| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
柠檬酸三钠表现出剂量依赖性抗增殖作用(0–12.5 mM;24 小时)[3]。在 G2/M 和 S 期,柠檬酸三钠(12.5 mM;72 小时)剂量依赖性地促进细胞凋亡和细胞周期停滞 [3]。 48后FAS、BAX、BID、AIF、EndoG、细胞色素c、PARP、GADD153、GRP78和caspase-3、-8、-9的表达上调,BCL-2和BCL-Xl的表达下调12.5 mM 柠檬酸三钠下的反应时间[3]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在小鼠肝脏中,腹腔注射柠檬酸三钠(120、240 和 480 mg/kg)可以显着降低 GSH-Px 活性并提高 MDA(丙二醛)水平 [1]。暴露于腹腔内柠檬酸三钠(120、240 和 480 mg/kg)的小鼠肝细胞表现出 caspase-3 活性的剂量依赖性增加,从而导致细胞凋亡 [1]。腹腔注射柠檬酸三钠(120、240 和 480 mg/kg;每周一次,持续三周)的小鼠会出现肾毒性 [2]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[3]
细胞类型: HaCaT 细胞 测试浓度: 0、2.5、5、7.5、10、12.5 mM 孵育持续时间:24小时 实验结果:以剂量依赖性方式抑制细胞活力。 细胞周期分析[3] 细胞类型: HaCaT 细胞 测试浓度: 12.5 mM 孵育时间:0、12、24、48、72小时 实验结果:一次剂量诱导细胞凋亡和细胞周期停滞在G2/M期和S期-依赖方式Expect。 蛋白质印迹分析[3] 细胞类型: HaCaT 细胞 测试浓度: 12.5 mM 孵育时间:12、24、48小时 实验结果:FAS、BAX、BID、AIF、EndoG、细胞色素c、PARP、GADD153、 GRP78 和 caspase -3、-8、-9 以及 BCL-2 和 BCL-X1 减少。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: 20 g male Kunming mice [2]
Doses: 120, 240, 480 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection; once a week for 3 weeks. Experimental Results: The activities of T-SOD and GSH-Px in the treatment group diminished with the increase of citric acid dose, the activity of NOS demonstrated an increasing trend, and the contents of H2O2 and MDA gradually diminished. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Tmax of 98-130min. Largely eliminated through hepatic metabolism with very little cleared by the kidneys. 19-39L. Total clearance of 313-1107mL/min. IN THE BODY, SODIUM CITRATE IS OXIDIZED TO BICARBONATE & EXCRETED IN THE URINE... Metabolism / Metabolites Citrate is metabolized to bicarbonate in the liver and plays a role as an intermediate in the citric acid cycle. IN THE BODY, SODIUM CITRATE IS OXIDIZED TO BICARBONATE... Biological Half-Life 18-54 min |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Sodium citrate is the trisodium salt of citric acid. It has a role as a flavouring agent and an anticoagulant. It contains a citrate(3-).
Sodium citrate is the sodium salt of citric acid. It is white, crystalline powder or white, granular crystals, slightly deliquescent in moist air, freely soluble in water, practically insoluble in alcohol. Like citric acid, it has a sour taste. From the medical point of view, it is used as alkalinizing agent. It works by neutralizing excess acid in the blood and urine. It has been indicated for the treatment of metabolic acidosis. Sodium Citrate is the sodium salt of citrate with alkalinizing activity. Upon absorption, sodium citrate dissociates into sodium cations and citrate anions; organic citrate ions are metabolized to bicarbonate ions, resulting in an increase in the plasma bicarbonate concentration, the buffering of excess hydrogen ion, the raising of blood pH, and potentially the reversal of acidosis. In addition, increases in free sodium load due to sodium citrate administration may increase intravascular blood volume, facilitating the excretion of bicarbonate compounds and an anti-urolithic effect. Sodium salts of citric acid that are used as buffers and food preservatives. They are used medically as anticoagulants in stored blood, and for urine alkalization in the prevention of KIDNEY STONES. See also: Anticoagulant sodium citrate solution (has subclass); sodium chloride; sodium citrate, unspecified form (component of) ... View More ... Drug Indication Used as an anticoagulant during plasmophoresis as well as a neutralizing agent in the treatment of upset stomach and acidic urine. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Citrate chelates free calcium ions preventing them from forming a complex with tissue factor and coagulation factor VIIa to promote the activation of coagulation factor X. This inhibits the extrinsic initiation of the coagulation cascade. Citrate may also exert an anticoagulant effect via a so far unknown mechanism as restoration of calcium concentration does not fully reverse the effect of citrate. Citrate is a weak base and so reacts with hydrochloric acid in the stomach to raise the pH. It it further metabolized to bicarbonate which then acts as a systemic alkalizing agent, raising the pH of the blood and urine. It also acts as a diuretic and increases the urinary excretion of calcium. |
| 分子式 |
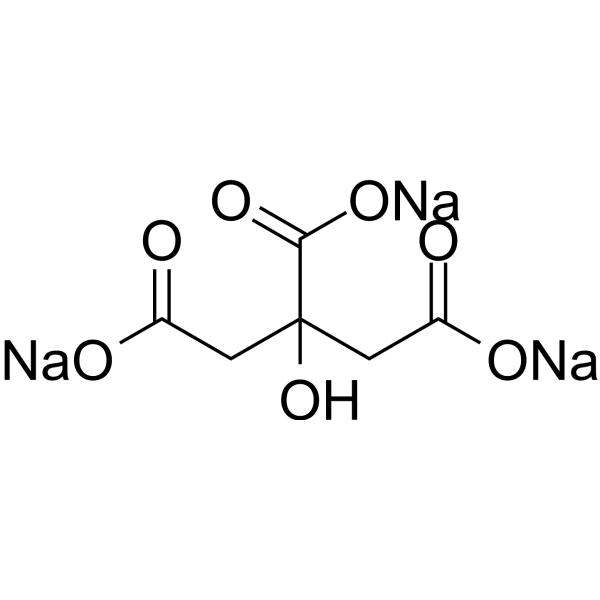
C6H5NA3O7
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
258.0690
|
| 精确质量 |
257.972
|
| CAS号 |
68-04-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Citric acid;77-92-9
|
| PubChem CID |
6224
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.008 g/mL at 20 °C
|
| 熔点 |
300°C
|
| tPSA |
140.62
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
16
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
211
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
HRXKRNGNAMMEHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-K
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C6H8O7.3Na/c7-3(8)1-6(13,5(11)12)2-4(9)10;;;/h13H,1-2H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)(H,11,12);;;/q;3*+1/p-3
|
| 化学名 |
trisodium;2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ~50 mg/mL (~193.75 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.8749 mL | 19.3746 mL | 38.7492 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7750 mL | 3.8749 mL | 7.7498 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3875 mL | 1.9375 mL | 3.8749 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。