| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
(14)C-DMT accumulates in rat brain cortical slices incubated at 37 °C. ... Most of the accumulated (14)C-DMT was associated with the cytoplasmic fraction. Of the portion associated with the crude mitochondrial fraction, 54.4% was associated with nerve-ending fraction. The hallucinogenic substance N',N'-dimethyltryptamine and its precursor N-methyltryptamine were found in 24-hr specimens of urine from 19 normal human subjects; the mean excretion rates were 386 ng 24 hr(-1) and 856 ng 24 hr(-1) respectively. The urinary excretion of both compounds was unrelated to age, sex, urinary volume, or creatinine, nor was any consistent diurnal pattern observed. Rates for the mono and dimethylated compounds were not correlated. Diet and the intestinal flora were excluded as a source of urinary dimethyltryptamine. Administration to 4 subjects of sufficient ammonium chloride to /decrease/ the /pH/ of the urine caused a transient increase in dimethyltryptamine excretion but no consistent increase in the rate for N-methyltryptamine. Acidification of the urine did not appear to be the determining factor in this result since in one subject the same drop in urinary pH was achieved by feeding methionine without any increase in dimethyltryptamine excretion. ... Eighteen volunteers with prior experience in the use of psychedelics received single oral doses of encapsulated freeze-dried ayahuasca (0.6 and 0.85 mg of DMT/kg of body weight) and placebo. Ayahuasca produced significant subjective effects, peaking between 1.5 and 2 hr, involving perceptual modifications and increases in ratings of positive mood and activation. ...Cmax values for DMT after the low and high ayahuasca doses were 12.14 ng/mL and 17.44 ng/mL, respectively. Tmax (median) was observed at 1.5 hr after both doses. The Tmax for DMT coincided with the peak of subjective effects. ... The endogenous hallucinogen, N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT), was labeled with (11)C and its regional distribution in rat brain studied. (11)C-DMT showed higher accumulation in the cerebral cortex, caudate putamen, and amygdaloid nuclei. Studies of the subcellular distribution of (11)C-DMT revealed the specific localization in the fractions enriched with serotonin receptors only when a very low dose was injected into rats. ... For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Following intraperitoneal administration, 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine and N,N-dimethyltryptamine are subject to both a very rapid uptake into, and clearance from, all tissues examined. The current studies in vivo confirm previous in vitro observations that the routes involved in the metabolism of these compounds include oxidative deamination, N-demethylation, O-demethylation, and N-oxidation. The analysis of metabolic profiles in various tissues led to the identification of the N-oxides as major metabolites... ... /From/ ... urine samples collected from three individuals that were administered ayahuasca ... /authors/ show that the major metabolite of the hallucinogenic component of ayahuasca, N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT), is the corresponding N-oxide... Further, very little DMT was detected in urine, despite the inhibition of monoamine oxidase afforded by the presence of the harmala alkaloids in ayahuasca. ... Behavioral aspects and metabolic fate of N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) were studied in mice pretreated with beta-diethylaminoethyl-diphenylpropylacetate (SKF 525-A), iproniazid or chlorpromazine (CPZ.). ... Dose-dependent increases with rapid uptake and disappearance in the brain, plasma and hepatic levels of DMT were measured with doses of 10 and 25 mg/kg DMT. ... It is concluded that DMT is metabolized chiefly by monoamine oxidase rather than by drug-metabolizing hepatic microsomal enzymes and that DMT-induced behavioral effects are due to the parent compound rather than its metabolite. Studies were conducted using tritiated DMT and DMT-N-oxide (DMT-NO), and metabolites were identified