| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
柠檬酸(0–12.5 mM;24 小时)以剂量依赖性方式表现出抗增殖活性 [3]。在 G2/M 和 S 期,柠檬酸(12.5 mM;72 小时)剂量依赖性地诱导细胞凋亡和细胞周期停滞 [3]。当暴露于12.5 mM 柠檬酸 48 小时[3]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
柠檬酸(120、240和480 mg/kg;腹腔注射)可显着降低小鼠肝脏中GSH-Px活性并诱导MDA(丙二醛)水平增加[1]。柠檬酸(120、240 和 480 mg/kg;腹腔注射)通过以剂量依赖性方式提高小鼠肝细胞中的 caspase-3 活性来促进细胞凋亡 [1]。 ?柠檬酸(120、240 和 480 mg/kg;腹腔注射;每周一次,持续 3 周)对小鼠产生肾毒性 [2]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[3]
细胞类型: HaCaT 细胞 测试浓度: 0、2.5、5、7.5、10、12.5 mM 孵育持续时间:24小时 实验结果:以剂量依赖性方式抑制细胞活力。 细胞毒性测定 [3] 细胞类型: HaCaT 细胞 测试浓度: 12.5 mM 孵育时间: 0, 12, 24, 48, 72 h 实验结果: 以剂量依赖性方式诱导细胞凋亡和细胞周期阻滞在G2/M期和S期。 蛋白质印迹分析[3] 细胞类型: HaCaT 细胞 测试浓度: 12.5 mM 孵育时间:12、24、48小时 实验结果:FAS、BAX、BID、AIF、EndoG、细胞色素c、PARP、GADD153、 GRP78 和 caspase -3、-8、-9 以及 BCL-2 和 BCL-X1 减少。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: 20 g male Kunming mice [2]
Doses: 120, 240, 480 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection; once a week for 3 weeks. Experimental Results: The activities of T-SOD and GSH-Px in the treatment group diminished with the increase of citric acid dose, the activity of NOS demonstrated an increasing trend, and the contents of H2O2 and MDA gradually diminished. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
/A portion/ of the circulating (mainly metabolic but also ingested) citric acid is excreted in urine, with 24-hour urine reference values between 1.5 and 3.68 mmol, corresponding to 0.29-0.71 g citric acid excreted per person per day. Metabolism / Metabolites Citric acid is a normal metabolite and an intermediate in cellular oxidative metabolism ... The acid is formed in the mitochondrion after condensation of acetate with oxaloacetate. The six-carbon acid is then successively degraded to a series of four-carbon acids, effectively accomplishing oxidation of acetate in the cell. In human (as well as in animal and plant) physiology, citric acid is a very common intermediate in one of the central biochemical cycles, the Krebs or tricarboxylic acid cycle, which takes place in every cell. It completes the breakdown of pyruvate formed from glucose through glycolysis, thereby liberating carbon dioxide and a further four hydrogen atoms which are picked up by electron transport molecules. Thus, in man approximately 2 kg of citric acid are formed and metabolised every day. This physiological pathway is very well developed and capable of processing very high amounts of citric acid as long as it occurs in low concentrations. Citric acid in reaction with enzyme citratase /citrate lyase/ yields oxaloacetic acid & acetic acid. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No data are available on cellulose and citric acid use during breastfeeding. However, the drug is not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, so it cannot enter the breastmilk. Cellulose and citric acid is acceptable to use during breastfeeding. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Interactions ... Citric acid aerosol inhalation caused decreases in dynamic respiratory compliance and forced expiratory volume in 0.1 s (FEV0.1). This airway constriction was significantly attenuated by MK-886, mepyramine, cromolyn sodium, and compound 48/80, but not by either methysergide or indomethacin. Both LTC4 and histamine infusion significantly increased the magnitude of citric acid-induced airway constriction in compound 48/80-pretreated guinea pigs. Citric acid inhalation caused significant increase in histamine level in the bronchoalveolar lavage sample, which was significantly suppressed by compound 48/80. The relative efficacy of citric, malic, malonic, oxalic and succinic acids, and deferoxamine mesylate on the toxicity, distribution and excretion in mice exposed to aluminum were compared. Chelating agents were administered ip at a dose equal to one-fourth of their respective LD50. To determine the effect of the various chelators on the toxicity of aluminum, various doses of aluminum nitrate (938-3188 mg/kg) were administered ip, followed by one of the chelators. Survival was recorded at the end of 14 days. ... Malic acid and deferoxamine mesylate were the most effective in increasing the urinary