| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Tyr1173 (IC50 = 26 nM); Tyr1173 (IC50 = 37 nM); Tyr992 (IC50 = 37 nM); Tyr992 (IC50 = 57 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:吉非替尼可有效抑制高表达和低表达 EGFR 的细胞系(包括 NR6、NR6M 和 NR6W 细胞系)中 EGFR 上的所有酪氨酸磷酸化位点。磷酸化位点 Tyr1173 和 Tyr992 不太敏感,需要更高浓度的吉非替尼进行抑制。吉非替尼在 NR6W 细胞中有效阻断 PLC-γ 的磷酸化,IC50 为 27nM。 NR6wtEGFR 和 NR6M 细胞系具有低水平的 PLC-γ 磷酸化,但 NR6M 细胞系中的水平对吉非替尼的抑制具有更强的抵抗力,IC50 分别为 43 nM 和 369 nM。 Gefitinib 在低 EGFR 和 EGFRvIII 表达细胞系中抑制 Akt 磷酸化,IC50 分别为 220 和 263nM。剂量范围为 0.1 至 0.5μM 的吉非替尼显着促进而非消除 NR6M 细胞的集落形成。然而,浓度为 2 μM 的吉非替尼完全阻断 NR6M 集落形成。在高 EGFR 表达细胞系和低 EGFR 表达细胞系中,吉非替尼在 EGF 刺激后 72 小时内以剂量依赖性方式快速抑制 EGFR 和 ERK 磷酸化。吉非替尼是这些 EGF 驱动的未转化 MCF10A 细胞的单层生长,IC50 为 20 NM。与单独放疗相比,吉非替尼(0.2 μM 和 0.5 μM)与放疗组合可显着抑制 LoVo 细胞的生长。激酶测定:盐酸吉非替尼是一种特异性结合并抑制 EGFR 酪氨酸激酶的抑制剂,在 NR6wtEGFR 细胞中的 IC50 值为 2-37 nM。吉非替尼在 NR6W 细胞中有效阻断 PLC-γ 的磷酸化,IC50 为 27nM。 NR6wtEGFR 和 NR6M 细胞系具有低水平的 PLC-γ 磷酸化,但 NR6M 细胞系中的水平对吉非替尼的抑制具有更强的抵抗力,IC50 分别为 43 nM 和 369 nM。 Gefitinib 在低 EGFR 和 EGFRvIII 表达细胞系中抑制 Akt 磷酸化,IC50 分别为 220 和 263nM。细胞测定:将指数生长的细胞(包括 NR6、NR6M、NR6M 和 NR6W 细胞)以 2000 个细胞/孔的浓度接种在 96 孔板中,使其粘附,随后在 PBS 中洗涤,并在含有 0.5% FCS 的培养基中孵育过夜。然后用不同浓度 (0-2 μM) 的吉非替尼或溶质对照 DMSO 和 EGF 处理细胞。诱导 NR6wtEGFR 和 NR6W 细胞增殖的最佳 EGF 浓度先前已确定,因此 NR6wtEGFR 和 NR6W 细胞分别补充有 10 nM 和 0.1 nM EGF。 NR6 和 NR6M 细胞中未添加 EGF。 72小时后,通过进行MTT增殖测定来测量细胞数量。
表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)在许多人类肿瘤中经常被扩增和/或突变,并且来自该受体的异常信号被认为是导致这些肿瘤中出现恶性表型的原因。吉非替尼是一种特异性结合和抑制EGFR酪氨酸激酶的小分子抑制剂,已被证明可以抑制一系列过表达EGFR的肿瘤细胞的生长、增殖、存活和侵袭。然而,吉非替尼的临床反应与EGFR水平和活性没有相关性,这表明下游信号传导和突变等其他分子机制在预测临床反应方面可能很重要。因此,我们研究了特异性EGFR抑制剂吉非替尼对表达天然存在的组成型活性EGFR变体EGFRvIII、低非转化水平EGFR和高转化水平EGFR的细胞的磷酸化水平、信号传导和生长的影响。结果显示,在表达EGFRvIII的细胞中,吉非替尼足以抑制EGFR磷酸化、EGFR介导的增殖和EGFR-介导的锚定非依赖性生长的水平不足以抑制这些特征。此外,数据表明,表达EGFRvIII的细胞长期暴露于低浓度吉非替尼(0.01-0.1微M)会导致受体磷酸酪氨酸负荷增加,ERK信号传导增加,并刺激增殖和锚定非依赖性生长,可能是通过诱导EGFRvⅢ二聚化。另一方面,较高浓度的吉非替尼(1-2微M)显著降低了EGFRvIII磷酸酪氨酸负荷、EGFRvⅢ介导的增殖和锚定非依赖性生长。需要进一步的研究来调查这些重要发现在临床环境中的意义。[1] 表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)在许多人类肿瘤中普遍过表达,为抗癌药物开发提供了新的靶点。ZD1839(“易瑞沙”)是一种对EGFR具有选择性的喹唑啉酪氨酸激酶抑制剂,在临床前研究和临床试验的早期阶段显示出良好的活性。然而,由于尚不清楚哪种肿瘤类型是该药物治疗的最佳靶点,因此已经研究了与ZD1839肿瘤敏感性相关的分子特征。在一组人类乳腺癌症和其他上皮肿瘤细胞系中,HER2-过表达肿瘤对ZD1839特别敏感。这些肿瘤细胞系的生长抑制与EGFR、HER2和HER3的去磷酸化有关,同时HER3与磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶的结合丧失,Akt活性下调。这些研究表明,HER2过表达的肿瘤特别容易受到HER家族酪氨酸激酶信号传导的抑制,并提出了治疗这些特别侵袭性肿瘤的新策略。[2] 转化生长因子α(TGF-α)是人类癌症的一种自分泌生长因子。TGF-α及其特异性受体表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)的过表达与侵袭性疾病和预后不良有关。EGFR已被提出作为抗癌治疗的靶点。已经开发出阻断配体诱导的EGFR激活的化合物。ZD-1839(易瑞沙)是一种口服活性喹唑啉衍生物,选择性抑制EGFR酪氨酸激酶,目前正在癌症患者中进行临床开发。在共表达EGFR和TGF-α的人卵巢(OVCAR-3)、乳腺(ZR-75-1,MCF-10A ras)和癌症(GEO)细胞中,评价了ZD-1839单独或与作用机制不同的细胞毒性药物(如顺铂、卡铂、奥沙利铂、紫杉醇、多烯紫杉醇、阿霉素、依托泊苷、拓扑替康和雷替曲塞)组合的抗增殖活性。ZD-1839在所有癌症细胞系中以剂量依赖性方式抑制软琼脂中的菌落形成。抗增殖作用主要是抑制细胞生长。然而,高剂量治疗导致细胞凋亡增加2-4倍。当用每种细胞毒性药物和ZD-1839治疗癌症细胞时,观察到生长抑制的剂量依赖性超加性增加。联合治疗显著增强了单药治疗诱导的凋亡细胞死亡。[4] 生长因子受体EGFR和erbB2的过表达在几种人类癌症中经常发生,并与侵袭性肿瘤行为和患者预后不良有关。我们研究了新型EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂ZD1839(Iressa)在体外和体内对表达不同水平EGFR和erbB2的人癌症细胞系生长的影响。ZD1839以低纳摩尔范围内的一半最大有效剂量有效抑制了EGFR过表达的A431和MDA-MB-231细胞在体外的增殖(50%-70%)。同时,ZD1839阻断了EGFR的自磷酸化,并阻止了EGF激活PLCγ1、ERK MAP激酶和PKB/Akt。它还抑制过表达erbB2的EGFR(+)癌症细胞系(SKBr3,SKOV3,BT474)增殖20%至80%,这种作用与抑制EGF-依赖性erbB2磷酸化和激活SKOV3细胞中ERK-MAP激酶和PKB/Akt有关。 总的来说,这些结果表明,在所研究的剂量下,ZD1839不仅在过表达EGFR的细胞中,而且在过表达erbB2的EGFR(+)细胞中都是一种强效的增殖抑制剂[6]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