and quantified using thin-layer chromatography and liquid scintillation counting techniques. Metabolite confirmation was obtained by incubation of alpha,alpha,beta,beta-tetradeutero-DMT (DDMT) with whole brain homogenate followed by combined gas chromatographic/mass spectrometric analyses. The metabolites of DMT were identified as indoleacetic acid (IAA), DMT-NO, N-methyltryptamine (NMT), 2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-beta-carboline (2-MTHBC), tryptamine (TA) and 1,2,3,4- tetrahydro-beta-carboline (THBC). DMT-NO was metabolized to give DMT, NMT, IAA and 2-MTHBC. Formation of these metabolites from DMT-NO was stimulated by anaerobic incubation. ... |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Interactions
... The effects of the monamine oxidase inhibitor iproniazid phosphate on DMT metabolism were also studied. Iproniazid inhibited the formation of IAA from DMT by 83 per cent. However, the formation of NMT and DMT-NO was inhibited by 90 per cent under these conditions. Thus, the reported extension of half-life and potentiation of DMT behavioral effects by iproniazid may be due to inhibition of NMT and DMT-NO formation rather than inhibition of monoamine oxidase. A cyclic pathway for the synthesis and metabolism of DMT in brain tissue is proposed. N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT), harmine, harmaline and tetrahydroharmine (THH) are the characteristic alkaloids found in Amazonian sacraments known as hoasca, ayahuasca, and yaje. Such beverages are characterized by the presence of these three harmala alkaloids, where harmine and harmaline reversibly inhibit monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) while tetrahydroharmine weakly inhibits the uptake of serotonin. Together, both actions increase central and peripheral serotonergic activity while facilitating the psychoactivity of DMT. ... The narcotic antagonist naloxone was tested to determine its possible interaction with N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) ... in adult male Holtzman rats ... increasing doses of DMT (1.0, 3.2, and 10.0 mg/kg) were administered i.p. to disrupt food-rewarded fixed ratio bar pressing in a dose related fashion. Pretreatment (5--10 min) with behaviorally ineffective doses of naloxone (1.0--5.6 mg/kg) dramatically enhanced the effects of DMT ... The content of DMT in the brain and liver of rats injected with DMT alone (10 mg/kg) and with a 5 min pretreatment of naloxone (3.2 mg/kg) was determined by radiochemical analysis at 30 and 90 min after (14)C-DMT injection. There was no significant difference for either brain or liver (14)C-DMT levels when control DMT rats were compared with the naloxone pretreated rats. These results seem to rule out interference by naloxone with the metabolism of DMT as a mechanism of the observed behavioral potentiation. The effects of various neuroleptics were studied on N, N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT, 3.2 mg/kg) ... induced hyperthermia in the rabbit. Complete dose-effect curves were obtained. The order of potency for antagonism of DMT-induced hyperthermia was: methiothepin greater than octoclothepin greater than or equal to oxyprothepin greater than perathiepin greater than dokloxythepin greater than mianserine greater than loxapine greater than oxypertine greater than chlorpromazine greater than pipamperone greater than fluphenazine greater than thiothixene greater than haloperidol greater than molindone...The results indicate that neuroleptics differ markedly in their specificity of antagonism of DMT ... which may act through different neurotransmitter mechanisms (tryptaminergic vs. adrenergic). For more Interactions (Complete) data for N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Mouse iv 32 mg/kg LD50 Mouse ip 47 mg/kg |
| 其他信息 |
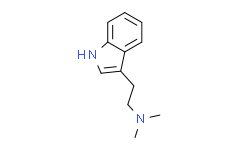
N,N-dimethyltryptamine is a tryptamine derivative having two N-methyl substituents on the side-chain. It is a tryptamine alkaloid and a member of tryptamines. It is functionally related to a tryptamine. It is a conjugate base of a N,N-dimethyltryptaminium.
