| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
通过引物延伸(SHAPE)化学分析的选择性2'-羟基酰化可以在任何RNA中以单核苷酸分辨率定量评估局部核苷酸的灵活性。SHAPE化学利用核糖2'-羟基的亲核反应性的基于结构的门控,通过核苷酸的受约束或灵活性。SHAPE化学是使用N-甲基isatoic酸酐(NMIA)开发的,该酸酐仅具有适度的亲电性,需要数十分钟才能形成核糖2'-O-加合物。在这里,我们为SHAPE化学设计并评估了一种更有用、快速作用的试剂。将硝基对位引入反应性羰基以形成1-甲基-7-硝基isatoic酸酐(1M7)产生一种试剂,该试剂与RNA反应明显更快地形成2'-O-加合物,并且对有利的自限制水解也更不稳定。使用1M7,RNA结构的单核苷酸分辨率询问在70秒内完成。使用1M7进行的SHAPE分析准确地报告了RNase P特异性结构域的二级和三级结构,并允许以高达91%的准确率预测该RNA的二级结构[1]。
|
|---|---|
| 酶活实验 |
许多生物过程是由RNA介导的,但大多数RNA的高阶结构是未知的,这使得很难理解RNA结构是如何控制功能的。在这里,我们描述了通过引物延伸和突变图谱(SHAPE MaP)分析的选择性2’-羟基酰化,这使得RNA功能基序的从头和大规模鉴定成为可能。通过大规模平行测序测量,在cDNA合成过程中,SHAPE的2'-羟基酰化位点被编码为非互补核苷酸。SHAPE MaP引导的建模确定了已知结构的复杂RNA中超过90%的可接受碱基对,我们用它来定义HIV-1 RNA基因组的新模型。HIV-1模型包含所有已知的结构基序和以前未知的元素,包括实验验证的假结。SHAPE MaP产生准确和高分辨率的二级结构模型,能够分析低丰度RNA,在单个实验中解开序列多态性,并最终使RNA结构分析民主化[2]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
SHAPE MaP在RNA结构探测策略中是独特的,因为它既能测量单核苷酸分辨率的灵活性,又能量化这些测量中的不确定性。我们报告了一个简单的分析框架,该框架结合了这些不确定性,可以检测任何两种状态之间的RNA结构差异,我们在这里使用它来检测健康小鼠滋养层干细胞中的RNA-蛋白质相互作用。我们通过在2分钟的细胞探测实验中分析三种模型细胞质和细胞核核糖核蛋白复合物来验证这种方法。相反,由替代的细胞内SHAPE探测方法产生的数据与SHAPE MaP产生的数据相关性较差(r=0.2),并且不能产生RNA-蛋白质相互作用的准确信号。然后,我们检查RNase MRP复合物中的RNA-蛋白质和RNA-底物相互作用,并通过比较细胞内相互作用位点与疾病相关突变,从分子表型方面表征这些非编码突变。总之,这些结果表明,SHAPE MaP可以在天然细胞条件下定义真正的相互作用位点并推断RNA功能,而对所涉及的蛋白质或RNA的先验知识有限。[3]
|
| 参考文献 |
[1]. A fast-acting reagent for accurate analysis of RNA secondary and tertiary structure by SHAPE chemistry. J Am Chem Soc . 2007 Apr 11;129(14):4144-5. doi: 10.1021/ja0704028.
[2]. RNA motif discovery by SHAPE and mutational profiling (SHAPE-MaP). Nat Methods . 2014 Sep;11(9):959-65. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3029. [3]. Detection of RNA-Protein interactions in living cells with SHAPE. Biochemistry . 2015 Nov 24;54(46):6867-75. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00977. |
| 其他信息 |
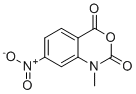
1-methyl-7-nitroisatoic anhydride is a 3,1-benzoxazin-1,4-dione having an N-methyl substituent and a nitro group at the 7-position. It is a benzoxazine and a C-nitro compound.
|
| 分子式 |
C9H6N2O5
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
222.15434
|
| 精确质量 |
222.027
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 48.66; H, 2.72; N, 12.61; O, 36.01
|
| CAS号 |
73043-80-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
73043-80-8;
|
| PubChem CID |
12535373
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.6±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
395.4±44.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
192.9±28.4 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.623
|
| LogP |
0.4
|
| tPSA |
98.03
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
0
|
| 重原子数目 |
16
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
350
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C(O1)N(C)C2=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=CC=C2C1=O
|
| InChi Key |
MULNCJWAVSDEKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C9H6N2O5/c1-10-7-4-5(11(14)15)2-3-6(7)8(12)16-9(10)13/h2-4H,1H3
|
| 化学名 |
1-Methyl-7-nitro-2H-3,1-benzoxazine-2,4(1H)-dione
|
| 别名 |
1M7; 1-methyl-7-nitro-3,1-benzoxazine-2,4-dione
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~225.07 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.5015 mL | 22.5073 mL | 45.0146 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.9003 mL | 4.5015 mL | 9.0029 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4501 mL | 2.2507 mL | 4.5015 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05462145 | RECRUITING | Device: Globe Pulsed Field System | Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Persistent Atrial Fibrillation |
Kardium Inc. | 2023-03-09 | Not Applicable |
|
|