吉非替尼 (100 mg/kg) 可改善 LoVo 肿瘤异种移植物放疗的抗肿瘤效果。吉非替尼对携带已建立的人 GEO 结肠癌异种移植物的裸鼠进行治疗,显示出对肿瘤生长的可逆剂量依赖性抑制,因为 GEO 肿瘤在治疗结束时恢复了对照的生长速度。
在体外和体内评估了ZD1839('ressa')对人肿瘤细胞(LoVo结直肠癌)辐射反应的影响,ZD1839是表皮生长因子受体酪氨酸激酶活性的特异性抑制剂。ZD1839(0.5μM,孵育第1-5天)显著增加了分次放射治疗(2 Gy,第1-3天)对体外生长的LoVo细胞的抗增殖作用(P=0.002)。与单独使用任何一种治疗方式相比,ZD1839在携带LoVo肿瘤异种移植物的小鼠中联合单次或分次放疗也显著增加了肿瘤生长抑制(Pс0.001)。当以分级方案给药时,ZD1839的放射性增强作用更为明显。这种现象可能归因于ZD1839对放射治疗组分之间肿瘤细胞再增殖的抗增殖作用。这些数据表明,使用ZD1839佐剂进行放射治疗可以增强治疗反应。因此,ZD1839联合放疗的临床研究是有必要的。[3] ZD-1839/吉非替尼对携带已建立的人GEO结肠癌癌症异种移植物的裸鼠的治疗显示了对肿瘤生长的可逆剂量依赖性抑制,因为GEO肿瘤在治疗结束时恢复了对照的生长速率。相比之下,使用细胞毒性药物(如拓扑替康、拉曲肽或紫杉醇)和ZD-1839的联合治疗在所有小鼠中都产生了肿瘤生长停滞。治疗结束后,肿瘤缓慢生长约4-8周,最终恢复到与对照组相似的生长速度。在注射GEO细胞后4-6周内,所有对照小鼠的GEO肿瘤达到与正常生活不相容的大小,在所有单药治疗的小鼠中,GEO肿瘤在6-8周内达到与正常生命不相容的尺寸。相反,在癌症细胞注射后10、12和15周,分别有50%的ZD-1839加拓扑替康、雷曲曲塞或紫杉醇治疗的小鼠仍然存活。这些结果证明了这种EGFR选择性酪氨酸激酶抑制剂的抗肿瘤作用,并为其与细胞毒性药物联合使用的临床评估提供了理论基础。[4] 单克隆抗体阻断表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)功能在体内对人类肿瘤具有主要的抗增殖作用。EGFR相关酪氨酸激酶的特异性抑制剂也观察到对其中一些相同肿瘤的类似抗增殖作用。其中一种抑制剂,口服活性吉非替尼/ZD1839(易瑞沙),对人类肿瘤异种移植物具有明显的抗增殖活性。我们现在表明,与抗EGFR一样,ZD1839的联合给药将增强细胞毒性药物对人类外阴(A431)、肺(A549和SK-LC-16 NSCL和LX-1)和前列腺(PC-3和TSU-PR1)肿瘤的疗效。对患有成熟肿瘤的小鼠口服ZD1839(每日五次x2)和细胞毒性药物(每3-4天i.p.x4),持续2周。按照这个时间表,ZD1839的最大耐受剂量(150mg/kg)诱导A431的部分消退,A431是一种表达高水平EGFR的肿瘤,在EGFR表达水平低但变化很大的肿瘤(A549、SKLC-16、TSU-PR1和PC-3)中抑制70-80%,对表达极低水平EGFR的LX-1肿瘤抑制50-55%。ZD1839在增强大多数细胞毒性药物对所有这些肿瘤的联合治疗中非常有效,无论EGFR状态如何,但需要将ZD1839的剂量减少到低于其单药最大耐受剂量,以获得最佳耐受性。当添加ZD1839时,铂、顺铂和卡铂作为单一药物对A431外阴、A549和LX-1肺以及TSU-PR1和PC-3前列腺肿瘤的明显生长抑制作用增加了几倍,A431和PC-3肿瘤有所消退。尽管紫杉烷、紫杉醇或多西他赛作为单一药物显著抑制了A431、LX-1、SK-LC-16、TSU-PR1和PC-3的生长,但当与ZD1839联合使用时,通常会看到部分或完全的消退。ZD1839对A549的生长抑制作用增加了10倍(>99%)。叶酸类似物依达拉特对A549、LX-1和TSU-PR1具有高度的生长抑制作用,而依达拉特与ZD1839联合使用可导致这些肿瘤的部分或完全消退。对于A431肿瘤,单独使用紫杉醇要么具有高度的生长抑制作用,要么诱导了一些消退,但当与ZD1839联合使用时,可以获得明显的消退。与吉西他滨联合使用既不会增加也不会降低基线细胞毒性疗效,而ZD1839与长春瑞滨联合使用的耐受性较差。总体而言,这些结果表明,ZD1839增强细胞毒性治疗不需要靶肿瘤中高水平的EGFR表达。他们还表明,ZD1839与各种广泛使用的细胞毒性药物联合使用具有显著的临床益处[5]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
盐酸吉非替尼是一种抑制剂,在 NR6wtEGFR 细胞中 IC50 值为 2-37 nM,选择性结合并抑制 EGFR 酪氨酸激酶。吉非替尼的 IC50 为 27 nM,可有效防止 NR6W 细胞中的 PLC-γ 磷酸化。 PLC-γ 磷酸化在 NR6wtEGFR 和 NR6M 细胞系中较低,但后者对吉非替尼抑制更具有抵抗力,IC50 值分别为 43 nM 和 369 nM。吉非替尼抑制低 EGFR 和 EGFRvIII 表达细胞系中的 Akt 磷酸化,IC50 值分别为 220 和 263 nM。
交联试验[1] 受体的交联如所述进行(Montgomery,2002)。简而言之,将经吉非替尼处理的细胞在冰冷的磷酸盐缓冲盐水(PBS)中洗涤两次,并在4°C下溶解在含有蛋白酶和磷酸酶抑制剂、10%甘油和1 mM双(磺基琥珀酰亚胺基)琥珀酸盐(BS3)的RIPA缓冲液中20分钟。随后加入终浓度为250 mM的甘氨酸5分钟,然后在14 000 g下离心10分钟。通过SDS-PAGE分离等量的蛋白质,并将其电印迹到硝化纤维膜上。如上所述,使用抗EGFR和抗磷酸酪氨酸抗体进行印迹和抗体孵育。 |
| 细胞实验 |
将呈指数生长的细胞(例如 NR6、NR6M、NR6M 和 NR6W 细胞)以 2000 个细胞/孔的密度接种到 96 孔板中,使其粘附,然后用 PBS 清洗,然后在含有 0.5% 的培养基中孵育过夜。燃料电池系统。之后,将细胞暴露于不同浓度 (0–2 μM) 的吉非替尼或溶质对照、DMSO 和 EGF。由于 NR6wtEGFR 和 NR6W 细胞在已知的 EGF 浓度下可以最佳增殖,因此将 10 nM 和 0.1 nM EGF 分别添加到 NR6wtEGFR 和 NR6W 细胞中。 NR6 和 NR6M 细胞不接受额外的 EGF。使用 MTT 增殖测定来量化 72 小时后的细胞数量。
