| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
SETD2 (IC50=18 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
EZM0414 抑制一组 MM 和 DLBCL 细胞系,t(4;14) 细胞的 IC50 为 0.24 μM,DLBCL 细胞系的 IC50 为 0.023 μM->10 μM [2]。
EZM0414对SETD2的抑制在MM和DLBCL细胞系中产生了有效的抗增殖作用。EZM0414对t(4;14)和非t(4;14) MM细胞系的增殖均有抑制作用,在MM细胞系的t(4;14)亚群中普遍观察到较高的抑制增殖活性。EZM0414在t(4;14)细胞系中的IC 50中值为0.24 μM,而在非t(4;14)细胞系中为1.2 μM。此外,对DLBCL细胞株的生长抑制作用表现出广泛的敏感性,ic50值从0.023 μM到bbb10 μM。[2] 在由47个靶点和72个激酶组成的安全面板中,EZM0414的体外测试显示,除D2 (IC50 = 13.0 μM,拮抗剂)和5-HT1B (IC50 = 3.2 μM,激动剂)外,所有靶点的IC50都在25 μM左右。[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在植入人 KMS-11 细胞的 NOD SCID 小鼠异种移植模型中,EZM0414(15 和 30 mg/kg,口服,BID,每日)可抑制肿瘤生长,且耐受性良好 [3]。在大鼠和小鼠中,EZM0414(50 mg/kg,口服)的口服生物利用度接近 100%,小鼠的 t1/2 值为 1.8 小时,大鼠为 3.8 小时 [3]。
在3个MM和4个DLBCL细胞系来源的异种移植模型中,与对照相比,EZM0414具有统计学上显著的抗肿瘤活性。在t(4;14) MM细胞系衍生的异种移植物模型KMS-11中,在前两个剂量下观察到强劲的肿瘤生长回归,最大TGI为95%。此外,两个非t(4;14) MM (RPMI-8226, MM. 1s)和两个DLBCL异种移植模型(TMD8, KARPAS422)显示> 75% TGI;另外两种DLBCL模型(WSU-DLCL2, SU-DHL-10)对EZM0414的反应显示出50%的TGI。在所有测试的模型中,观察到的抗肿瘤作用与肿瘤内H3K36me3水平的降低相关,表明体内SETD2甲基转移酶活性的靶向抑制。[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
SETD2(1434-1711)测定[3]
生化试验监测了s -腺苷-蛋氨酸(SAM)的氚化甲基与残基26-40对应的生物素化组蛋白3肽的结合。底物肽的序列为biotin- ahx - rksapatggvkkkphr - nh2和3H-SAM,购自American radiollabelled Chemicals, Inc.。在384孔分析板上,将40L酶与1L化合物或DMSO孵育30分钟,然后与10L底物溶液开始反应。实验在室温下进行,实验缓冲液由25 mM比辛,pH 8.0, 7.5 mM-巯基乙醇,0.002%吐温-20和0.01%牛皮肤明胶(BSG)组成。在产物形成的线性部分,用10L的1 mM s -腺苷-同型半胱氨酸(SAH)和1 mM SAM来淬灭反应。从淬火反应中,将50L转移到链霉亲和素涂覆的闪光板 上,孵育至少2h,然后用0.1% Tween-20洗涤一次。链霉亲和素包被板捕获的3h标记肽的信号通过Topcount板读取器计数。抑制百分比(%I)和IC50值分别由式1和式2计算。%𝐼=(1−(𝑆−𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑚𝑎𝑥−𝑚𝑖𝑛))(eq - 1) %𝐼=(100−𝑏𝑜𝑡𝑡𝑜𝑚)(1 +(𝐼𝐶50𝐼)𝑛)+𝑏𝑜𝑡𝑡𝑜𝑚(eq 2)分钟的信号完全抑制SETD2从井20嗯SAH的最终浓度和最大的信号从井DMSO而不是化合物。计算IC50时,bottom为理论最小%I, I为缓蚀剂浓度,n为Hill斜率。化合物IC50的测定是通过测试10个浓度的化合物,将其稀释3倍,最终浓度为4 nM酶和底物浓度等于0.7M肽和2M SAM的KM值。 筛选方法:[3] 384孔源板中的EZM0414 (10 nL)直接加入到包被聚d -赖氨酸(PDL)的384孔培养板中。将A549细胞接种于浓度为80000细胞/ mL的实验培养基中,并添加到PDL包被板上,每孔体积为50µL。将培养皿放在实验台上约20分钟,使细胞在孔底沉淀。37℃,5% CO2孵育3天。三天后,将培养皿从培养箱中取出,让培养皿达到室温。将培养基从板中吸出,每孔加50µL的100%甲醇,孵育30分钟。用抽吸法去除甲醇,每孔115µL洗涤缓冲液(1X PBS加0.05%吐温-20 (v/v))洗涤3次。接下来,每孔加入50µL奥德赛阻断缓冲液+ 0.1%吐温-20,在室温下孵育1小时。去除阻断缓冲液,洗涤3次,每孔加入20µL一抗(抗组蛋白H3三甲基K36在奥德赛缓冲液中以0.1%吐温-20 (v/v)稀释1:1000),在4°C下孵育过夜(16小时)。每孔115µL洗涤缓冲液(1X PBS加0.05% Tween-20 (v/v))洗涤5次。每孔加入20µL二抗(1:500 800CW山羊抗兔IgG (H+L)抗体,1:1000 DRAQ5在含0.1%吐温-20 (v/v)的Odyssey缓冲液中),室温孵育1小时。用每孔115µL的缓冲液(1X PBS,含0.05%吐温-20 (v/v))洗涤5次,然后用每孔115µL的水洗涤3次。冲洗后,将平板倒置在薄的纸巾床上离心1分钟,转速高达1000 rpm,以去除多余的试剂,然后在室温下干燥,避免直接暴露在光线下。在Licor Odyssey系统上对底片成像,该系统测量700 nm和800 nm波长的综合强度。 为了抑制CYP1A2,在上述溶液中加入1 μL终浓度为40 μM的特异性药物底物(非那西丁:8 mM)。为了抑制CYP2B6,在上述溶液中加入1 μL的特异性药物底物(安非他酮:10 mM),终浓度为50 μM。