| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
μ/κ-opioid receptor
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Eluxadoline(ELD)是局部作用的,具有多种药理作用,包括m-OR和κ阿片受体激动剂和δ阿片受体拮抗剂。它的口服生物利用度可以忽略不计,但已被美国食品和药物管理局正式批准用于IBS-D治疗。由于其集体药理学特性,ELD显著降低肠道运动能力,并降低药物引起便秘的概率[1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Eluxadoline(ELD)是一种最近批准的药物,在IBS-D的管理和治疗中显示出潜在的治疗效果。然而,由于其水溶性差,导致溶解率和口服生物利用度低,其应用受到限制。目前的研究目标是制备负载ELD的eudragit(EG)纳米颗粒(ENPs),并研究其对大鼠的抗腹泻活性。借助Box-Behnken Design Expert软件对制备的负载ELD的EG NP(ENP1-ENP14)进行优化。基于粒径(286±3.67 nm)、PDI(0.263±0.01)和ζ电位(31.8±3.18 mV)对所开发的制剂(ENP2)进行优化。优化后的制剂(ENP2)表现出最大药物释放的持续释放行为,并遵循Higuchi模型。成功地利用慢性约束应激(CRS)建立了IBS-D大鼠模型,该模型导致排便频率增加。体内研究显示,与纯ELD相比,ENP2显著降低了排便频率和疾病活动指数。因此,研究结果表明,所开发的基于eudragit的聚合物纳米颗粒可以作为一种潜在的途径,通过口服给药有效递送艾鲁沙多林,用于肠易激综合征腹泻治疗[1]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
使用Box-Behnken响应面方法实验设计(design Expert®软件版本13)来优化负载洗脱多林的eudragit纳米颗粒(ENP)(3个因素,3个水平)。选择的自变量是:eudragit聚合物的重量(X1)、%w/v、PVA(X2)和超声处理时间(X3),以及它们的高、中、低水平,用于制备14种制剂,如表1所示。粒度(Y1)、多分散指数(Y2)和ζ电位(Y3)是所检查的响应。此外,绘制了3D响应面图,以显示特定因素如何影响测量的响应[1]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
体外药物释放研究[1]
进行了体外药物释放研究,分析了优化制剂的药物释放行为和释放机制。使用透析膜法测定纯ELD和优化制剂(ENP2)的分析。将纯ELD和ENP2(5 mL)装入透析袋(Spectra/Por®Standard RC Tubing,MWCO 12 KDa)中,并在两端打结。然后,将袋子浸入含有pH 1.2和pH 6.8的溶解介质(200 mL)的烧杯中,保持在37±2°C的温度下,并在100 rpm下搅拌。在预先估计的时间间隔内,从每个烧杯中取出0.5 mL等分试样,并通过添加新鲜介质来维持水槽条件[31]。此外,通过HPLC方法分析等分试样的药物含量,并计算药物释放百分比并绘制其与时间的关系图。[30]. 所有研究一式三份(n=3)。此外,通过将药物释放结果拟合到不同的数学模型中,包括零阶、一阶、Higuchi和Korsmeyer-Peppas动力学模型,估计了ELD在pH(1.2和6.8)下从优化制剂中的药物释放机制 |
| 动物实验 |
In this study, the IBS rat model was induced by chronic restraint stress (CRS) as described by Lu et al. All rats were randomly divided into two groups (24 rats in the model group and 6 rats in the control group) after 7 days of adaptation. The rats in the model group were subjected to CRS using an elastic bandage to restrict the movement of the upper body and forelimbs and then anesthetized with ether. Their fore shoulders, upper forelimbs, and thoracic trunk were wrapped in elastic bandage for 2 h each day for 14 days to produce a steady and consistent amount of stimulation to restrict but not prevent movement. The control animals were anesthetized with ether but not restrained. [1]
Grouping and Administration The rats were divided into five groups (n = 6) as follows: Normal control group (NC): normal rats received saline (1 mL/kg). IBS control group (IBS-C): CRS rats received saline (1 mL/kg). Reference group (REF): CRS rats received loperamide (LRD) at 10 mg/kg. Pure drug group (ELD-std): CRS rats received (20 mg/kg). Formulation group (ENP2): CRS rats received (20 mg/kg). Treatments were administered orally, started 6 h after IBS induction, and continued for 14 consecutive days. Body weights were recorded daily. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The oral absorption of eluxadoline is poor - estimated to be 1.02%, this could be attributed to poor in vitro GI permeability, and its zwitterionic nature leading to a negatively charged molecule across the GI pH range. 82% excreted in feces, <1% excreted in urine. Metabolism / Metabolites The metabolism of eluxadoline is currently unclear, however evidence suggests limited glucoronidation forms an acyl glucuronide metabolite that is then excreted into urine. Biological Half-Life The mean plasma elimination half-life ranged from 3.7 hours to 6 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In preregistration clinical trials, serum aminotransferase elevations were uncommon during eluxadoline therapy and in pooled analyses ALT elevations above 3 times the upper limit of normal occurred in 2% to 3% of eluxadoline- vs 1% of placebo-treated subjects. More detailed analysis found rare instances of marked ALT and AST elevations with eluxadoline therapy, not seen with placebo treatment. These more marked elevations were sometimes accompanied by abdominal pain and signs of sphincter of Oddi spasm (as can occur with opioid therapy) or pancreatitis. The abnormalities also arose largely in patients without a gallbladder or with a history of pancreatitis or hepato-biliary disease. Subsequent to the approval of eluxadoline and its more widescale use, over a hundred reports of pancreatitis (including 2 deaths) were reported to the Food and Drug Administration and eluxadoline was given a “black box” warning regarding its use in persons without a gallbladder. The clinical features of these reactions have not been well described, but they typically arise within the first few weeks of treatment with severe abdominal pain and vomiting sometimes accompanied by marked ALT and AST elevations with or without increases in amylase and lipase. Jaundice is rare and the liver test abnormalities are most likely due to partial bile duct obstruction. There have been no reports of severe acute hepatitis or acute liver failure attributed to eluxadoline therapy. Likelihood score: C (probable cause of acute liver injury, likely due to bile duct spasm or obstruction). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of eluxadoline during breastfeeding. Because it has opioid agonist activity, an alternate drug is preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding 81% |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