增殖试验[1] 将指数增长的细胞以2000个细胞/孔的浓度在96孔板中以六倍接种,使其粘附,随后在PBS中洗涤,并在含有0.5%FCS的培养基中孵育过夜。然后用不同浓度的易瑞沙或溶质对照DMSO和EGF处理细胞。先前已经确定了诱导NR6wtEGFR和NR6W细胞增殖的最佳EGF浓度,因此分别向NR6wtEGFR和NR6W细胞中添加了10和0.1 nM EGF(Pedersen等人,未发表的观察结果)。NR6和NR6M细胞未添加EGF。72小时后,通过进行3-[4,5-二甲基噻唑-2-基]-2,5-二苯基溴化四唑(MTT)增殖试验来测量细胞量。 非锚定生长的软琼脂试验[1] 将指数生长的细胞(1×105)悬浮在溶解在DMEM+0.5%FCS中的3 ml 0.5%(w/v)NuSieve低熔点琼脂中,并将其铺在覆盖有溶解在DMEM+0.5%FCS中的0.5%琼脂的六孔板上。然后用不同浓度的易瑞沙或溶质对照DMSO处理细胞。先前已经确定了诱导NR6wtEGFR和NR6W细胞锚定非依赖性生长的EGF的最佳浓度,因此分别添加了10和0.1 nM EGF(Pedersen等人,未发表的观察结果)。NR6和NR6M未受到EGF的刺激。每种情况下,每周三次用新鲜培养基补充培养物。3周后,用结晶紫对平板进行染色,并计数>50个细胞的菌落。 体外增殖分析[6] 将细胞(5×104)在正常生长培养基中一式三份铺成24孔细胞培养簇。24小时后,细胞用吉非替尼或DMSO载体再处理48小时。然后使用血细胞计数器对细胞进行计数。通过台盼蓝染色评估的细胞存活率始终≥95%,并且不随药物治疗而改变。增殖计算为48小时治疗期间细胞数量的增加。ZD1839的作用相对于对照培养物中观察到的细胞数量的增加而表现出来。所有实验均在每个细胞系的3个不同场合进行。 体外细胞凋亡分析[6] 用吉非替尼处理后,通过胰蛋白酶收集贴壁细胞,并与非贴壁细胞结合。洗涤细胞并将其重新悬浮在PBS中。使用Cytospin 2将细胞悬浮液(50μl)施加到显微镜载玻片上。然后将细胞固定在多聚甲醛中,用赫斯特染色处理2分钟。然后通过确定含有具有凋亡形态的细胞核的细胞比例来定量凋亡。每种处理对100个细胞进行三次评估。 |
| 动物实验 |
Female nude mice (cba nu/nu) aged 8–10 weeks are intra-dermal injected with LoVo cells.
100 mg/kg Once daily by oral administration (0.1 mL/10 g body weight) for 14 days Growth of tumours in athymic mice and drug treatments [6] MDA-MB-231 or SKOV3 cells (2 × 106) in a 200 μl solution of 10% FCS with 50% (v/v) Matrigel were injected s.c. into each flank (2 tumours/mouse) of each mouse (n = 15) and allowed to form tumours over a period of 21 days. Mice were then gavaged daily with 75 mg/kg Gefitinib/ZD1839 or vehicle for 14 days. Tumour diameters were caliper-measured twice a week and tumour volume was calculated from the following formula: tumour volume = (width)2 × length/2. At the end of the experiment, tumours were removed from the mice, divided and processed for immunohistochemistry or stored in liquid nitrogen. The growth-inhibitory effect of Gefitinib/ZD1839 was calculated from the following formula: equation image, where d is final tumour volume after ZD1839 treatment, c is tumour volume before ZD1839 treatment, b is final tumour volume after control treatment and a is tumour volume before control treatment. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Absorbed slowly after oral administration with a mean bioavailability of 60%. Peak plasma levels occurs 3-7 hours post-administration. Food does not affect the bioavailability of gefitinib. Elimination is by metabolism (primarily CYP3A4) and excretion in feces. Excretion is predominantly via the feces (86%), with renal elimination of drug and metabolites accounting for less than 4% of the administered dose. 1400 L [IV administration] 595 mL/min [IV administration] Metabolism / Metabolites Primarily hepatic via CYP3A4. Three sites of biotransformation have been identified: metabolism of the N-propoxymorpholino-group, demethylation of the methoxy-substituent on the quinazoline, and oxidative defluorination of the halogenated phenyl group. Gefitinib has known human metabolites that include O-Desmethyl Gefitinib and 4-Defluoro-4-hydroxy