为了抑制CYP2C8,在上述溶液中加入1 μL的特异性药物底物(紫杉醇:1 mM),终浓度为5 μM。为了抑制CYP2C9,在上述溶液中加入1 μL终浓度为200 μM的特异性药物底物(Tolbutamide: 40 mM)。为了抑制CYP2C19,在上述溶液中加入1 μL的特异性药物底物((s)-甲苯妥英:10 mM),终浓度为50 μM。为了抑制CYP2D6,在上述溶液中加入1 μL的特异性药物底物(右美沙芬:2 mM),终浓度为10 μM。为了抑制CYP3A4,在上述溶液中加入1 μL的特异性药物底物(咪达唑仑:1 mM),最终浓度为5 μM。37℃预热5 min,加入终浓度为1 mM的10 mM NADPH溶液20 μL, 37℃开始反应。在指定时间点加入400 μL冷淬溶液(甲醇含内标物[IS: 100 nM阿普唑仑,500 nM拉贝他洛尔,2 μM酮洛芬])停止反应(非那西丁:20 min;安非他酮:20分钟;紫杉醇:10分钟;甲苯磺丁胺:20分钟;(s)-甲苯妥英:20分钟;右美沙芬:20分钟;咪达唑仑:5分钟)。样品涡旋5分钟,4℃下3220 g离心40分钟。然后将100 μL上清液转移到加100 μL水的96孔板上(取决于LC-MS信号响应和峰形),进行LC-MS/MS分析。所有的实验都是重复进行的。[3] |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞增殖试验测定EZM0414在MM和DLBCL细胞系组中的ic50值。研究人员对EZM0414的肿瘤生长抑制(TGI)作用进行了评估。western blot检测H3K36me3水平,评价靶接合性。在7天的体外细胞实验中,评估了MM和DLBCL标准护理(SOC)药物联合抑制SETD2的潜力。[2]
以0.5 × 10-3 ~ 10 μmol/L的浓度依赖性处理对数生长期细胞系,最终DMSO浓度为0.2%体积/体积(v/v)。细胞以确定的(1.25 × 105个细胞/mL)电镀密度,一式三份,在96孔板上镀。实验板在37°C 5% CO2的湿化气氛中孵育。每隔3-4天,用钙素AM测定活细胞数,并在Acumen高含量成像仪上进行分析。细胞计数后,将细胞分裂回原电镀密度,更换生长培养基和化合物。用第14天的最终分裂调整活细胞数/mL计算抑制率。技术重复的抑制百分比平均值用于绘制浓度响应曲线,并计算每个时间点的绝对半最大抑制浓度(IC50)值。计算第4、7、11和14天的生长情况:1。计算第4 - 7天、第7 - 11天和第11-14天的分裂因子。分裂因子是第X天(4、7或11天)的活细胞/mL除以细胞被分裂回2的密度。对于第4天至第7天的细胞生长,将第7天的活细胞/mL密度乘以第4天的分裂因子。2. 对于第7天至第11天的细胞生长,将第11天的活细胞/mL密度乘以第4天和7个分裂因子。3. 对于第11天至第14天的细胞生长,将第14天的活细胞/mL密度乘以第4,7和11天的分裂因子。5. 在半对数图上绘制生长(Y轴为活细胞/mL,对数,X轴为天数)。[3] 以浓度依赖性浓度0.5 × 10-3 ~ 10 μmol/L的EZM0414处理对数相细胞系,最终DMSO浓度为0.2% v/v。将细胞以确定的镀密度在96孔板(1.25 × 105细胞/mL)中镀三次(用于第0 - 7天的疗程)或在6孔板(3.75 × 105细胞/mL)中镀(用于第7天的剩余时间的疗程)。实验板在37°C 5% CO2的湿化气氛中孵育。在第0、4、7天读取培养皿,在第4天补充化合物/培养基。第7天,将6孔板胰蛋白酶化,离心,重新悬浮在新鲜培养基中进行Vi-CELL计数。每个处理的细胞以原始密度重新镀于96孔板,一式三份,并以相同的化合物浓度重新处理。在第7天(播种第7天的另一个基线读数)、第11天和第14天读取培养皿,在第11天补充化合物/培养基。通过使用CellTiter-Glo®进行发光细胞活力测定,通过测量细胞腺苷-5 ' -三磷酸(ATP)来定量增殖,使用EnSpire多模微孔板阅读器检测发光。第14天的最终原始发光值用于计算抑制率。用技术重复的抑制百分比平均值绘制浓度响应曲线,并计算每个时间点的绝对IC50值。[3] 从培养箱中取出Caco-2板,用预温HBSS (10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4)洗涤2次,然后在37°C下孵育30分钟。对照化合物原液用DMSO稀释得到1 mM溶液,再用HBSS (10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4)稀释得到5 μM工作溶液。实验化合物的原液在DMSO中稀释得到1 mM溶液,然后用辅助信息稀释得到5 μM工作溶液。构像设计驱动发现EZM0414:一种选择性的、有效的SETD2抑制剂,用于临床研究SI-47 HBSS (10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4)。培养体系中DMSO的终浓度为0.5%。测定药物在根尖向基底外侧方向的转运速率。在Transwell插入物(顶端室)中加入75 μL的受试化合物和对照化合物的工作溶液,在接收板(基底外侧室)孔中填充235 μL的HBSS (10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4)。为测定药物在基底外侧至根尖方向的转运速率,将受试化合物和对照化合物的工作溶液分别取235 μL滴入受检板孔(基底外侧室),然后在Transwell插入物(根尖室)中填充75 μL HBSS (10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4)。在新的96孔板上,将10 μL工作溶液转移到40 μL HBSS (10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4)上,然后加入200 μL含有适当内标(IS)的冷乙腈或甲醇,制备Time 0样品。37℃孵育2小时。孵育结束时,将10 μL供体侧(A→B通量的根尖室,B→A的基底侧室)至40 μL HBSS (10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4)和50 μL受体侧(A→B通量的根尖室,B→A的根尖室)的样品转移到新的96孔板的孔中,然后加入4体积含有适当内标(IS)的冷乙腈或甲醇。样品涡旋5分钟,然后3220 g离心40分钟。在LC-MS/MS分析前,取上清液100µL与适当体积的超纯水混合。[3] |