Dimethyltryptamine is a DEA Schedule I controlled substance. Substances in the DEA Schedule I have no currently accepted medical use in the United States, a lack of accepted safety for use under medical supervision, and a high potential for abuse. It is a Hallucinogenic substances substance. An N-methylated indoleamine derivative, a serotonergic hallucinogen found in several plants, especially Prestonia amazonica (Apocynaceae) and in mammalian brain, blood, and urine. It apparently acts as an agonist at some types of serotonin receptors and an antagonist at others. N,N-Dimethyltryptamine has been reported in Acacia confusa, Anadenanthera peregrina, and other organisms with data available. An N-methylated indoleamine derivative and serotonergic hallucinogen which occurs naturally and ubiquitously in several plant species including Psychotria veridis. It also occurs in trace amounts in mammalian brain, blood, and urine, and is known to act as an agonist or antagonist of certain SEROTONIN RECEPTORS. See also: Psychotria viridis whole (part of). Drug Indication Some people use this compound as a psychedelic inducing agent. Mechanism of Action DMT acts as a non-selective agonist at most or all of the serotonin receptors. N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is a hallucinogen found endogenously in human brain that is commonly recognized to target the 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A receptor or the trace amine-associated receptor to exert its psychedelic effect. DMT has been recently shown to bind sigma-1 receptors, which are ligand-regulated molecular chaperones whose function includes inhibiting various voltage-sensitive ion channels. Thus, it is possible that the psychedelic action of DMT might be mediated in part through sigma-1 receptors. ... The psychotomimetic agent dimethyltryptamine (DMT) has been identified as an endogenous compound in the central nervous system of rodents using a sensitive electron capture gas chromatographic technique. DMT along with its proposed precursor, tryptamine, were identified and quantitated as the heptafluorobutyryl derivatives. A specific high affinity binding site on synaptosomal membranes has been proposed for DMT. This proposal is based on equilibrium dialysis experiments which indicate that DMT at a concentration of 1X10-5M will displace d-LSD on isolated membranes but will not displace bound serotonin at the same concentration. When DMT interacts with the synaptosomal membranes at a concentration of 5X10-10M, the membrane-bound enzyme adenylate cyclase is stimulated such that adenosine3', 5'-monophosphate (cAMP) is produced at a rate of 100 pM/min/mg of protein (2.3 times the endogenous rate). It has also been shown that its presumed precursor, tryptamine, inhibits this process. ... From data obtained in this study it has been postulated that DMT may have in vivo activity similar to those proposed for neurotransmitters or other neuroregulatory agents. ... The interactions of the indolealkylamine N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) with 5-hydroxytryptamine1A (5-HT1A) and 5-HT2 receptors in rat brain were analyzed using radioligand binding techniques and biochemical functional assays. The affinity of DMT for 5-HT1A sites labeled by (3)H-8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (3)H-8-OH-DPAT) was decreased in the presence of 1X10-4 M GTP, suggesting agonist activity of DMT at this receptor. Adenylate cyclase studies in rat hippocampi showed that DMT inhibited forskolin-stimulated cyclase activity, a 5-HT1A agonist effect. DMT displayed full agonist activity with an EC50 of 4X10-6 M in the cyclase assay. In contrast to the agonist actions of DMT at 5-HT1A receptors, DMT appeared to have antagonistic properties at 5-HT2 receptors. The ability of DMT to compete for (3)H-ketanserin-labeled 5-HT2 receptors was not affected by the presence of 1X10-4 M GTP, suggesting antagonist activity of DMT at 5-HT2 receptors. In addition, DMT antagonized 5-HT2-receptor-mediated phosphatidylinositol (PI) turnover in rat cortex at concentrations above 1X10-7 M, with 70% of the 5-HT-induced PI response inhibited at 1X10-4 M DMT. Micromolar concentrations of DMT produced a slight PI stimulation that was not blocked by the 5-HT2 antagonist ketanserin. These studies suggest that DMT has opposing actions on 5-HT receptor subtypes, displaying agonist activity at 5-HT1A receptors and antagonist activity at 5-HT2 receptors. ... The sigma-1 receptor pharmacophore includes an alkylamine core, also found in the endogenous compound N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT). DMT acts as a hallucinogen, but its receptor target has been unclear. DMT bound to sigma-1 receptors and inhibited voltage-gated sodium ion (Na+) channels in both native cardiac myocytes and heterologous cells that express sigma-1 receptors. ... DMT induced hypermobility in wild-type mice but not in sigma-1 receptor knockout mice. These biochemical, physiological, and behavioral experiments indicate that DMT is an endogenous agonist for the sigma-1 receptor. For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 分子式 |
C12H16N2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
188.27
|
| 精确质量 |
188.131
|
| CAS号 |
61-50-7
|
| PubChem CID |
6089
|
| 外观&性状 |
Crystals ... also reported as plates from ethanol and light petroleum
Solid |
| LogP |
2.5
|
| tPSA |
19
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
1
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
14
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
179
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
DMULVCHRPCFFGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C12H16N2/c1-14(2)8-7-10-9-13-12-6-4-3-5-11(10)12/h3-6,9,13H,7-8H2,1-2H3
|
| 化学名 |
2-(1H-indol-3-yl)-N,N-dimethylethanamine
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.3115 mL | 26.5576 mL | 53.1152 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.0623 mL | 5.3115 mL | 10.6230 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5312 mL | 2.6558 mL | 5.3115 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。