excretion of aluminum. Citric acid was the most effective in increasing the fecal excretion of aluminum. Malonic, oxalic and succinic acids had no overall beneficial effects. Citric acid would appear to be the most effective agent of those tested in the prevention of acute aluminium intoxication. ... When aluminum hydroxide and citric acid (133 mg Al/kg and 62 mg/kg, respectively) were simultaneously given orally to mice, fetal skeletal development defects resulted. The primary purpose of this study was to determine the relative usefulness of various measures to monitor body aluminum burden in weanling rats fed various amounts of aluminum (0.39 umol aluminum/g diet for 29 days, approximately 40 umol aluminum/g diet with or without citrate for 29 days and approximately 100 umol aluminum/g diet with citrate for 12 or 29 days) or injected ip with graded doses of aluminum (0.01, 4.6, 11.8, 23.5 or 94 umol aluminum). Twenty four hours prior to sacrifice, all rats were injected ip with either desferrioxamine (75 mg) or buffer. All seven indices of aluminum exposure monitored (eg: tibia, liver, kidney and serum aluminum concn; changes in serum aluminum concn in response to desferrioxamine; urinary aluminum excretion with and without desferrioxamine treatment) were highly (p< 0.001) correlated to parenteral aluminum exposure. Ingestion of citrate had small but significant effects on aluminum retention. /Citrate/ For more Interactions (Complete) data for CITRIC ACID (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat oral 3000 mg/kg; 12000 mg/kg; 11700 mg/kg /observed in separate experiments/ LD50 Rat oral 6730 mg/kg LD50 Mouse iv 42 mg/kg /From table/ LD50 Mouse oral 5040 mg/kg /From table/ For more Non-Human Toxicity Values (Complete) data for CITRIC ACID (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Mesh Heading: Anticoagulants, chelating Agents /EXPL THER/ Regional citrate anticoagulation (RCA) is an effective form of anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) in patients with contraindications to heparin. Its use has been very limited, possibly because of the need for special infusion solutions and difficult monitoring of the metabolic effects./The objective of this study was/ to investigate the safety and the feasibility of an RCA method for continuous veno-venous hemofiltration (CVVH) using commercially available replacement fluid. We evaluated 11 patients at high risk of bleeding, requiring CVVH. RCA was performed using commercially available replacement fluid solutions to maintain adequate acid-base balance. We adjusted the rate of citrate infusion to achieve a post-filter ionized calcium concentration [iCa] <0.4 mmol/L when blood flow was <250 mL/min, or <0.6 mmol/L when blood flow was >250 mL/min. When needed, we infused calcium gluconate to maintain systemic plasma [iCa] within the normal range. Twenty-nine filters ran for a total of 965.5 hr. Average filter life was 33.6+/-20.5 hr. Asymptomatic hypocalcemia was detected in 6.9% of all samples. No [iCa] values <0.9 mmol/L were observed. Hypercalcemia (1.39+/-0.05 mmol/L) occurred in 2.5% of all samples. /The authors/ observed hypernatremia (threshold 153 mmol/L) and alkalosis (threshold 7.51) in only 9.3% and 9.4% respectively of all samples, mostly concomitantly. No patient showed any signs of citrate toxicity. /They/ developed a protocol for RCA during CVVH using commercially available replacement fluid that proved safe, flexible and applicable in an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) setting. It has ... been used to dissolve urinary bladder calculi, & as mild astringent. Citrate ... of ... value in alleviation of chronic metabolic acidosis ... from chronic renal insufficiency or syndrome of renal tubular acidosis ... usually prescribed in form of sodium citrate and citric acid soln, USP ... Potassium citrate, up to 10 g daily, has been used as a potassium supplement; the potassium and sodium salts have been used, in similar dosages, as mild diuretics in humans. Drug Warnings A study of abdominal pain and severity of other side effects attributed to Picolax, a combination of citric acid, magnesium oxide and sodium picosulfate, was conducted among 