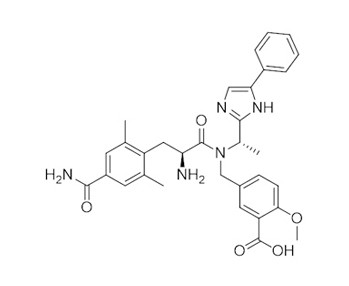
Eluxadoline is an amino acid amide obtained by the formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4-carbamoyl-2,6-dimethyl-L-phenylalanine with the secondary amino group of 2-methoxy-5-({[(1S)-1-(4-phenylimidazol-2-yl)ethyl]amino}methyl)benzoic acid. It has mixed opioid receptor activity and is used for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhoea. It has a role as a mu-opioid receptor agonist, a delta-opioid receptor antagonist, a kappa-opioid receptor agonist and a gastrointestinal drug. It is a member of imidazoles, a methoxybenzoic acid, a member of benzamides, a L-phenylalanine derivative and an amino acid amide.
Eluxadoline is a DEA Schedule IV controlled substance. Substances in the DEA Schedule IV have a low potential for abuse relative to substances in Schedule III. It is a Other substances substance. Eluxadoline is a mixed mu-opioid receptor agonist, kappa-opioid receptor agonist, and a-delta opioid receptor antagonist indicated for use in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D). The mu-, kappa-, and delta-opioid receptors mediate endogenous and exogenous opioid response in the central nervous system and peripherally in the gastrointestinal system. Agonism of peripheral mu-opioid receptors results in reduced colonic motility, while antagonism of central delta-opioid receptors results in improved analgesia, making eluxadoline usable for the symptoms of both pain and diarrhea characteristic of IBS-D. Marketed under the tradename Viberzi (FDA), eluxadoline is an antimotility agent that decreases bowel contractions, inhibits colonic transit, and reduces fluid/ion secretion resulting in improved symptoms of abdominal pain and reductions in the Bristol Stool Scale. Eluxadoline is a mu-Opioid Receptor Agonist. The mechanism of action of eluxadoline is as an Opioid mu-Receptor Agonist. Eluxadoline is a mixed opioid receptor agonist (mu) and antagonist (delta) that is used to treat diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel disease. Eluxadoline is associated with a low rate of serum aminotransferase elevations that appear to be due to isolated instances of sphincter of Oddi spasm and/or pancreatitis that occurs most frequently in persons without a gallbladder. Drug Indication For the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D). FDA Label Truberzi is indicated in adults for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhoea (IBS D). Treatment of diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel Syndrome Mechanism of Action Eluxadoline is a mu-opioid receptor agonis, kappa opioid receptor agonist and a delta opioid receptor antagonist. Eluxadoline is used for diarrhea predominant IBS because it reduces intestinal contractility and normalizes stress-induced acceleration of upper GI transit. Antagonistic activity at the delta receptor minimizes the constipating effect usually seen by mu-opioid receptor agonists alone. Because of it's limited systemic bioavailability, there may be less side effects associated with the use of eluxadoline in comparison with other therapies used to treat diarrhea predominant IBS. |
| 分子式 |
C32H35N5O5
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
569.66
|
| 精确质量 |
569.263
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 67.47; H, 6.19; N, 12.29; O, 14.04
|
| CAS号 |
864821-90-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
864825-13-8 (HCl);864821-90-9;
|
| PubChem CID |
11250029
|
| 外观&性状 |
Solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
834.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
458.3±34.3 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.2 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.640
|
| LogP |
4.35
|
| tPSA |
164.63
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
11
|
| 重原子数目 |
42
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
917
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
N(C(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1C(C)=CC(C(=O)N)=CC=1C)(CC1C=CC(OC)=C(C(=O)O)C=1)[C@H](C1=NC=C(C2C=CC=CC=2)N1)C
|
| InChi Key |
QFNHIDANIVGXPE-FNZWTVRRSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C32H35N5O5/c1-18-12-23(29(34)38)13-19(2)24(18)15-26(33)31(39)37(17-21-10-11-28(42-4)25(14-21)32(40)41)20(3)30-35-16-27(36-30)22-8-6-5-7-9-22/h5-14,16,20,26H,15,17,33H2,1-4H3,(H2,34,38)(H,35,36)(H,40,41)/t20-,26-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
5-(((S)-2-amino-3-(4-carbamoyl-2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N-((S)-1-(5-phenyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl)ethyl)propanamido)methyl)-2-methoxybenzoic acid
|
| 别名 |
JNJ 27018966; JNJ27018966; JNJ-27018966; Trade name: Viberzi
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7554 mL | 8.7772 mL | 17.5543 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3511 mL | 1.7554 mL | 3.5109 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1755 mL | 0.8777 mL | 1.7554 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。