| 动物实验 |
Pharmacokinetics [3]
Study Design: A single intravenous (IV) dose was administered to the animal. Fasted animals were also dosed orally (PO). At the designated time points, blood was collected via the dorsal metatarsal vein in mice. Blood was transferred into collection tubes containing K2-EDTA. For plasma analysis, blood was immediately processed for plasma by centrifugation and stored in a freezer set to be maintained at approximately -80C until analysis. Sample Preparation: The desired serial concentrations of working solutions were achieved by diluting stock solution (1 mg/mL in DMSO) of analyte with 50% acetonitrile in water. Ten microliters of working solutions were added to 10 μL of the blank animal plasma to achieve calibration standards of 0.5-1000 ng/mL in a total volume of 20 μL. The resulting 20 µL standard samples were added to 200 μL of acetonitrile for protein precipitation. All samples were then vortexed for 30 seconds. After centrifugation at 4°C and 4000 rpm (ca. 3740 x g) for 15 minutes, the supernatant was diluted with water. Analytical Method: Concentrations in extracted samples were determined by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) using reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Analytes were monitored using Electron Spray Ionization (ESI) with multiple reaction monitoring in positive ion mode. Peak areas were integrated by Analyst® where concentrations were determined by a weighted (1/x2 ) linear or quadratic regression of peak area ratios (peak area of analyte/peak area of IS) versus the theoretical concentrations of the plasma calibration standards. Pharmacokinetic Analysis: Individual plasma concentration-time data of mice were analyzed by non-compartmental methods using the Linear/Log trapezoidal method (IV) or the Linear-up/Log-down trapezoidal method (PO) (Phoenix WinNonlin 6.1, Certara, Princeton, NJ). After IV dosing, clearance (CL), steady-state volume of distribution (Vss), terminal elimination half-life (t½), area under the curve from time zero to infinity (AUCINF), mean resonance time from time zero to infinity (MRTINF), and terminal phase volume of distribution (Vz) were calculated. After PO dosing, maximum observed concentration (Cmax), time of Cmax (tmax), terminal elimination half-life (t½), area under the curve from time zero to infinity (AUCINF), mean resonance time from time zero to infinity (MRTINF), apparent