Gefitinib. Biological Half-Life 48 hours [IV administration] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In large early clinical trials, elevations in serum aminotransferase levels occurred in 9% to 13% of patients treated with standard doses of gefitinib, and 2% to 4% of patients had to stop therapy because of elevations above 5 times the upper limit of normal. Serum enzyme elevations typically arise after 4 to 12 weeks of treatment with a hepatocellular pattern. Immunoallergic and autoimmune features have not been described, but rash is common in patients receiving gefitinib. Most cases of liver injury due to gefitinib in the literature have been minimally or not symptomatic, and the injury resolved within 1 to 2 months of stopping the drug. Restarting therapy was usually but not always followed by rapid recurrence of serum enzyme elevations, and corticosteroid therapy did not appear to prevent this recurrence. In some instances, lower doses were tolerated with minimal or no ALT elevations. Periodic monitoring of liver tests during therapy is recommended. Despite the frequency of serum aminotransferase elevations during gefitinib therapy, cases of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice are rare. Cases of severe and fatal hepatotoxicity have been reported to the sponsor and monitoring of liver tests during therapy is recommended. Likelihood score: B (likely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of gefitinib during breastfeeding. Because gefitinib is 90% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, its half-life is about 48 hours and it might accumulate in the infant. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during gefitinib therapy. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding 90% primarily to serum albumin and alpha 1-acid glycoproteins (independent of drug concentrations). |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
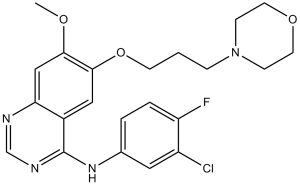
Gefitinib is a member of the class of quinazolines that is quinazoline which is substituted by a (3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)nitrilo group, 3-(morpholin-4-yl)propoxy group and a methoxy group at positions 4,6 and 7, respectively. An EGFR kinase inhibitor used for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. It has a role as an epidermal growth factor receptor antagonist and an antineoplastic agent. It is an aromatic ether, a member of monochlorobenzenes, a member of monofluorobenzenes, a secondary amino compound, a tertiary amino compound, a member of quinazolines and a member of morpholines.
