| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
盐酸氯普鲁卡因对小鼠的致死剂量(LD50)为皮下注射950 mg/kg,静脉注射97 mg/kg[2]。
|
|---|---|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Thanks to its low risk for systemic toxicity, chloroprocaine has a rapid onset of action that usually ranges between 6 to 12 minutes. The duration of chloroprocaine-induced anesthesia may be up to 60 minutes. The absorption rate of local anesthetics depends on the total dose and concentration of chloroprocaine, as well as the route of administration, the vascularity of the administration site, and the presence or absence of epinephrine in the anesthetic injection. The presence of epinephrine reduces the rate of absorption and plasma concentration of local anesthetics. The systemic exposure to chloroprocaine following its topical ocular administration has not been evaluated. Like most local anesthetics and their metabolites, chloroprocaine is mainly excreted by the kidneys. The urinary excretion of chloroprocaine may be affected by urinary perfusion and factors that have an effect on urinary pH. PROCAINE IS READILY ABSORBED FOLLOWING PARENTERAL ADMIN ... DOES NOT LONG REMAIN @ SITE OF INJECTION. ... FOLLOWING ABSORPTION, PROCAINE IS RAPIDLY HYDROLYZED ... /PROCAINE/ ... Binding of the anesthetic to proteins in the serum and to tissues reduces the concentration of free drug in the systemic circulation and, consequently, reduces toxicity. ... /Ester local anesthetics/ are hydrolyzed and inactivated primarily by a plasma esterase, probably plasma cholinesterase. The liver also participates in hydrolysis of local anesthetics. /Local anesthetics/ THE SYSTEMIC TOXICITY OF CHLOROPROCAINE IS LESS THAN THAT OF ALL OTHER LOCAL ANESTHETICS BECAUSE OF ITS RAPID HYDROLYSIS BY PLASMA CHOLINESTERASE ... WHICH SHORTENS THE PLASMA HALF-LIFE. ... ENZYMATIC HYDROLYSIS OF PROCAINE /GIVES/ ... PARA-AMINOBENZOIC ACID & DIETHYLAMINOETHANOL. FORMER IS EXCRETED IN URINE TO EXTENT OF ABOUT 80%, EITHER UNCHANGED OR IN CONJUGATED FORM. ONLY 30% OF DIETHYLAMINOETHANOL CAN BE RECOVERED IN URINE; REMAINDER UNDERGOES METABOLIC DEGRADATION ... /PROCAINE/ For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CHLOROPROCAINE (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites In plasma, chloroprocaine is quickly metabolized by pseudocholinesterases, a group of enzymes that perform the hydrolysis of the ester linkage. In ocular tissues, chloroprocaine is metabolized by nonspecific esterases. The hydrolysis of chloroprocaine leads to the production of ß-diethylaminoethanol and 2-chloro-4-aminobenzoic acid, which inhibits the action of the sulfonamides. 2-DIETHYLAMINOETHYL 4-AMINO-2-CHLOROBENZOATE YIELDS 4-AMINO-2-CHLOROBENZOIC ACID IN GUINEA PIGS. LIVETT, BH & RM LEE, BIOCHEM PHARMAC 17, 385 (1968). /FROM TABLE/ HYDROLYZED /CHIEFLY/ BY PLASMA PSEUDOCHOLINESTERASES /& ALSO BY ESTERASES IN LIVER/ AS DIETHYLAMINOETHANOL & 2-CHLORO-4-AMINOBENZOIC ACID /HUMAN, PARENTERAL. ANIMAL STUDIES SUGGEST THAT SOME LOCAL ANESTHETICS MAY UNDERGO BILIARY RECYCLING/ /CHLOROPROCAINE HCL/ Chloroprocaine is rapidly metabolized in plasma by hydrolysis of the ester linkage by pseudocholinesterase. Route of Elimination: Chloroprocaine is rapidly metabolized in plasma by hydrolysis of the ester linkage by pseudocholinesterase. Urinary excretion is affected by urinary perfusion and factors affecting urinary pH. Half Life: 21 +/- 2 seconds Biological Half-Life In adults, the average _in vitro_ plasma half-life of chloroprocaine is 21 seconds for males and 25 seconds for females. In neonates, the average _in vitro_ plasma half-life is 43 seconds. Following intrapartum epidural anesthesia, the apparent _in vivo_ half-life of chloroprocaine detected in maternal plasma was 3.1 minutes (range from 1.5 to 6.4 minutes). ... Plasma half-life /is/ approximately 25 seconds. