被四水柠檬酸锂抑制[2]。四水柠檬酸锂可减少鸡肝细胞中的脂滴积累并加速能量代谢。四水柠檬酸锂可增强线粒体活性和抗氧化状态,保护细胞免受内质网应激[2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
用 100–200 mg/kg 四水柠檬酸锂治疗可降低血清肌酐和血尿素氮(肾损伤的两个指标)。当给予雄性C57BL/6J小鼠四水柠檬酸锂时,草酸钙晶体形成的量显着减少。四水柠檬酸锂可减轻草酸钙晶体带来的氧化应激。 MCP-1、IL-1β 和 IL-6 是炎症细胞因子的例子,它们受草酸钙刺激并被柠檬酸锂四水合物抑制。此外,柠檬酸锂四水合物可以减轻草酸钙晶体诱导的肾小管损伤和细胞凋亡[1]。给动物服用四水柠檬酸锂可以防止它们体重增加或脂肪堆积[3]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
柠檬酸锂/lithium citrate(LC)作为一种常见的食品添加剂,也是一种精神药物,通常以四水合物的形式存在,可以在高于室温的温度下逐渐失去其结晶水并转化为LC无水物。为了快速区分四水合物和无水物,并研究LC水合物在温度影响下的脱水动力学,本研究利用太赫兹时域光谱(THz-TDS)。实验结果表明,LC四水合物在室温下在1.66 THz附近有一个明显的吸收峰,而LC无水物在0.5-3.0 THz没有吸收峰。LC四水合物的吸收峰强度在从25°C加热到100°C时持续降低。基于LC四水合物在1.66 THz附近的归一化吸收峰面积,研究了其脱水速率随加热温度的变化,并用Arrhenius方程拟合了它们之间的关系。LC四水合物的反应活化能为495.1±17.8 J/g,与传统的差示扫描量热法(DSC)测量值的偏差约为3.7%。这些结果表明,THz-TDS可以提供一种检测结晶水合物的有效方法,并可用于研究结晶水合物的脱水动力学,具有快速、无标记和准确的优点。 [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34649122/]
沙丁胺醇是一种通过改善肺部中大气道来治疗肺部疾病的药物。沙丁胺醇药物在PEG10001500200040006000双水相体系中的分配 + lithium citrate/柠檬酸三锂 + 水在T时测定 = 298.15 K.研究了聚合物分子量(MMP)对双峰和连接线组成的影响。结果表明,随着MMP的增加,两相区扩大。盐析能力使用Setschenow模型进行量化,双峰曲线由非线性3参数方程建模。此外,电解质Wilson和渗透病毒模型已被充分应用于拟合联络线组成。此外,还实施了所研究的ATPSs,以研究沙丁胺醇药物在富盐相和富聚合物相上的分配。观察到,PEG1000的ATPSs对于将沙丁胺醇提取到富含聚合物的相是优质的,而PEG6000的ATPSss更有利于将药物提取到富含盐的相。 [https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9852274/#Abs1] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Lithium Citrate can cause developmental toxicity according to state or federal government labeling requirements.