Gefitinib (originally coded ZD1839) is a drug used in the treatment of certain types of cancer. Acting in a similar manner to erlotinib (marketed as Tarceva), gefitinib selectively targets the mutant proteins in malignant cells. It is marketed by AstraZeneca under the trade name Iressa. Gefitinib is a Kinase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of gefitinib is as a Protein Kinase Inhibitor. Gefitinib is a selective tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitor used in the therapy of non-small cell lung cancer. Gefitinib therapy is associated with transient elevations in serum aminotransferase levels and rare instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury. Gefitinib has been reported in Penicillium brocae with data available. Gefitinib is an anilinoquinazoline with antineoplastic activity. Gefitinib inhibits the catalytic activity of numerous tyrosine kinases including the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which may result in inhibition of tyrosine kinase-dependent tumor growth. Specifically, this agent competes with the binding of ATP to the tyrosine kinase domain of EGFR, thereby inhibiting receptor autophosphorylation and resulting in inhibition of signal transduction. Gefitinib may also induce cell cycle arrest and inhibit angiogenesis. (NCI04) A selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the EPIDERMAL GROWTH FACTOR RECEPTOR (EGFR) that is used for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER. Drug Indication For the continued treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer after failure of either platinum-based or docetaxel chemotherapies. FDA Label Gefitinib Mylan is indicated as monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic nonâsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with activating mutations of EGFRâTK. Iressa is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer with activating mutations of epidermal-growth-factor-receptor tyrosine kinase. Mechanism of Action Gefitinib is an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase that binds to the adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-binding site of the enzyme. EGFR is often shown to be overexpressed in certain human carcinoma cells, such as lung and breast cancer cells. Overexpression leads to enhanced activation of the anti-apoptotic Ras signal transduction cascades, subsequently resulting in increased survival of cancer cells and uncontrolled cell proliferation. Gefitinib is the first selective inhibitor of the EGFR tyrosine kinase which is also referred to as Her1 or ErbB-1. By inhibiting EGFR tyrosine kinase, the downstream signaling cascades are also inhibited, resulting in inhibited malignant cell proliferation. Pharmacodynamics Gefitinib inhibits the intracellular phosphorylation of numerous tyrosine kinases associated with transmembrane cell surface receptors, including the tyrosine kinases associated with the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR-TK). EGFR is expressed on the cell surface of many normal cells and cancer cells. