| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Natural alkaloid
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
经鉴定,Harmaline及其衍生物可作为抗耐多药药物,用于治疗多种高耐药和巴基斯坦耐多药大肠杆菌临床分离株。这些化合物可能为进一步研究耐多药大肠杆菌感染的治疗方法提供线索。[1]
在Control (Salin)组和Experiment (Harmaline)组进行实验,生成用于开发预测模型的数据集。由于数据集的样本数量有限,我们使用了对小数据集有效的模型。在不同的回归模型组(线性模型、集成模型和树模型)中,集成模型,特别是LGB方法,可以获得更好的性能。结果表明,在10倍交叉验证中,第一峰潜伏期的平均平方误差为0.0002,平均绝对误差为0.01。该研究表明,机器学习在预测第一次峰值延迟方面具有潜力,无需大量的动物试验就可以进行可靠的估计。这种智能预测系统有助于有效地分析健康和不健康脑细胞的第一峰潜伏期变化,简化实验并提供对捕获信号的更详细的见解。[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
抑郁症是一种以持续情绪低落、快感缺乏和认知障碍为特征的精神障碍,影响着世界人口的3.8%,其中包括5%的成年人。槟榔是一种药用植物,据报道对阿尔茨海默病、帕金森病和抑郁症有有效的治疗作用。本研究旨在评价哈玛拉籽提取物对慢性不可预测轻度应激(CUMS)大鼠的行为学和药理作用,并探讨其作用机制。对cms暴露的大鼠分别给予75和150 mg/kg, ig, 2周。采用高效液相色谱法测定提取液中Harmaline和Harmaline生物碱的浓度。采用ICP-MS对种子进行重金属分析。结果表明,150 mg/kg剂量的苦参草显著降低了cums暴露大鼠的抑郁样行为,表现为增加蔗糖偏好测试(SPT)中的蔗糖消耗量,减少强迫游泳测试(FST)中的静止时间和血浆皮质酮水平,增加升高+迷宫(EPM)中张开双臂的时间,改善被动回避测试(PAT)中的记忆和学习。此外,P. harmala降低了暴露于CUMS的大鼠大脑中的单胺氧化酶a (MAO-A)水平,并增加了5-羟色胺(5-HT)、多巴胺(DA)和去甲肾上腺素(NA)水平。麻瓜可降低大鼠脑促炎转录因子核因子-κB (NF-κB)的表达,提高抗氧化核因子红细胞2相关因子2 (Nrf2)的表达。此外,苦参还能改善大鼠脑内脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)和原肌球蛋白受体激酶B (TrkB)蛋白的表达。综上所述,150 mg/kg剂量的苦参可通过改善神经递质水平、减少氧化应激、抑制神经炎症和激活BDNF/TrkB通路,更有效地预防cums暴露大鼠的抑郁样行为,这些都是抑郁症发病机制中的重要因素。[2]
|
| 酶活实验 |
精神药物β -碳碱生物碱对5-羟色胺、多巴胺、苯二氮卓和咪唑啉受体具有高亲和力,并能刺激蓝斑神经元,在植物和哺乳动物中都是由色氨酸衍生的吲哚烷基胺通过与醛的Pictet-Spengler缩合内源性形成的。细胞色素P450 1A1(18.5)、1A2(20)和2D6(100)催化了harmaline的o -去甲基化,CYP1A1(98.5)、CYP1A2(35)、CYP2C9(16)、CYP2C19(30)和CYP2D6(115)催化了harmaline的o -去甲基化(相对活性)。芳构化酶(CYP19)、CYP1A2、CYP2C9、CYP2D6、CYP3A4、合并重组细胞色素P450或人肝微粒体(HLMs)均未实现harmaline脱氢/芳构化为harmaline。计算了各同工酶和混合HLMs介导的o -去甲基化的动力学参数。正碱的K(cat) (min(-1))和Ku (uM)值分别为:CYP1A1、10.8和11.8;CYP1A2, 12.3和13.3;CYP2C9, 5.3和175;CYP2C19、10.3、160;CYP2D6分别为39.9和1.4。其值分别为:CYP1A1、45.2和52.2;CYP1A2分别为9.2和14.7;CYP2C9、11.9和117;CYP2C19、21.4和121;CYP2D6分别为29.7和7.4。利用单克隆抗体进行的抑制研究证实,CYP1A2和CYP2D6是导致混合HLMs中harmaline(分别为20%和50%)和harmaline(分别为20%和30%)o -去甲基化的主要同工酶。CYP2D6的周转率是CYP2D6底物中最高的。最后,与野生型小鼠相比,cyp2d6转基因小鼠的鼠碱和鼠碱o -去甲基化酶活性增加。这些发现提示多态性CYP2D6在Harmine和harmaline的药理学和毒理学中起作用。 PMID:12649384 ; Yu AM et al; J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305 (1): 315-22 (2003)
|
| 细胞实验 |
背景:本研究旨在阐明苦参生物碱提取物、苦参碱(HAR)和苦参碱(HAL)对HCT-116结直肠癌细胞的潜在抗癌作用及其机制。方法与结果:从苦参种子中提取苦参生物碱。用苦参生物碱提取物、HAR和HAL处理HCT-116细胞。MTT法检测细胞毒性,流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡活性,吖啶橙(AO)/溴化乙啶(EB)双染色,流式细胞术分析细胞周期分布。实时荧光定量PCR检测bcl -2相关X蛋白(Bax)和糖原合成酶激酶-3 β (GSK3β) mRNA表达量。western blotting检测Bax、Bcl-2、GSK3β和p53蛋白的表达。结果表明,在作用24 h和48 h后,苦参生物碱提取物、HAR和HAL对HCT116细胞具有显著的细胞毒性。结果表明,苦参生物碱提取物可诱导HCT116细胞株G2期细胞凋亡和细胞周期阻滞。GSK3β、Bcl-2表达下调,Bax、p53表达上调。结论:本研究结果表明,苦参生物碱提取物具有一定的抗癌活性,可进一步开发抗癌化疗药物。
