| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
P2Y11 (pKi = 7.35); P2Y11 (IC50 = 463 nM); P2Y11 (Ki = 44.3 nM); P2Y1 (Ki = 187 µM); P2Y2 (Ki = 28.9 µM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
NF157 的选择性不如 P2X1,但对 P2Y11 的选择性比 P2Y1(>650 倍)、P2Y2(>650 倍)、P2X2(3 倍)、P2X3(8 倍)、P2X4(>22)更高-倍)和 P2X7(>67 倍)[1]。 NF157(30 和 60 µM;24 小时)以剂量依赖性方式显着减少 II 型胶原蛋白的分解。当应用 60 µM NF157 时,II 型胶原蛋白几乎完全从 TNF-α (10 ng/mL) 诱导的降解中恢复 [2]。 NF157(30 和 60 µM;24 小时)显着降低 NF-κB 荧光素酶活性,同时几乎完全恢复 TNF-α (10 ng/mL) 触发的 p65 核易位 [2]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
重组P2X受体8f/NF157的电生理评估。[1]
使用先前描述的方案,在重组表达各种大鼠(r)和人(h)P2X亚型(rP2X1、hP2X1、rPX2、rP2X3、hP2X3、rP2X4、hP2X4、rP2X7)的X.laevis卵母细胞上评估了NF157对P2X受体的抑制效力。浓度-抑制曲线和IC50值来自Hill方程对合并数据的非线性最小二乘拟合。rP2X2受体的非致敏特性允许在ATP持续刺激期间通过联合施加NF157来量化稳态条件下的内向电流抑制。从共同施加有效浓度的NF157后电流振幅立即减小推断,电流抑制几乎是瞬间发生的。经典的Cheng-Prusoff方程可用于计算rP2X2受体的NF157的Ki值。通过峰值电流测量确定NF157对P2X受体脱敏的抑制效力。如前所述,通过同时应用激动剂和拮抗剂通常无法准确评估脱敏受体的IC50值,因为在两种化合物达到结合平衡之前,激动剂诱导的电流会因脱敏而开始下降。为了解决这个问题,表达脱敏P2X受体的卵母细胞在持续存在NF157的情况下用ATP攻击之前,用NF157预平衡15秒。我们之前已经证明,苏拉明衍生物竞争性阻断P2X受体。因此,如果NF157在达到峰值电流反应所需的时间内没有与受体显著分离,ATP只能与NF157未占据的受体结合,导致伪不可逆型抑制。在这些条件下,Ki和IC50值将相等。因此,我们假设从峰值电流测量中推断出的IC50值接近或等于Ki值。在任何情况下,Ki值与IC50值的最大偏差为2倍,因为ATP的浓度接近其EC50值。所有结果均以平均值±SEM的形式呈现,来自至少三个实验。 |
| 细胞实验 |
蛋白质印迹分析[2]
细胞类型: SW1353 细胞 测试浓度: 30 和 60 µM 孵育时间: 24 小时 实验结果:减少 TNF-α 诱导的 NF-κB 激活。 NF-κB启动子萤光素酶测定[2] 通过测量NF-κB启动子萤光素酶活性来评估NF-κB的转录活性。将NF-κB启动子荧光素酶和β-半乳糖苷酶质粒用Lipofectamine 2000转染入SW1353细胞。在存在或不存在浓度为30和60μM的NF157的情况下,用10ng/ml TNF-α处理人软骨细胞SW1353细胞24小时。制备细胞裂解物,并使用光度计上的Secrete PairTM双发光测定试剂盒测定萤光素酶活性和β-半乳糖苷酶活性。萤光素酶活性被标准化为β-半乳糖苷酶活性。 |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Selective and potent P2Y(11) receptor antagonists have yet to be developed, thus impeding an evaluation of this G protein-coupled receptor mainly expressed on immune cells. Taking suramin with moderate inhibitory potency as a template, 18 ureas with variations of the methyl groups of suramin and their precursors were functionally tested at P2Y(11), P2Y(1), and P2Y(2) receptors. Fluorine substitution of the methyl groups of suramin led to the first nanomolar P2Y(11) antagonist (8f, NF157, pK(i): 7.35). For selectivity, 8f was also tested at various P2X receptors. 8f displayed selectivity for P2Y(11) over P2Y(1) (>650-fold), P2Y(2) (>650-fold), P2X(2) (3-fold), P2X(3) (8-fold), P2X(4) (>22-fold), and P2X(7) (>67-fold) but no selectivity over P2X(1). QSAR studies confirm that residues with favored resonance and size parameters in the aromatic linker region can indeed lead to an increased potency as is the case for 8f. A symmetric structure linking two anionic clusters seems to be required for bioactivity. 8f may be helpful for studies evaluating the physiological role of P2Y(11) receptors. [1]
This study presents the synthesis and structure−activity relationships of a series of suramin analogues and led to the discovery of the first nanomolar potency P2Y11 receptor antagonist 8f with at least 650-fold selectivity for P2Y11 over P2Y1 and P2Y2, and a 3- to >67-fold selectivity over P2X2,3,4,7 receptors. 8f is, however, approximately equipotent at P2Y11 and P2X1 receptors. A symmetric structure linking two anionic clusters seems to be required for bioactivity. QSAR studies reveal that a substitution with favored values for resonance (R), size (B5), and partial charges of the amide group oxygen in ortho-position of the residue R (Q(Oortho)) in the aromatic linker region can indeed lead to an increased potency as is the case for the fluorine derivative 8f. The QSAR results may guide the directed synthesis and development of further potent and selective (also against P2X1) P2Y11 ligands. Thus, this study and the novel ligand 8f may be helpful to obtain a deeper insight into the physiological and pathophysiological role of P2Y11 receptors. [1] Osteoarthritis is a major global health burden. Joint destruction resulting from excessive degradation of type II collagen and aggrecan in the articular extracellular matrix by metalloproteinases and aggrecanases, respectively, is a major pathological hallmark of osteoarthritis. However, the exact mechanisms remain poorly