total clearance (CL/F), bioavailability (%F), and estimated fraction absorbed (Fa) were calculated. [3] In vivo efficacy analysis in mice Animals were quarantined for 7 days before the study. The treatments were started for the efficacy study when the mean tumor volume reached about 119 mm3 . Based on the tumor volume, mice were randomly assigned to respective groups such that the mean starting tumor volume was the same between groups. EZM0414 dissolved in methyl cellulose/Tween-80 in water (0.5% CMC/0.1% Tween-80 (Sigma-Aldrich)), or vehicle alone was administered p.o. to NOD SCID mice (n = 10 per dose group). [3] All study animals were monitored not only for tumor growth but also behavior such as mobility, food and water consumption, body weight, eye/hair matting, and any other abnormal effects. The measurement of tumor volume was conducted twice a week throughout the efficacy study with a caliper and the tumor volume (mm3 ) was estimated using the formula, Tumor Volume = a x b2 /2, where “a” and “b” are the long and short diameters of a tumor. The tumor volumes were used for calculating the tumor growth inhibition (TGI, an indicator of antitumor effectiveness) value using the formula: TGI = (1-T/C) × 100%, where “T” and “C” is the mean relative volumes (tumor growth) of the tumors in the treated (T) and the control (C) groups, respectively, on a given day after tumor inoculation. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
While both EZM0414 and analogue 7 showed favorable PK profiles following 50 mg/kg po administration in mice, EZM0414 had ∼2-fold higher exposure (AUC) with better oral bioavailability (F) than 7, a trend that was observed in rats as well. Table 3 presents a comparison of the PK parameters for EZM0414, 7, and the starting parent compound 3. Improving the lipophilic efficiency of the earlier series vastly enhanced the overall PK profile, with a 17-fold increase in overall exposure levels (AUC0–∞) achieved in CD-1 mice at 50 mg/kg following oral administration with EZM0414. With regard to the potential for drug–drug interactions as perpetrator of CYP enzymes, EZM0414 exhibited only weak inhibition of CYP isoform 2C8 (4.8 μM), and no inhibition of other tested isoforms was seen (IC50 > 30 μM for isoforms 1A2, 2B6, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, and 3A4). Analogue 7 showed modest inhibition of isoforms 2B6 (3.2 μM) and 2D6 (10.8 μM), with IC50 > 25 μM for the remaining isoforms tested. Additional characterization of EZM0414 indicated a favorable safety pharmacology profile. In vitro testing of EZM0414 in a safety panel consisting of 47 targets and a diversity panel of 72 kinases showed IC50 > 25 μM for all targets except D2 (IC50 = 13.0 μM, antagonist) and 5-HT1B (IC50 = 3.2 μM, agonist).[3]