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Harmaline, a known type A monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor in adult brain of various species was found to elevate whole brain levels of dopamine and serotonin (5-HT) in rat fetuses of mothers injected 2-4 hr before Caesarean delivery. Similar stimulatory effects were observed for the norepinephrine metabolite 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy-phenylglycol (MHPG), however, no significant effect was obtained for norepinephrine. The dopamine metabolite, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) and the 5-HT metabolite 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid (5-HIAA) were decreased with the same treatment. These results imply that harmaline or one of its metabolites may cross the placental barrier to affect the fetal brain system not merely as a type A MAO inhibitor (i.e., relatively 5-HT-specific), but possibly also as a stimulatory agent for aldehyde reductase or catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) or alternately as an agent inhibiting the conjugation, efflux, or turnover of biogenic amine metabolites such as MHPG. Metabolism / Metabolites The psychotropic beta-carboline alkaloids, showing high affinity for 5-hydroxytryptamine, dopamine, benzodiazepine, and imidazoline receptors and the stimulation of locus coeruleus neurons, are formed endogenously from tryptophan-derived indolealkylamines through the Pictet-Spengler condensation with aldehydes in both plants and mammals. Cytochromes P450 1A1 (18.5), 1A2 (20), and 2D6 (100) catalyzed the O-demethylation of harmaline, and CYP1A1 (98.5), CYP1A2 (35), CYP2C9 (16), CYP2C19 (30), and CYP2D6 (115) catalyzed that of harmine (relative activities). The dehydrogenation/aromatization of harmaline to harmine was not carried out by aromatase (CYP19), CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, pooled recombinant cytochromes P450, or human liver microsomes (HLMs). Kinetic parameters were calculated for the O-demethylations mediated by each isozyme and by pooled HLMs. K(cat) (min(-1)) and Ku (uM) values for harmaline were: CYP1A1, 10.8 and 11.8; CYP1A2, 12.3 and 13.3; CYP2C9, 5.3 and 175; CYP2C19, 10.3 and 160; and CYP2D6, 39.9 and 1.4. Values for harmine were: CYP1A1, 45.2 and 52.2; CYP1A2, 9.2 and 14.7; CYP2C9, 11.9 and 117; CYP2C19, 21.4 and 121; and CYP2D6, 29.7 and 7.4. Inhibition studies using monoclonal antibodies confirmed that CYP1A2 and CYP2D6 were the major isozymes contributing to both harmaline (20% and 50%, respectively) and harmine (20% and 30%) O-demethylations in pooled HLMs. The turnover numbers for CYP2D6 are among the highest ever reported for a CYP2D6 substrate. Finally, CYP2D6-transgenic mice were found to have increased harmaline and harmine O-demethylase activities as compared with wild-type mice. These findings suggest a role for polymorphic CYP2D6 in the pharmacology and toxicology of harmine and harmaline. Harmaline has known human metabolites that include Harmalol. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Harmaline and its Derivatives Against the Infectious Multi-Drug Resistant Escherichia coli. Med Chem. 2017;13(5):465-476.