understood. Currently, there are few non-invasive therapies capable of slowing or halting the progression of the disease. In the present study, we investigated the involvement of the P2Y11 purinergic protein and its receptor P2Y11R in TNF-α-mediated degradation of the extracellular matrix in SW1353 cell line chondrocytes using the novel P2Y11R antagonist NF157. To our knowledge, this is the first study to explore the effects of NF157 in OA. Our results indicate that P2Y11R may indeed play a role in TNF-α-induced degradation of extracellular matrix in OA as treatment with NF157 significantly reduced expression of metalloproteinase (MMP)-3, MMP-13, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs (ADAMTS)-4 and ADAMTS-5, and ameliorated degradation of type II collagen and aggrecan in SW1353 chondrocytes in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, we show that treatment with NF157 significantly reduced nuclear translocation of p65 and subsequent activation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB). [2] NF-κB is well-recognized as a key pro-inflammatory transcription factor that promotes the development and progression of OA as well as many other inflammatory diseases. A recent study from Japan demonstrated that activation of the P2Y11 receptor via γ-radiation-induced release of ATP activated NF-κB through the p38/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. In a related study, the authors showed that treatment with NF157 inhibited activation of NF-κB Another study demonstrated that ATP selectively targeted p65 to activate NF-κB through the P2Z purinoceptor, which like P2Y11R, has a high affinity for ATP. In the present study, we showed that TNF-α-induced nuclear translocation of p65 could be suppressed by blockage of P2Y11R with 30 and 60 µM NF157 in a dose-dependent manner. Additionally, we confirmed that antagonism of P2Y11R with NF157 significantly decreased NF-κB luciferase activity in a dose-dependent manner. The findings of our study demonstrate for the first time that blockage of the P2Y11 purinoceptor using the selective P2Y11 antagonist NF157 can significantly prevent degradation of the components of the articular ECM by downregulating TNF-α-induced expression of MMP-3, MMP-13, ADAMTS-4, and ADAMTS-5, subsequent degradation of type II collagen and aggrecan, and activation of NF-κB. These positive results suggest that NF157 may have potential as a targeted therapeutic agent for the treatment and prevention of excessive degradation of type II collagen and aggrecan in OA. Further study is required to better understand the complex mechanisms through which these results were achieved. [2] |
| 分子式 |
C49H34F2N6O23S6
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
1305.19
|
| 精确质量 |
1435.89
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 45.09; H, 2.63; F, 2.91; N, 6.44; O, 28.19; S, 14.74
|
| CAS号 |
104869-26-3
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to pink solid powder
|
| LogP |
11.271
|
| tPSA |
551.01
|
| InChi Key |
UDVIAMRWOLIUAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C49H34F2N6O23S6/c50-33-9-7-25(47(60)54-35-11-13-39(83(69,70)71)31-19-29(81(63,64)65)21-41(43(31)35)85(75,76)77)17-37(33)56-45(58)23-3-1-5-27(15-23)52-49(62)53-28-6-2-4-24(16-28)46(59)57-38-18-26(8-10-34(38)51)48(61)55-36-12-14-40(84(72,73)74)32-20-30(82(66,67)68)22-42(44(32)36)86(78,79)80/h1-22H,(H,54,60)(H,55,61)(H,56,58)(H,57,59)(H2,52,53,62)(H,63,64,65)(H,66,67,68)(H,69,70,71)(H,72,73,74)(H,75,76,77)(H,78,79,80)
|
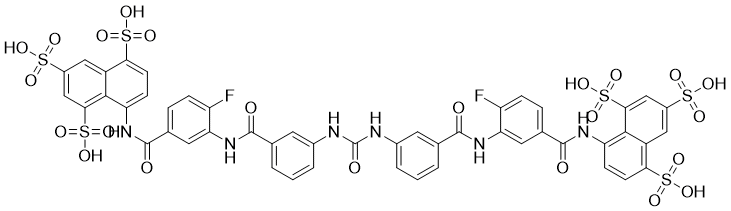
| 化学名 |
8-[[4-fluoro-3-[[3-[[3-[[2-fluoro-5-[(4,6,8-trisulfonaphthalen-1-yl)carbamoyl]phenyl]carbamoyl]phenyl]carbamoylamino]benzoyl]amino]benzoyl]amino]naphthalene-1,3,5-trisulfonic acid
|
| 别名 |
NF-157; NF 157; NF157
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ~1 mg/mL (~0.70 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.7662 mL | 3.8309 mL | 7.6617 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.1532 mL | 0.7662 mL | 1.5323 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0766 mL | 0.3831 mL | 0.7662 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。