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
SETD2 Inhibitor EZM0414 is an orally bioavailable selective inhibitor of the histone methyltransferase (HMT) SETD2 (SET domain containing 2, histone lysine methyltransferase), with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon oral administration, SETD2 inhibitor EZM0414 binds to SETD2 and inhibits its activity. This prevents several key biological processes that are mediated by SETD2, including the methylation of histones and non-histone proteins, transcriptional regulation, RNA splicing, DNA damage repair and B cell development and maturation. The inhibition of SETD2 by EZM0414 may inhibit tumor cell proliferation. SETD2 plays multiple important roles in oncogenesis.
Introduction: SETD2 is the only known histone methyltransferase (HMT) capable of catalyzing H3K36 trimethylation (H3K36me3) in vivo. It plays an important role in several biological processes including B cell development and maturation, leading to the hypothesis that SETD2 inhibition in these settings could provide anti-tumor effects. The normal process of B cell development/maturation renders B cells susceptible to genetic vulnerabilities that can result in a dysregulated epigenome and tumorigenesis, including in multiple myeloma (MM) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). For example, 15%-20% of MM harbors the high risk (4;14) chromosomal translocation, resulting in high expression of the multiple myeloma SET domain (MMSET) gene. MMSET is an HMT that catalyzes H3K36me1 and H3K36me2 formation and extensive scientific work has established overexpressed MMSET as a key factor in t(4;14) myeloma pathogenesis. To the best of our knowledge MMSET has eluded drug discovery efforts, however, since t(4;14) results in high levels of the H3K36me2 substrate for SETD2, inhibiting SETD2 offers promise for targeting the underlying oncogenic mechanism driven by MMSET overexpression in t(4;14) MM patients. In addition, SETD2 loss of function mutations described to date in leukemia and DLBCL are always heterozygous, suggesting a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor role for SETD2. This observation points to a key role for SETD2 in leukemia and lymphoma biology and suggests that therapeutic potential of SETD2 inhibition may also exist in these or similar settings. EZM0414 is a first-in-class, potent, selective, orally bioavailable small molecule inhibitor of the enzymatic activity of SETD2. We explored the anti-tumor effects of SETD2 inhibition with EZM0414 in MM and DLBCL preclinical studies to validate its potential as a therapy in these tumor types.