267 patients, 55 of whom had inflammatory bowel disease, all of whom were given a full single dose of Picolax as preparation for radiology or endoscopy. The frequency of increased abdominal pain and severe side effects after Picolax administration was similar in the patients with inflammatory bowel disease and the patients with other colonic disorders. None of the patients with iron deficiency in whom investigations had yielded negative results reported severe side effects; this was significantly different from the proportion reporting severe side effects among the patients with inflammatory bowel disease, the irritable bowel syndrome and diverticular disease. The increase in the mean number of stools/24 hr after Picolax was lower in the patients with inflammatory bowel disease than in the other diagnostic groups. On review 2-4 wk after examination none of the patients with inflammatory bowel disease reported deterioration in their symptoms. Following the occurrence of aluminum encephalopathy in four patients with chronic renal failure, 34 azotemic patients seen during the same year and five volunteers who took varying combinations of aluminum hydroxide and an alkalinizing citrate (Shohl's) solution were studied. It was found that the four encephalopathic cases were older than the 34 azotemic patients (68 years + or - 14 standard deviation, versus 50 + or - 13, p< 0.05), had a higher mean serum aluminum value (727 ug/l + or - 320 versus 92 + or - 73, p< 0.005), had taken more aluminum hydroxide (5 g/day + or - 0.9 versus 1.6 + or - 1.8, p< 0.01), and more Shohl's solution (64 ml/day + or - 19 versus 20 + or - 29, p< 0.01). In all 38 patients the serum aluminum values correlated directly with age (p=0.01), aluminum hydroxide (p=0.001) and concomitant citrate intake (p=0.004). In the five healthy volunteers the 24 hr urinary aluminum excretion increased from a baseline of 22 ug + or - 19 standard deviation to 167 + or - 109 (p=0.05) during aluminum hydroxide intake, rising to 580 + or - 267 (p=0.01) during the simultaneous intake of citrate and aluminum hydroxide. Corresponding serum aluminum values were 11 ug/l + or - 2 standard deviation, 44 + or - 34 (p= 0.1), and 98 + or - 58 (p<0.05). Thus citrate seems to enhance aluminum absorption and may cause encephalopathy in patients with chronic renal failure, especially the elderly. |
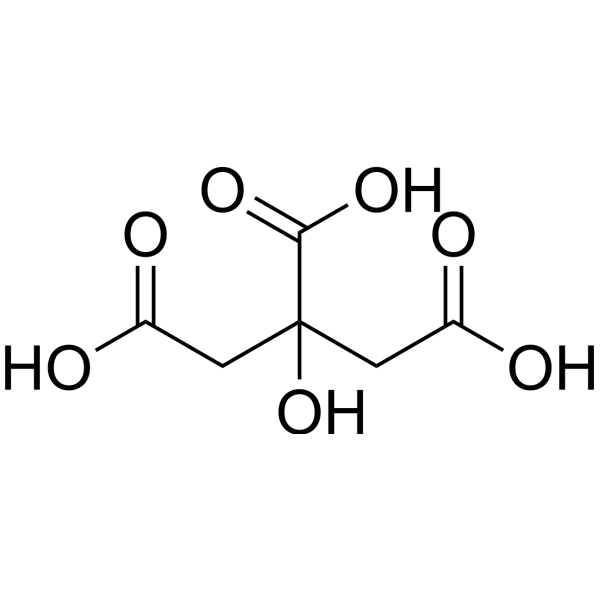
| 分子式 |
C6H8O7
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
192.1235
|
| 精确质量 |
192.027
|
| CAS号 |
77-92-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Lithium citrate tetrahydrate;6080-58-6;Citric acid triammonium;3458-72-8;Sodium citrate dihydrate;6132-04-3;Citric acid trisodium;68-04-2;Citric acid monohydrate;5949-29-1;Ferric citrate;3522-50-7;Citric acid-d4;147664-83-3;Citric acid-13C6;287389-42-8;Hydroxycitric acid tripotassium hydrate;6100-05-6;Citric acid-13C3;302912-06-7
|
| PubChem CID |
311
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.8±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
309.6±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
153-159 °C(lit.)
|
| 闪点 |
155.2±24.4 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.575
|
| LogP |
-1.72
|
| tPSA |
132.13
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
13
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
227
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C6H8O7/c7-3(8)1-6(13,5(11)12)2-4(9)10/h13H,1-2H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)(H,11,12)
|
| 化学名 |
2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ~100 mg/mL (~520.51 mM)
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~520.51 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (13.01 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (13.01 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (13.01 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 100 mg/mL (520.51 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.2051 mL | 26.0254 mL | 52.0508 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.0410 mL | 5.2051 mL | 10.4102 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5205 mL | 2.6025 mL | 5.2051 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。