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of chloroprocaine during breastfeeding. Based on the low excretion of other local anesthetics into breastmilk and the extremely short half-life of chloroprocaine, it is unlikely to adversely affect the breastfed infant. However, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Compared to the other clinically used local anesthetics, chloroprocaine has one of the lowest protein binding percentages. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
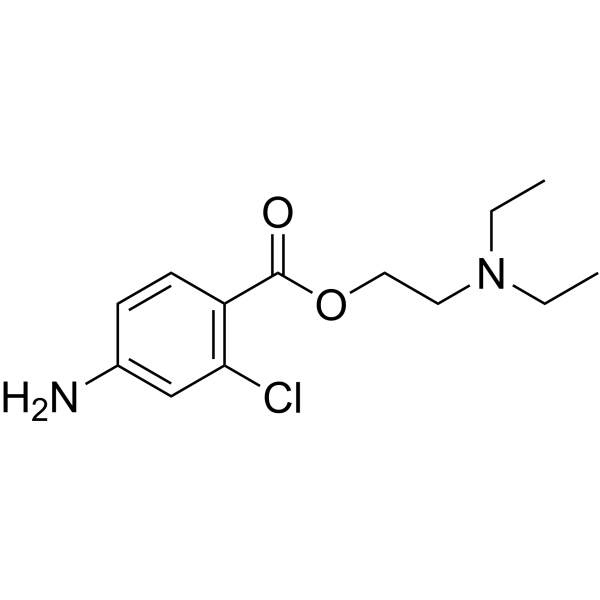
Chloroprocaine is procaine in which one of the hydrogens ortho- to the carboxylic acid group is substituted by chlorine. It is used as its monohydrochloride salt as a local anaesthetic, particularly for oral surgery. It has the advantage over lidocaine of constricting blood vessels, so reducing bleeding. It has a role as a local anaesthetic, a peripheral nervous system drug and a central nervous system depressant. It is a benzoate ester and a member of monochlorobenzenes. It is functionally related to a 2-diethylaminoethanol and a 4-amino-2-chlorobenzoic acid.
Chloroprocaine is an ester local anesthetic commonly available in its salt form, chloroprocaine hydrochloride. Similar to other local anesthetics, it increases the threshold for electrical excitation in nerves by slowing the propagation of the nerve impulse and reducing the rate of rise of the action potential. The pharmacological profile of chloroprocaine is characterized by a short latency and duration, similar to the one observed with [lidocaine]. Chloroprocaine can be given as an injection, and is available in formulations with and without methylparaben as a preservative. Both can be given as intrathecal injections for peripheral and central nerve block, but only the preservative-free formulation can be used for lumbar and caudal epidural blocks. Topical chloroprocaine for ophthalmic use was approved by the FDA in September 2022 for ocular surface anesthesia. Chloroprocaine is an Ester Local Anesthetic. The physiologic effect of chloroprocaine is by means of Local Anesthesia. Chloroprocaine hydrochloride is a local anesthetic given by injection during surgical procedures and labor and delivery. Chloroprocaine, like other local anesthetics, blocks the generation and the conduction of nerve impulses, presumably by increasing the threshold for electrical excitation in the nerve, by slowing the propagation of the nerve impulse and by reducing the rate of rise of the action potential. See also: Chloroprocaine Hydrochloride (has salt form). Drug Indication Chloroprocaine for intrathecal injection is indicated for the production of subarachnoid block (spinal anesthesia) in adults. It is also indicated for the production of local anesthesia by infiltration, peripheral and central nerve block, and a preservative-free form can also be used for lumbar and caudal epidural blocks. Topical chloroprocaine for ophthalmic use is indicated for ocular surface anesthesia. Mechanism of Action Chloroprocaine acts mainly by binding to the alpha subunit on the cytoplasmic region of voltage-gated sodium channels and inhibiting sodium influx in neuronal cell membranes. This lowers the nerve membrane permeability to sodium and decreases the rate of rise of