| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg | |||
| 500mg | |||
| 1g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Metabolism / Metabolites
Two main routes of metabolism responsible for the degradation of imidacloprid were identified. The first is oxidative cleavage, yielding 6-chloronicotinic acid, which is conjugated with glycine to form a hippuric acid-type conjugate. These two metabolites together represented most of the identified metabolites, or about 30% of the recovered radiolabel. Of minor importance in terms of quantity is dechlorination of the pyridinyl moiety, producing the 6-hydroxy nicotinic acid and its methylmercapturic acid derivative, probably as a degradation product of a glutathione conjugate. The 6-methylmercapto nicotinic acid conjugated with glycine, and the glycine conjugate constituted 5.6% of the recovered radiolabel. The second important biodegradation step starts with hydroxylation of the imidazolidine ring at the 4 or 5 position, and about 16% of the recovered radiolabel was identified as the sum of 4- and 5-hydroxy imidacloprid. The loss of water yields the olefinic compound. These biotransformation products and the unchanged parent compound were excreted in urine and feces, while the guanidine compound was a less important metabolite and was eliminated only in feces (A623). |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Imidacloprid acts on the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; the chlorination inhibits degradation by acetylcholine-esterase (L1130). Toxicity Data LD50: 450 mg/kg (Oral, Rat) (L1130) LD50: 131 mg/kg (Oral, Mouse) (L1130) LD50: >5000 mg/kg (Dermal, Rat) (L1130) LD50: 69 mg/m3 (Inhalation (aerosol), Rat) (L1130) LD50: 5 323 mg/m3 (Inhalation (dust), Rat) (L1130) |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
2-Imidazolidinimine, 1-[(6-chloro-3-pyridinyl)methyl]-N-nitro- has been reported in Streptomyces canus and Ganoderma lucidum with data available.
Imidacloprid is a neonicotinoid insecticide, which is a class of neuro-active insecticides modeled after nicotine. Nicotine was identified and used as an insecticide and rat poison as early as the 1600’s. Its effectiveness as an insecticide spurred a search for insecticidal compounds that have selectively less effect on mammals, which led to the discovery of neonicotinoids. Neonicotinoids, like nicotine, bind to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors of a cell. In mammals, nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are located in cells of both the central and peripheral nervous systems. In insects these receptors are limited to the CNS. While low to moderate activation of these receptors causes nervous stimulation, high levels overstimulate and block the receptors causing paralysis and death. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is broken down by acetylcholinesterase to terminate signals from these receptors. However, acetylcholinesterase cannot break down neonicotinoids and the binding is irreversible. Because most neonicotinoids bind much more strongly to insect neuron receptors than to mammal neuron receptors, these insecticides are selectively more toxic to insects than mammals. The low mammalian toxicity of neonicotinoids can be explained in large part by their lack of a charged nitrogen atom at physiological pH. The uncharged molecule can penetrate the insect blood–brain barrier, while the mammalian blood–brain barrier filters it. However, Some neonicotinoid breakdown products are toxic to humans, especially if they have become charged. Because of their low toxicity and other favorable features, neonicotinoids are among the most widely used insecticides in the world. Most neonicotinoids are water-soluble and break down slowly in the environment, so they can be taken up by the plant and provide protection from insects as the plant grows. Neonicotinoids are currently used on corn, canola, cotton, sorghum, sugar beets and soybeans. They are also used on the vast majority of fruit and vegetable crops, including apples, cherries, peaches, oranges, berries, leafy greens, tomatoes, and potatoes. The use of neonicotinoids has been linked in a range of studies to adverse ecological effects, including honey-bee colony collapse disorder (CCD) and loss of birds due to a reduction in insect populations. This has led to moratoriums and bans on their use in Europe. See also: Imidacloprid (preferred); Imidacloprid; Moxidectin (component of); Imidacloprid; Ivermectin (component of). |
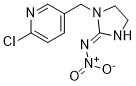
| 分子式 |
C9H10CLN5O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
255.66
|
| 精确质量 |
255.052
|
| CAS号 |
105827-78-9
|
| PubChem CID |
86418
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.6±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
442.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
136-144ºC
|
| 闪点 |
221.3±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.706
|
| LogP |
-0.43
|
| tPSA |
86.34
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
17
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
319
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
YWTYJOPNNQFBPC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C9H10ClN5O2/c10-8-2-1-7(5-12-8)6-14-4-3-11-9(14)13-15(16)17/h1-2,5H,3-4,6H2,(H,11,13)
|
| 化学名 |
N-[1-[(6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl]-4,5-dihydroimidazol-2-yl]nitramide
|
| 别名 |
Confidor Admire Imidacloprid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.9114 mL | 19.5572 mL | 39.1144 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7823 mL | 3.9114 mL | 7.8229 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3911 mL | 1.9557 mL | 3.9114 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。