| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
研究发现,CCC(300 mg/L)导致百合叶和茎的生物量大幅上升,百合球茎中赤霉酸(GA)含量显着下降,吲哚-3-乙酸增加(IAA) 叶子中的含量。
|
|---|---|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Chlormequat was determined in four /sow/ milk samples in the range of 0.4 ng/g to 1.2 ng/g... The distribution of Chlorocholine chloride (CCC) in the eggs of laying hens was studied using 15N-CCC. Twelve layers (37 weeks old) were divided into four groups and used in this study consisting of three feeding phases. In phase one (7 days), all the hens received a CCC-free diet [165 g CP/kg dry matter (DM); 11.58 MJ ME/kg DM]. In phase two (11 days), four levels of 15N-CCC: 0, 5, 50 and 250 ppm were added to the respective diets, while in phase three (7 days), CCC-free feed was again offered. Egg samples were taken and the 15N content of egg yolk and albumin were determined. At the end of phase two, there was a significant (p < 0.05) increase in 15N content in egg yolk from hens fed the 50 and 250 ppm CCC diets and in albumin from hens fed the 250 ppm CCC diet. The estimated 15N-CCC residue was 1.71, 6.64, 28.80 ppm in egg yolk and 1.58, 1.08 and 4.50 ppm in albumin from hens fed 5, 50 and 250 ppm CCC, respectively. The CCC residue, from quantitative analysis ranged from 0.21 to 0.93 and 0.93 to 2.43 ppm in yolk of hens fed 50 and 250 ppm CCC, respectively, whereas a range of 0.40-1.46 ppm, was found in the albumin of hens fed 250 ppm. The difference in measured CCC in yolk and albumin and that estimated from 15N-CCC could have been due to breakdown products of 15N-CCC. Seven days after withdrawal of 15N-CCC, the estimated 15N-CCC residue in egg yolk decreased to 0.43, 2.45 and 15.59 ppm, on 5, 50 and 250 ppm CCC dietary treatments, respectively, and to 2.46 ppm in albumin from hens fed 250 ppm CCC. The higher increase in 15N content could have been due to a higher incorporation of 15N-CCC into yolk than albumin during the process of rapid yolk deposition. This experiment showed that consumed CCC is distributed both into yolk and albumin in a dose dependent manner and that CCC is metabolized in laying hens. However, the level of CCC in the diet which could lead to accumulation of detectable CCC levels in eggs as observed in this study, is much higher than the established maximum residual limits in grains. In mammals, following oral administration, 97% is eliminated within 24 hr, principally as the unchanged substance. Metabolism / Metabolites An experiment was conducted to evaluate the metabolic products of chlorocholine chloride (CCC) in eggs and meat of laying hens fed a diet containing (15)N-CCC. Ten brown laying hens were randomly divided into two groups of five each. One group was offered (15)N-CCC free diet while the other group received a diet with 100 ppm (15)N-CCC for 11 days. Samples of eggs and meat from the laying hens were collected. Egg yolks and albumen were separated. Meat was collected from the breast and femur. The metabolic products of CCC were measured using ion trap electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ion trap-ESI-MS/MS). Determination of CCC or its metabolites in eggs and meat showed that CCC was metabolized to choline. Corresponding MS/MS spectra were obtained for m/z 104 (choline) or 105 ((15)N-choline), whereas nothing was detected at m/z 122 (CCC) or 123 ((15)N-CCC). The results from this study indicate that CCC will be metabolized in tissues of laying hens. When (14)C-labeled CCC was applied to kohlrabi, cauliflower, or tomatoes, degradation of CCC was very small. The first product was probably choline which entered the plant pool. Small amounts of labeled methyl groups from choline were found as S-methyl methionine. CCC was not degraded when applied to sugarcane. In alfalfa, CCC was slowly metabolized and was primarily incorporated into choline of phosphatidylcholine. Almond seedlings were treated with labeled CCC. Translocation to leaves and to the roots was observed. (14)CO2 was formed within 2 h after application. Radioactivity was observed in 17 known amino acids, an unidentified ninhydrin positive compound, malic acid, citric acid, choline and 2-chloroethylamine. When CCC was incubated in rumen contents or juice under anaerobic conditions, microbial degradation of CCC did not occur. For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for CHLORMEQUAT CHLORIDE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Chlormequat chloride appears as white crystals with a fishlike odor. Used as a plant growth regulator. Said to be effective for cereal grains, tomatoes, and peppers. (EPA, 1998)
Chlormequat chloride is an organic chloride salt comprising equal numbers of chlormequat and chloride ions. A gibberellin biosynthesis inhibitor, it is used as a plant growth retardant to produce plants with sturdier, thicker stalks, facilitating the havesting of ornamental flowers and cereal crops. It has a role as a plant growth retardant and an agrochemical. It is an organic chloride salt and a quaternary ammonium salt. It contains a chlormequat. A plant growth regulator that is commonly used on ornamental plants. Mechanism of Action Chlormequat chloride has been reported in the literature to act at the nicotinic receptor site of the neuromuscular junction. The test material may act as a depolarizing agent at this site, leading to muscular excitation followed by muscle weakness. Acute toxicity may lead to respiratory arrest. Acute toxicity of chlormequat chloride has also been reported to differ by species, which is likely due to sensitivity to depolarizing neuromuscular blockers. |
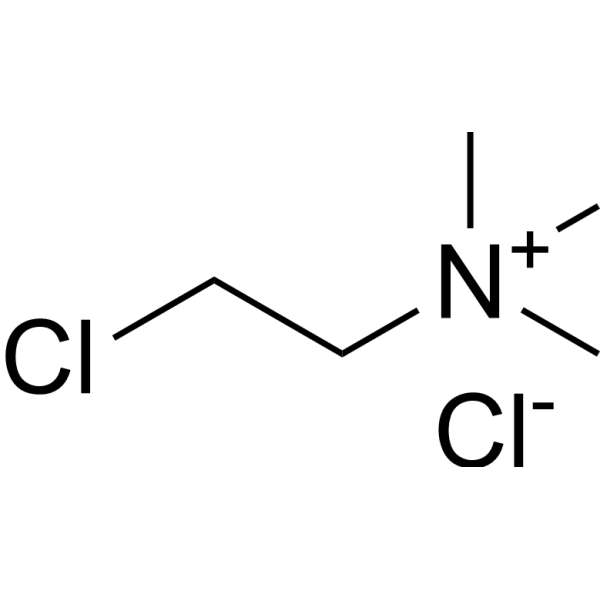
| 分子式 |
C5H13CL2N
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
158.0694
|
| 精确质量 |
157.042
|
| CAS号 |
999-81-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Chlorocholine-d4 chloride;Chlorocholine-d9 chloride;1219257-11-0
|
| PubChem CID |
13836
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 熔点 |
239-243 °C (dec.)(lit.)
|
| tPSA |
0
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
1
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
8
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
46.5
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
UHZZMRAGKVHANO-UHFFFAOYSA-M
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C5H13ClN.ClH/c1-7(2,3)5-4-6;/h4-5H2,1-3H3;1H/q+1;/p-1
|
| 化学名 |
2-chloroethyl(trimethyl)azanium;chloride
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.3263 mL | 31.6316 mL | 63.2631 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.2653 mL | 6.3263 mL | 12.6526 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.6326 mL | 3.1632 mL | 6.3263 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。