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is frequently amplified and/or mutated in a number of human tumours and abnormal signalling from this receptor is believed to contribute to the malignant phenotype seen in these tumours. Gefitinib is a small molecule inhibitor that specifically binds and inhibits the EGFR tyrosine kinase and has been shown to inhibit the growth, proliferation, survival and invasion of a range of tumour cells overexpressing EGFR. However, clinical response to gefitinib has failed to correlate with EGFR levels and activity, indicating that other molecular mechanisms such as downstream signalling and mutations could be of importance in predicting clinical response. We therefore investigated the effect of the specific EGFR inhibitor gefitinib on the phosphorylation level, signalling and growth of cells expressing the naturally occurring constitutively active EGFR variant EGFRvIII, a low nontransforming level of EGFR and a high transforming level of EGFR. Results show that levels of gefitinib sufficient to suppress EGFR phosphorylations, EGFR-mediated proliferation and EGFR-mediated anchorage-independent growth are not sufficient to inhibit these features in cells expressing EGFRvIII. Furthermore, the data indicate that long-term exposure of EGFRvIII-expressing cells to low concentrations of gefitinib (0.01-0.1 microM) result in increased phosphotyrosine load of the receptor, increased signalling to ERK and stimulation of proliferation and anchorage-independent growth, presumably by inducing EGFRvIII dimerisation. Higher concentrations of gefitinib (1-2 microM), on the other hand, significantly decreased EGFRvIII phosphotyrosine load, EGFRvIII-mediated proliferation and anchorage-independent growth. Further studies are needed to investigate the implications of these important findings in the clinical setting.[1] The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is commonly overexpressed in many human tumors and provides a new target for anticancer drug development. ZD1839 ("Iressa"), a quinazoline tyrosine kinase inhibitor selective for the EGFR, has shown good activity in preclinical studies and in the early phase of clinical trials. However, because it remains unclear which tumor types are the best targets for treatment with this agent, the molecular characteristics that correlate with tumor sensitivity to ZD1839 have been studied. In a panel of human breast cancer and other epithelial tumor cell lines, HER2-overexpressing tumors were particularly sensitive to ZD1839. Growth inhibition of these tumor cell lines was associated with the dephosphorylation of EGFR, HER2, and HER3, accompanied by the loss of association of HER3 with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and down-regulation of Akt activity. These studies suggest that HER2-overexpressing tumors are particularly susceptible to the inhibition of HER family tyrosine kinase signaling and suggest novel strategies to treat these particularly aggressive tumors.[2] Transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-alpha) is an autocrine growth factor for human cancer. Overexpression of TGF-alpha and its specific receptor, the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), is associated with aggressive disease and poor prognosis. The EGFR has been proposed as a target for anticancer therapy. Compounds that block ligand-induced EGFR activation have been developed. ZD-1839 (Iressa) is a p.o.