the action potential. Therefore, chloroprocaine inhibits signal conduction and leads to a reversible nerve conduction blockade. The progression of anesthesia depends on the diameter, myelination and conduction velocity of nerve fibers, and the order of loss of nerve function is the following: 1) pain, 2) temperature, 3) touch, 4) proprioception, and 5) skeletal muscle tone. Local anesthetics prevent the generation and the conduction of the nerve impulse. Their primary site of action is the cell membrane. ... Local anesthetics block conduction by decreasing or preventing the large transient increase in the permeability of excitable membranes to Na+ that normally is produced by a slight depolarization of the membrane. ... As the anesthetic action progressively develops in a nerve, the threshold for electrical excitability gradually increases, the rate of rise of the action potential declines, impulse conduction slows, and the safety factor for conduction decreases; these factors decrease the probability of propagation of the action potential, and nerve conduction fails. ... /Local anesthetics/ can block K+ channels. ... blockade of conduction is not accompanied by any large or consistent change in resting membrane potential due to block of K+ channels. /Local anesthetics/ ... SITE AT WHICH LOCAL ANESTHETICS ACT, AT LEAST IN ... CHARGED FORM, IS ACCESSIBLE ONLY FROM THE INNER SURFACE OF THE MEMBRANE. ... LOCAL ANESTHETICS APPLIED EXTERNALLY FIRST MUST CROSS THE MEMBRANE BEFORE THEY CAN EXERT A BLOCKING ACTION. /LOCAL ANESTHETICS/ ... /TWO POSSIBILITIES:/ ACHIEVE BLOCK BY INCR SURFACE PRESSURE OF LIPID LAYER THAT CONSTITUTES NERVE MEMBRANE ... CLOSING PORES THROUGH WHICH IONS MOVE. ... /OR:/ AFFECT PERMEABILITY BY INCR DEGREE OF DISORDER OF MEMBRANE. /LOCAL ANESTHETICS/ ... ACID SALT MUST BE NEUTRALIZED IN TISSUE & FREE AMINE LIBERATED BEFORE DRUG CAN PENETRATE TISSUES & PRODUCE ANESTHETIC ACTION. ... FORM OF MOLECULE ACTIVE IN NERVE FIBERS IS CATION. ... CATION ... COMBINES WITH SOME RECEPTOR IN MEMBRANE TO PREVENT GENERATION OF ACTION POTENTIAL. /LOCAL ANESTHETICS/ ... /SUGGESTED/ THAT PROCAINE ... DIMINISHES RELEASE OF ACETYLCHOLINE BY MOTOR-NERVE ENDINGS. /PROCAINE/ |
| 分子式 |
C13H19CLN2O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
270.7549
|
| 精确质量 |
306.09
|
| CAS号 |
133-16-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Chloroprocaine hydrochloride;3858-89-7
|
| PubChem CID |
8612
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.17g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
402.6ºC at 760mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
173-174ºC
|
| 闪点 |
197.3ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
1.08E-06mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.553
|
| LogP |
3.804
|
| tPSA |
55.56
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
18
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
259
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CCN(CC)CCOC(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)NCl
|
| InChi Key |
VDANGULDQQJODZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C13H19ClN2O2/c1-3-16(4-2)7-8-18-13(17)11-6-5-10(15)9-12(11)14/h5-6,9H,3-4,7-8,15H2,1-2H3
|
| 化学名 |
2-(diethylamino)ethyl 4-amino-2-chlorobenzoate
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6934 mL | 18.4672 mL | 36.9344 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7387 mL | 3.6934 mL | 7.3869 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3693 mL | 1.8467 mL | 3.6934 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。