[2]. Peganum harmala L. seed extract attenuates anxiety and depression in rats by reducing neuroinflammation and restoring the BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway and monoamines after exposure to chronic unpredictable mild stress. Metab Brain Dis . 2024 Aug 22. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01416-6. [3]. Comparison of Regression Methods to Predict the First Spike Latency in Response to an External Stimulus in Intracellular Recordings for Cerebellar Cells. Stud Health Technol Inform . 2024 Aug 22:316:796-800. [4]. Cytotoxicity of alkaloids isolated from Peganum harmala seeds on HCT116 human colon cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Jun 13;51(1):732. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09655-7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38872006/ |
| 其他信息 |
Harmaline is a harmala alkaloid in which the harman skeleton is methoxy-substituted at C-7 and has been reduced across the 3,4 bond. It has a role as a oneirogen. It derives from a hydride of a harman.
Harmaline has been reported in Passiflora phoenicia, Daphnia pulex, and other organisms with data available. A beta-carboline alkaloid isolated from seeds of PEGANUM. Mechanism of Action Three psychological active principles from the seeds of Peganum harmala L., harmine, harmaline and harmalol, showed vasorelaxant activities in isolated rat thoracic aorta preparations precontracted by phenylephrine or KCl with rank order of relaxation potency of harmine > harmaline > harmalol. The vasorelaxant effects of harmine and harmaline (but not harmalol) were attenuated by endothelium removal or pretreatment with a nitric oxide (NO) synthase Nomega-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester. In cultured rat aortic endothelial cells, harmine and harmaline (but not harmalol) increased NO release, which was dependent on the presence of external Ca2+. In endothelium-denuded preparations, pretreatment of harmine, harmaline or harmalol (3-30 microM) inhibited phenylephrine-induced contractions in a non-competitive manner. Receptor binding assays indicated that all 3 compounds interacted with cardiac alpha1-adrenoceptors with comparable affinities (Ki value around 31 - 36 microM), but only harmine weakly interacted with the cardiac 1,4-dihydropyridine binding site of L-type Ca2+ channels (Ki value of 408 microM). Therefore, the present results suggested that the vasorelaxant effects of harmine and harmaline are attributed to their actions on the endothelial cells to release NO and on the vascular smooth muscles to inhibit the contractions induced by the activation of receptor-linked and voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. The vasorelaxant effect of harmalol was not endothelium-dependent. Therapeutic Uses /EXPL THER/ Oxidative modification of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles has been implicated in the process of atherogenesis. Antioxidants that prevent LDL from oxidation may reduce atherosclerosis. We have investigated the protective effect of Peganum harmala-extract (P-extract) and the two major alkaloids (harmine and harmaline) from the seeds of P. harmala against CuSO4-induced LDL oxidation. Through determination of the formation of malondialdehyde (MDA) and conjugated diene as well as the lag phase, the extract (P-extract) and compounds were found to possess an inhibitory effect. Moreover, harmaline and harmine reduced the rate of vitamin E disappearance and exhibited a significant free radical scavenging capacity (DPPH*). However, harmaline had a markedly higher antioxidant capacity than harmine in scavenging or preventive capacity against free radicals as well as inhibiting the aggregation of the LDL protein moiety (apolipoprotein B) induced by oxidation. The results suggested that P. harmala compounds could be a major source of compounds that inhibit LDL oxidative modification induced by copper. |
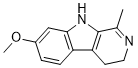
| 分子式 |
C13H14N2O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
214.26
|
| 精确质量 |
214.11
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 72.87; H, 6.59; N, 13.07; O, 7.47
|
| CAS号 |
304-21-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
304-21-2
|
| PubChem CID |
3564
|
| 外观&性状 |
Orthorhombic bipyramidal prisms, tablets from methanol, rhombic octahedra from ethanol
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
426.4±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
232-234 °C(lit.)
|
| 闪点 |
211.7±28.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.647
|
| LogP |
0.66
|
| tPSA |
37.38
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
16
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
302
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CC1=NCCC2=C1NC3=C2C=CC(=C3)OC
|
| InChi Key |
RERZNCLIYCABFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C13H14N2O/c1-8-13-11(5-6-14-8)10-4-3-9(16-2)7-12(10)15-13/h3-4,7,15H,5-6H2,1-2H3
|
| 化学名 |
7-methoxy-1-methyl-4,9-dihydro-3H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole
|
| 别名 |
Harmaline; 304-21-2; Dihydroharmine; Harmidine; Armalin; 3,4-Dihydroharmine; Harmalol methyl ether; O-Methylharmalol;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.6672 mL | 23.3361 mL | 46.6723 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.9334 mL | 4.6672 mL | 9.3345 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4667 mL | 2.3336 mL | 4.6672 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。