-active, quinazoline derivative that selectively inhibits the EGFR tyrosine kinase and is under clinical development in cancer patients. The antiproliferative activity of ZD-1839 alone or in combination with cytotoxic drugs differing in mechanism(s) of action, such as cisplatin, carboplatin, oxaliplatin, paclitaxel, docetaxel, doxorubicin, etoposide, topotecan, and raltitrexed, was evaluated in human ovarian (OVCAR-3), breast (ZR-75-1, MCF-10A ras), and colon cancer (GEO) cells that coexpress EGFR and TGF-alpha. ZD-1839 inhibited colony formation in soft agar in a dose-dependent manner in all cancer cell lines. The antiproliferative effect was mainly cytostatic. However, treatment with higher doses resulted in a 2-4-fold increase in apoptosis. A dose-dependent supra-additive increase in growth inhibition was observed when cancer cells were treated with each cytotoxic drug and ZD-1839. The combined treatment markedly enhanced apoptotic cell death induced by single-agent treatment. [4] Overexpression of the growth factor receptors EGFR and erbB2 occurs frequently in several human cancers and is associated with aggressive tumour behaviour and poor patient prognosis. We have investigated the effects of ZD1839 (Iressa), a novel EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, on the growth, in vitro and in vivo, of human cancer cell lines expressing various levels of EGFR and erbB2. Proliferation of EGFR-overexpressing A431 and MDA-MB-231 cells in vitro was potently inhibited (50%-70%) by ZD1839 with half-maximally effective doses in the low nanomolar range. In parallel, ZD1839 blocked autophosphorylation of EGFR and prevented activation of PLC-gamma 1, ERK MAP kinases and PKB/Akt by EGF. It also inhibited proliferation in EGFR(+) cancer cell lines overexpressing erbB2 (SKBr3, SKOV3, BT474) by between 20% and 80%, effects which correlated with inhibition of EGF-dependent erbB2 phosphorylation and activation of ERK MAP kinase and PKB/Akt in SKOV3 cells. Oral administration of ZD1839 inhibited the growth of MDA-MB-231 and SKOV3 tumours, established as xenografts in athymic mice, by 71% and 32%, respectively. Growth inhibition coincided with reduced proliferation but no change in apoptotic index. Collectively, these results show that ZD1839, at the doses studied, is a potent inhibitor of proliferation not only in cells overexpressing EGFR but also in EGFR(+) cells that overexpress erbB2[6]. |
| 分子式 |
C22H24CLFN4O3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
446.90
|
| 精确质量 |
446.152
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 59.13; H, 5.41; Cl, 7.93; F, 4.25; N, 12.54; O, 10.74
|
| CAS号 |
184475-35-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
184475-35-2;857091-32-8; 184475-56-7; 184475-55-6; 1173976-40-3; 1173976-40-3; 1228664-49-0
|
| PubChem CID |
123631
|
| 外观&性状 |
White solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
