| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
rEP2 ( IC50 = 50 nM )
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Evatanepag(以前称为 CP-533536)是 EP2 受体前列腺素 E2 (PGE2) 的有效选择性激动剂。它诱导局部骨形成,EC50 为 0.3 nM。 C 激酶测定:Evatanepag (CP-533536) 是一种 EP2 受体选择性前列腺素 E2 (PGE2) 激动剂,可诱导局部骨形成,EC50 为 0.3 nM。 CP-533536 是一种有效的选择性 EP2 激动剂。 CP-533536 在大鼠骨折愈合模型中以单剂量局部给药时表现出治愈骨折的能力。 CP-533536 在体外表现出优异的针对 EP2 的效力以及针对广泛的其他靶标的选择性。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
P-533536 在大鼠骨折愈合模型中以单剂量局部给药时表现出治愈骨折的能力。 CP-533536 在体外表现出优异的针对 EP2 的效力以及针对广泛的其他靶标的选择性。
为了进一步表征非前列腺素类EP2激动剂Evatanepag (CP-533536) 对肥大细胞(MC)的潜在抑制作用,我们在hdm致敏小鼠中进行了体内研究。将hdm致敏BALB/c小鼠暴露于Evatanepag (CP-533536) 中。评估气道反应性、炎症和LMC活性。[2] 图10A描述了对HDM空气过敏原致敏10天的小鼠气道对甲胆碱的反应性,并在致敏的第1天至第4天暴露于EP2选择性激动剂Evatanepag (CP-533536) 。用HDM致敏和刺激的小鼠表现出对甲胆碱的气道反应性显著增加。局部给药0.3 mg·kg−1的Evatanepag (CP-533536) 可防止空气过敏原引起的RL升高,其反应性约为未处理小鼠的一半。然而,在3mg·kg−1剂量下没有出现这种效应。[2] 在暴露于Evatanepag (CP-533536) 的小鼠中,还评估了气道中不同的炎症细胞募集(图10B)。在hdm致敏小鼠中诱导强嗜酸性粒细胞募集。Evatanepag (CP-533536) 预处理未改变气道炎性细胞计数差异。[2] 最后,通过测量肺部mMCP-1浓度来评估hdm诱导的LMC激活。图10C显示肺提取物匀浆中mMCP-1浓度与总蛋白归一化。在hdm暴露小鼠中,mMCP-1局部过表达的因子为5.4。Evatanepag (CP-533536) 对mMCP-1的影响没有统计学意义,但3 mg·kg−1剂量对mcp -1活性的抑制作用约为48% (P = 0.13)。[2] |
||
| 酶活实验 |
Evatanepag (CP-533536) 是一种前列腺素 E2 (PGE2) 激动剂,对 EP2 受体具有选择性,EC50 为 0.3 nM,可刺激局部骨形成。 CP-533536 是一种有效的选择性 EP2 激动剂。在大鼠骨折愈合模型中,CP-533536 显示出作为局部单剂量骨折治疗的前景。 CP-533536 在体外表现出优异的针对 EP2 的效力以及针对广泛的其他靶标的选择性。
EP2选择性激动剂的筛选[3] 化合物根据其选择性结合EP2受体的能力进行分类以进一步表征。EP2受体激动作用被定义为化合物选择性结合EP2受体并增加细胞内cAMP水平的能力。 受体结合。[3] 通过稳定转染表达PGE2 EP1、-2、-3或-4受体亚型以及前列腺素D2、前列腺素F2α、前列环素和凝血素的HEK-293细胞制备膜。按照Castleberry等人的描述测量受体结合。 cAMP的测定。[3] 在HEK-293/EP2细胞系中,用1 mM 3-异丁基-1-甲基黄嘌呤(3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine)在37℃预处理2 × 105个细胞10 min,然后用指定浓度的测试化合物在37℃处理12 min,测定细胞cAMP水平。根据制造商的说明,使用RIA试剂盒定量cAMP。 血浆Evatanepag (CP-533536) 分析[3] 将血浆样品解冻,每个样品20个×l注入带有涡轮离子喷雾源的PE-Sciex API 3000三重四极柱质谱仪中。采用Luna苯己基柱(4.6 × 50 mm × 3 ×m)进行分离。Evatanepag (CP-533536) 和内标在负离子模式下采用多反应监测,分别通过467.3/303.2 m/z和388.3/198.1 m/z的质量跃迁进行测定。该方法的线性动态范围为1 ~ 2000 ng/ml。质量控制标准的平均准确度为80-116%。[2] |
||
| 细胞实验 |
Mast cell (MC)刺激和释放试验[2]
小鼠细胞(C57.1, PDMC和LMC)在无SCF和il -3的培养基中用1 μg·mL−1 dnp特异性IgE致敏2小时。敏化后,将细胞洗涤并重悬于HEPES缓冲液中(10 mM HEPES [pH 7.4], 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 0.4 mM Na2HPO4_7H2O, 5.6 mM葡萄糖,1.8 mM CaCl2_2H2O和1.3 mM MgSO4_7H2O),含0.04% BSA。将细胞接种于v -底96孔板上,最终体积为100 μL,共50,000个细胞,用10−5 M丁甲酚素、10−5 M PGE2或载液(含0.1% DMSO的PBS)处理30分钟,10−5 M AH6809 (LMC)或载液(含20%乙醇的PS)在37℃、5% v/v CO2下处理1小时。野生型(WT) BALB/c的PDMCs也被增加浓度的butaprost(10−6 M, 3·10−6 M和3·10−5 M)处理,细胞被50 ng·mL−1 DNP-HSA作为抗原(Ag)刺激30分钟。用100 ng·mL−1在无SCF和il -3培养基中致敏LAD2 MCs 2小时。用500 ng·mL−1生物素化hIgE致敏RS-ATL8细胞16小时。用100 ng·mL−1嵌合hIgE anti-NP致敏FcεRI - / - hFcεRI+ BALB/c小鼠PDMCs 16小时。致敏后,将细胞洗净,用含0.04% BSA的HEPES缓冲液重悬,接种于v底96孔板上,最终体积为300 μL (LAD2)的细胞为15万个,最终体积为320 μL (PDMCs)的细胞为20万个。释放前2天,取5万个RS-ATL8细胞以100 μL的终体积培养,获得10万个粘附细胞。细胞在37°C下用5% v/v CO2处理2小时15分钟,方法如下:butaprost和Evatanepag (CP-533536) 浓度递增(10−7 M, 3·10−7 M, 10−6 M, 3·10−6 M, 10−5 M, 3·10−5 M, 10−4 M,或3·10−4 M)或载具(含0.1% DMSO的PBS)在LAD2中的浓度;Evatanepag (CP-533536) (10−12 M, 10−11 M, 10−10 M, 10−9 M, 10−8 M, 10−7 M, 10−6 M, 10−5 M,或10−4 M)在RS-ATL8;和butaprost(10−6米,3·10−6 M,或10−5米)从Fc PDMCsεRI−−/ hFcεRI +老鼠。分别用100 ng·mL - 1 SA (LAD2)、1000 ng·mL - 1 SA (RS-ATL8)或50 ng·mL - 1 NP-BSA(来自fc - ε ri - / - hfc - ε ri +小鼠的PDMC)在37℃、5% v/v CO2条件下攻毒30分钟。将细胞置于冰水中停止脱粒,细胞悬液在4°C, 1500 rpm离心10分钟。 |
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 参考文献 |
|
||
| 其他信息 |
Evatanepag is a monocarboxylic acid.