[2] Targeting SETD2 with a small molecule inhibitor results in significantly reduced growth of t(4;14) MM, as well as non-t(4;14) MM and DLBCL cell lines, in both in vitro and in vivo preclinical studies. In addition, in vitro synergy was observed with EZM0414 and certain SOC agents commonly used in MM and DLBCL, supporting the combination of SETD2 inhibition with current MM and DLBCL therapies. This work provides the rationale for targeting SETD2 in B cell malignancies such as MM, especially t(4;14) MM, as well as DLBCL, and forms the basis for conducting Phase 1/1b clinical studies to evaluate the safety and activity of EZM0414 in patients with R/R MM and DLBCL.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C22H29FN4O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
400.49
|
| 精确质量 |
428.26
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 67.26; H, 7.76; F, 4.43; N, 13.07; O, 7.47
|
| CAS号 |
2411748-50-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
EZM0414 TFA;2411759-92-5
|
| PubChem CID |
146395245
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to light yellow solid powder
|
| LogP |
2.8
|
| tPSA |
68.4 Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
610
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
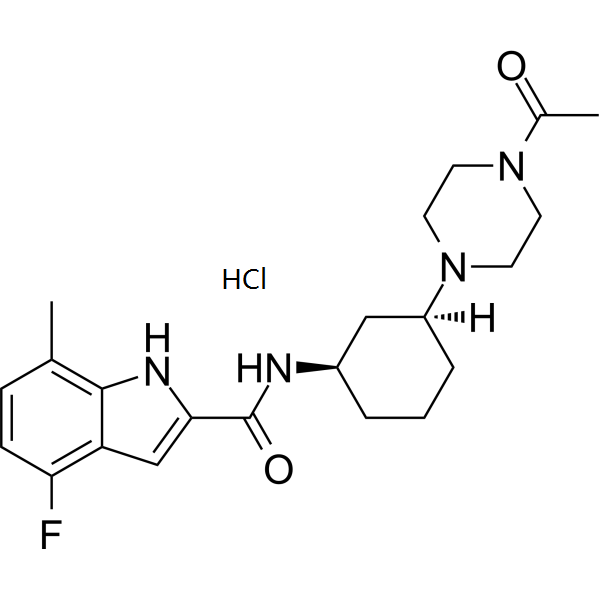
C1C=C(C2NC(=CC=2C=1F)C(N[C@@H]1CCC[C@H](N2CCN(CC2)C(=O)C)C1)=O)C
|
| InChi Key |
PGNLXEBQMQHFNK-SJORKVTESA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H29FN4O2/c1-14-6-7-19(23)18-13-20(25-21(14)18)22(29)24-16-4-3-5-17(12-16)27-10-8-26(9-11-27)15(2)28/h6-7,13,16-17,25H,3-5,8-12H2,1-2H3,(H,24,29)/t16-,17+/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
N-[(1R,3S)-3-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)cyclohexyl]-4-fluoro-7-methyl-1H-indole-2-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
EZM0414 HCl; EZM-0414 HCl 2411748-50-8; KCY37T9RXU; EZM-0414; UNII-KCY37T9RXU; N-[(1R,3S)-3-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)cyclohexyl]-4-fluoro-7-methyl-1H-indole-2-carboxamide; N-((1R,3S)-3-(4-Acetylpiperazin-1-yl)cyclohexyl)-4-fluoro-7-methyl-1H-indole-2-carboxamide; 1H-Indole-2-carboxamide, N-((1R,3S)-3-(4-acetyl-1-piperazinyl)cyclohexyl)-4-fluoro-7-methyl-;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4969 mL | 12.4847 mL | 24.9694 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4994 mL | 2.4969 mL | 4.9939 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2497 mL | 1.2485 mL | 2.4969 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。