586.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
119-1200C
|
| 闪点 |
308.7±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.621
|
| LogP |
4.11
|
| tPSA |
68.74
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
545
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
ClC1=C(C([H])=C([H])C(=C1[H])N([H])C1C2C(=C([H])C(=C(C=2[H])OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N2C([H])([H])C([H])([H])OC([H])([H])C2([H])[H])OC([H])([H])[H])N=C([H])N=1)F
|
| InChi Key |
XGALLCVXEZPNRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H24ClFN4O3/c1-29-20-13-19-16(12-21(20)31-8-2-5-28-6-9-30-10-7-28)22(26-14-25-19)27-15-3-4-18(24)17(23)11-15/h3-4,11-14H,2,5-10H2,1H3,(H,25,26,27)
|
| 化学名 |
N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholin-4-ylpropoxy)quinazolin-4-amine
|
| 别名 |
Gefitinib; ZD-1839; ZD1839; ZD 1839; Brand name: Iressa
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2376 mL | 11.1882 mL | 22.3764 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4475 mL | 2.2376 mL | 4.4753 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2238 mL | 1.1188 mL | 2.2376 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03292133 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: EGF816 Drug: Gefitinib |
Lung Cancer | Massachusetts General Hospital | October 31, 2017 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03122717 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Gefitinib Drug: Osimertinib |
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute | May 9, 2017 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT03758287 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Gefitinib Drug: CT053PTSA |
Non-small Cell Lung Cancer | Sunshine Lake Pharma Co., Ltd. | November 2016 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT03849768 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Gefitinib Drug: HS-10296 |
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer | Jiangsu Hansoh Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. |
February 1, 2019 | Phase 3 |
| NCT02856893 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Gefitinib Drug: Osimertinib |
NSCLC | European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer - EORTC |
October 10, 2017 | Phase 2 |
A, effect of metformin (MET) alone and in combination with gefitinib (GEF) on cell proliferation, on anchorage-independent growth ability of NSCLC cell lines, and on the induction of apoptosis in CALU-3, CALU-3 GEF-R, and H1299 cell lines.Clin Cancer Res.2013 Jul 1;19(13):3508-19. |
Effects on the downstream pathway by combined treatment of metformin and gefitinib. Western blotting of EGFR, MAPK, AKT p70S6K, and S6 activation following treatment with the indicated concentration of metformin and gefitinib in CALU-3 and CALU-3 GEF-R cell lines. β-Actin was included as a loading control.Clin Cancer Res.2013 Jul 1;19(13):3508-19. |
Effects of the combination treatment of metformin and gefitinib on NSCLC tumor xenografts.Clin Cancer Res.2013 Jul 1;19(13):3508-19. |
 |
 |