| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Rats were fed a diet containing 5.19% of Allura Red. It was observed that 0.1% and 29% of the intact dye was excreted in the urine and feces respectively. In later studies, rats and dogs were pretreated daily with nonradioactive Allura Red. Subsequently, the animals were dosed with the 35S labelled compound and studied for up to 72 hours for excretion and distribution patterns of the color. Both species showed limited absorption of the compound with the major route of excretion being via the feces. In the dog 92-95% of the recovered radioactivity appeared in the feces within 72 hours while in the rat 76-92% of the recovered radioactivity appeared in the feces within this time period. Urinary recoveries of the color in rats and dogs, respectively varied between 5.7 and 19.8% and 2.7 and 3.6%. After sacrifice, significant retention of radioactivity was located in the intestinal contents of both species and in the washed intestines of the rats. This was thought to be due to adhesion of the compound to the intestinal wall, since the total carcass and viscera of these animals contained <0.4% of the administered dose. Metabolism / Metabolites Several metabolites, possibly resulting from azo-reduction in the gastrointestinal tract (two identified as aromatic amines, p-cresidine sulfonic acid being the major one), were also found in the feces and urine. Finally, significant retention in the washed intestines of rat was observed, probably due to adhesion to the intestinal wall. Cresidinesulfonic acid was found to be the major metabolite of Allura Red in the urine of these two species, whereas the parent compound was not measurable. In addition, two other unidentifiable metabolites were found in the urine of the rats. In the rat fecal extracts, cresidinesulfonic acid was a major metabolite along with two unknowns and the parent compound. The dog fecal sample revealed an identical metabolite pattern as seen in the rat, and in addition, a third unknown was discovered. One of the urinary unknowns demonstrated an Rf value which was identical to that of the one of the fecal unknowns suggesting that they were one and the same. The other unknowns exhibited distinctive Rf values which indicated that these metabolites were different. It has been postulated that azo reduction by gut flora of the dye will yield the two components of the parent compound: 2-methoxy-5-methyl-aniline-4-sulfonic acid (cresidine-4-sulfonic acid) and 1-amino-2-naphthol-6-sulfonic acid. It appears that negligible quantities of intact Red are absorbed and excreted in the urine, and that the major portion of the color is excreted as metabolites in the feces. |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Interactions
In this study, the color and its alumina lake were applied to the subjects volvar forearms (200 subjects) as an aqueous solution for 10 alternate days, for 24-hr periods, followed by a 14-day rest period. Challenge batches were then applied under occlusion to fresh skin sites on the subjects scapular backs for 24 hours. The color did not produce either irritation or allergic responses during the induction phase nor contact dermatitis in the challenge period. ... Allura Red and its lake were evaluated on sites under occlusion for five 48-hr, alternate-day periods. These sites had been previously irradiated for 5 min with Xenon light which had been filtered through a window-glass equivalent to limit the exposure to non-erythema-producing, long-wave radiation. A 10-day rest period followed this induction exposure, and then the color was applied to fresh skin sites, irradiated for 5 min with Xenon and subsequently removed and the sites were evaluated. Allura Red was shown not to produce photosensitization on the 25 subjects studied. In 2006, the Korea Food and Drug Administration reported that combinations of dietary colors such as allura red AC, tartrazine, sunset yellow FCF, amaranth, and brilliant blue FCF are widely used in food manufacturing. Although individual tar food colors are controlled based on acceptable daily intake (ADI), there is no apparent information available for how combinations of these additives affect food safety. In the current study, the potencies of single and combination use of /dyes/ were examined on neural progenitor cell (NPC) toxicity, a biomarker for developmental stage, and neurogenesis, indicative of adult central nervous system (CNS) functions. /allura red AC/ and /amaranth/ reduced NPC proliferation and viability in mouse multipotent NPC, in the developing CNS model. Among several combinations tested in mouse model, combination of /tartrazine/ and /brilliant blue FCF/ at 1000-fold higher than average daily intake in Korea significantly decreased numbers of newly generated cells in adult mouse hippocampus, indicating potent adverse actions on hippocampal neurogenesis. However, other combinations including /allura red AC/ and /amaranth/ did not affect adult hippocampal neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus. Evidence indicates that single and combination use of most tar food colors may be safe with respect to risk using developmental NPC and adult hippocampal neurogenesis... Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Dog oral (male) > 5,000 mg/kg bw[EPA/Office of Pollution Prevention and Toxics; High Production Volume (HPV) Challenge Program's Robust Summaries and Test Plans for: 2-Naphthalenesulfonic acid, 6-hydroxy-5- LD50 Rat oral >10,000 mg/kg bw[EPA/Office of Pollution Prevention and Toxics; High Production Volume (HPV) Challenge Program's Robust Summaries and Test Plans for: 2-Naphthalenesulfonic acid, 6-hydroxy-5- LD50 Rabbit dermal 10,000 mg/kg bw |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
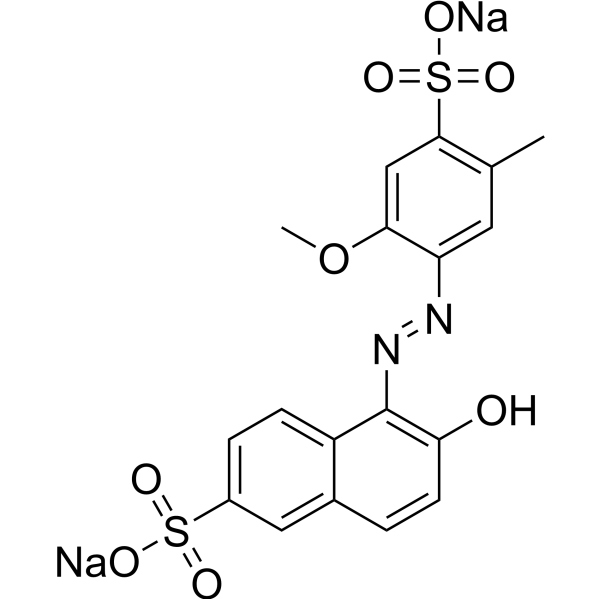
Allura red AC is a naphthalenesulfonic acid.
|
| 分子式 |
C18H14N2NA2O8S2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
496.4219
|
| 精确质量 |
495.998
|
| CAS号 |
25956-17-6
|
| PubChem CID |
33258
|
| 外观&性状 |
Brown to reddish brown solid powder
|
| 熔点 |
300ºC
|
| LogP |
5.247
|
| tPSA |
185.34
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
809
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
CEZCCHQBSQPRMU-UHFFFAOYSA-L
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H16N2O8S2.2Na/c1-10-7-14(16(28-2)9-17(10)30(25,26)27)19-20-18-13-5-4-12(29(22,23)24)8-11(13)3-6-15(18)21;;/h3-9,21H,1-2H3,(H,22,23,24)(H,25,26,27);;/q;2*+1/p-2
|
| 化学名 |
disodium;6-hydroxy-5-[(2-methoxy-5-methyl-4-sulfonatophenyl)diazenyl]naphthalene-2-sulfonate
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ~100 mg/mL (~201.44 mM)
DMSO : ~62.5 mg/mL (~125.90 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0144 mL | 10.0721 mL | 20.1442 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4029 mL | 2.0144 mL | 4.0288 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2014 mL | 1.0072 mL | 2.0144 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT01901705 | Completed | Drug: Indigo naturalis ointment Drug: Placebo |
Psoriasis | China Medical University Hospital | 2013-02 | Phase 2 |