Lithium citrate tetrahydrate is a hydrate that is the tetrahydrate form of lithium citrate. It is used as a source of lithium for the treatment of anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, and depression. It has a role as an antidepressant. It contains a lithium citrate (anhydrous). Lithium Citrate is the citrate salt of lithium, a monovalent cation with antimanic activity. Although the exact mechanism is unclear, lithium might exert its mood-stabilizing effect via reduction of catecholamine concentration mediated through transneuronal membrane transport of sodium ion by sodium-potassium-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase (Na-K-ATPase). Alternatively, lithium may decrease cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) concentrations, which would desensitize hormonal-sensitive adenylyl cyclase receptors. Furthermore, lithium, in recommended dosage, blocks the activity of inositol-1-phosphatase, thereby resulting in the subsequent decrease of postsynaptic second messengers, diacylglycerol and inositol triphosphate, that contribute to chronic cell stimulation by altering electrical activity in the neuron. See also: Lithium Citrate (annotation moved to). Drug Indication Lithium is used as a mood stabilizer, and is used for treatment of depression and mania. It is often used in bipolar disorder treatment. Mechanism of Action The precise mechanism of action of Li+ as a mood-stabilizing agent is currently unknown. It is possible that Li+ produces its effects by interacting with the transport of monovalent or divalent cations in neurons. An increasing number of scientists have come to the conclusion that the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate is the key factor in understanding how lithium works. Lithium has been shown to change the inward and outward currents of glutamate receptors (especially GluR3), without a shift in reversal potential. Lithium has been found to exert a dual effect on glutamate receptors, acting to keep the amount of glutamate active between cells at a stable, healthy level, neither too much nor too little. It is postulated that too much glutamate in the space between neurons causes mania, and too little, depression. Another mechanism by which lithium might help to regulate mood include the non-competitive inhibition of an enzyme called inositol monophosphatase. Alternately lithium's action may be enhanced through the deactivation of the GSK-3B enzyme. The regulation of GSK-3B by lithium may affect the circadian clock. GSK-3 is known for phosphorylating and thus inactivating glycogen synthase. GSK-3B has also been implicated in the control of cellular response to damaged DNA. GSK-3 normally phosphorylates beta catenin, which leads to beta catenin degratation. When GSK-3 is inhibited, beta catenin increases and transgenic mice with overexpression of beta catenin express similar behaviour to mice treated with lithium. These results suggest that increase of beta catenin may be a possible pathway for the therapeutic action of lithium. Pharmacodynamics Although lithium has been used for over 50 years in treatment of bipolar disorder, the mechanism of action is still unknown. Lithium's therapeutic action may be due to a number of effects, ranging from inhibition of enzymes such as glycogen synthase kinase 3, inositol phosphatases, or modulation of glutamate receptors. |
| 分子式 |
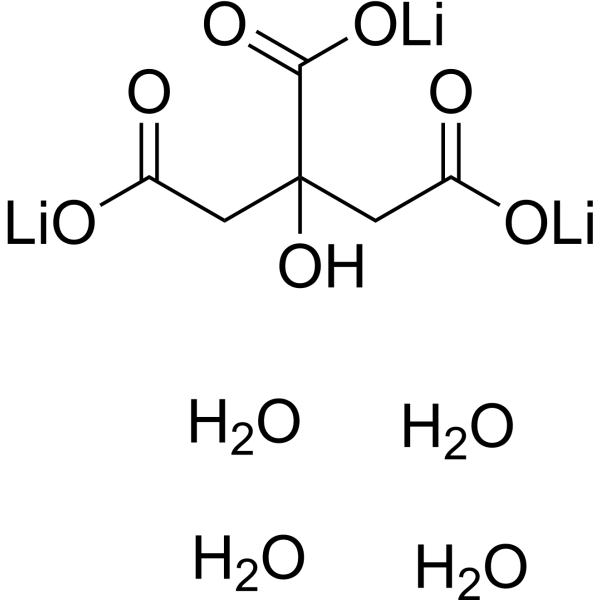
C6H13LI3O11
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
281.9838
|
| 精确质量 |
282.093
|
| CAS号 |
6080-58-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Sodium citrate dihydrate;6132-04-3;Citric acid;77-92-9;Hydroxycitric acid tripotassium hydrate;6100-05-6;Lithium citrate;919-16-4
|
| PubChem CID |
2724118
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 沸点 |
309.6ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
112 °C
|
| 闪点 |
155.2ºC
|
| tPSA |
177.54
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
5
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
11
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
20
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
211
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
[Li+].[Li+].[Li+].C(C(=O)[O-])C(CC(=O)[O-])(C(=O)[O-])O.O.O.O.O
|
| InChi Key |
HXGWMCJZLNWEBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C6H8O7.3Li.4H2O/c7-3(8)1-6(13,5(11)12)2-4(9)10;;;;;;;/h13H,1-2H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)(H,11,12);;;;4*1H2/q;3*+1;;;;/p-3
|
| 化学名 |
trilithium;2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate;tetrahydrate
|
| 别名 |
6080-58-6; Trilithium citrate tetrahydrate; LITHIUM CITRATE TETRAHYDRATE; Lithium citrate tribasic tetrahydrate; Lithonate s; Lithonate (TN); Lithium citrate [USP]; trilithium;2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate;tetrahydrate;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ≥ 100 mg/mL (~354.64 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 50 mg/mL (177.32 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。
请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5464 mL | 17.7318 mL | 35.4635 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7093 mL | 3.5464 mL | 7.0927 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3546 mL | 1.7732 mL | 3.5464 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。