Evatanepag has been used in trials studying the treatment of Tibial Fractures. Sulfonamides, exemplified by 3a, were identified as highly selective EP(2) agonists. Lead optimization led to the identification of CP-533536, 7f, a potent and selective EP(2) agonist. CP-533536 demonstrated the ability to heal fractures when administered locally as a single dose in rat models of fracture healing. [1] Purpose: Agonism of the prostaglandin E2 receptor, E-prostanoid receptor 2 (EP2), may represent an alternative protective mechanism in mast cell (MC)-mediated diseases. Previous studies have suggested that activation of the MC EP2 receptor prevents pathological changes in the murine models of allergic asthma. This work aimed to analytically validate the EP2 receptor on MCs as a therapeutic target. Methods: Murine MC lines and primary cultures, and MCs bearing the human immunoglobulin E (IgE) receptor were subjected to IgE-mediated activation subsequent to incubation with selective EP2 agonists. Two molecularly unrelated agonists, butaprost and CP-533536, were tested either in vitro or in 2 in vivo models of allergy. Results: The diverse range of MC populations was consistently inhibited through selective EP2 agonism in spite of exhibiting a heterogeneous phenotype. Such inhibition occurred in both mouse and human IgE (hIgE)-mediated activation. The use of molecularly unrelated selective EP2 agonists allowed for the confirmation of the specificity of this protective mechanism. This effect was further demonstrated in 2 in vivo murine models of allergy where MCs are a key to pathological changes: cutaneous anaphylaxis in a transgenic mouse model expressing the hIgE receptor and aeroallergen-induced murine model of asthma. Conclusions: Selective EP2 agonism is a powerful pharmacological strategy to prevent MCs from being activated through IgE-mediated mechanisms and from causing deleterious effects. The MC EP2 receptor may be an effective pharmacological target in allergic and other MC-mediated conditions.[2] The observed in vivo EP2-driven effect could presumably counteract diseases based on IgE-mediated MC overactivation or hyper-releasability. We thereby assessed LMC activity and airway responses in HDM-sensitized BALB/c mice, which exhibited increased airway MC activity according to mouse mMCP-1 protease determination. The selective EP2-agonist CP-533536 partially (albeit insignificantly) prevented the ability of airway MCs to release mMCP-1. The CP-533536 effect was less than that of butaprost13 as anticipated by its more limited inhibitory effect in vitro. In parallel with preventing airway MC activity, CP-533536 also reduced HDM aeroallergen-induced increased RL response to methacholine. This confirms earlier findings that butaprost suppressed airway hyper-reactivity and inflammation.13 CP-533536 produced a nonsignificant reduction in eosinophilic inflammation, which may be explained by its relatively limited ability to reduce MC activity (compared to butaprost).[2] The morbidity and mortality associated with impaired/delayed fracture healing remain high. Our objective was to identify a small nonpeptidyl molecule with the ability to promote fracture healing and prevent malunions. Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) causes significant increases in bone mass and bone strength when administered systemically or locally to the skeleton. However, due to side effects, PGE2 is an unacceptable therapeutic option for fracture healing. PGE2 mediates its tissue-specific pharmacological activity via four different G protein-coupled receptor subtypes, EP1, -2, -3, and -4. The anabolic action of PGE2 in bone has been linked to an elevated level of cAMP, thereby implicating the EP2 and/or EP4 receptor subtypes in bone formation. We identified an EP2 selective agonist, CP-533,536, which has the ability to heal canine long bone segmental and fracture model defects without the objectionable side effects of PGE2, suggesting that the EP2 receptor subtype is a major contributor to PGE2's local bone anabolic activity. The potent bone anabolic activity of CP-533,536 offers a therapeutic alternative for the treatment of fractures and bone defects in patients.[3] We have presented data that the EP2 receptor subtype is important in skeletal healing. Further, a selective and potent functional EP2 receptor agonist, CP-533,536, induced healing of critical defects in the canine ulna and dramatically accelerated healing in the tibial osteotomy model. A single injection of CP-533,536, administered in a PLGH sustained release matrix at the time the bone defect was created, was efficacious in accelerating healing. Thus, given the high unmet medical need for fracture healing therapy and the current limitations of therapeutic procedures such as autographs and allographs, the potent bone anabolic capacity of CP-533,536 offers a promising therapeutic alternative for the enhancement of bone healing and treatment of bone defects and fractures in patients.[3] |
| 分子式 |
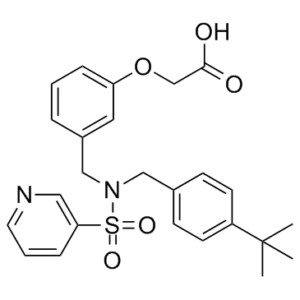
C25H28N2O5S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
468.57
|
| 精确质量 |
468.171
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 64.08; H, 6.02; N, 5.98; O, 17.07; S, 6.84
|
| CAS号 |
223488-57-1
|
| 相关CAS号 |
223490-49-1 (sodium); 223488-57-1 (free acid)
|
| PubChem CID |
9890801
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
660.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
353.0±34.3 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.600
|
| LogP |
4.78
|
| tPSA |
105.18
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
10
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
722
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
S(C1=C([H])N=C([H])C([H])=C1[H])(N(C([H])([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C(C=1[H])OC([H])([H])C(=O)O[H])C([H])([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])(=O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
WOHRHWDYFNWPNG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C25H28N2O5S/c1-25(2,3)21-11-9-19(10-12-21)16-27(33(30,31)23-8-5-13-26-15-23)17-20-6-4-7-22(14-20)32-18-24(28)29/h4-15H,16-18H2,1-3H3,(H,28,29)
|
| 化学名 |
2-[3-[[(4-tert-butylphenyl)methyl-pyridin-3-ylsulfonylamino]methyl]phenoxy]acetic acid
|
| 别名 |
Evatanepag; CP-533536; CP 533536; 223488-57-1; CP-533536 free acid; 2-[3-[[(4-tert-butylphenyl)methyl-pyridin-3-ylsulfonylamino]methyl]phenoxy]acetic acid; 2-(3-((N-(4-(tert-butyl)benzyl)pyridine-3-sulfonamido)methyl)phenoxy)acetic acid; CP533536
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1342 mL | 10.6708 mL | 21.3415 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4268 mL | 2.1342 mL | 4.2683 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2134 mL | 1.0671 mL | 2.1342 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00533377 | Completed | Drug: CP-533, 536 Drug: Placebo |
Tibial Fractures | Pfizer | January 2008 | Phase 2 |
|
|