| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Natural product; Balanus albicostatus and Bugula neritina
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
从C.monnieri的果实中纯化了四种天然产物,并通过化学合成获得了自然界中痕量的其他五种化合物。这些化合物的一般化学结构特征在补充材料中进行了描述。光谱数据与参考文献一致,共鉴定出9种化合物,分别为蛇床子素(1)、欧前胡素(2)、异戊烯林(3)、月桂烯醇(4)、8-环氧戊基香豆素(5)、梅兰津水合物(6)、2′-脱氧甲丙嗪水合物(7)、8-甲基丁烯香豆素(8)和Micromarin-F(9)。1.
化合物的AF活性[1] 表1总结了化合物1-9对白肋滨藜和苦草的EC50和LC50值。化合物1-9的沉降率和死亡率详见补充材料。美国海军项目作为天然防污剂效力标准的标准要求是,在静态生物测定中活性低于25μg mL−1。除梅兰津水合物(6)外,所有化合物的EC50值均低于25μg mL-1,并显示出对藤壶沉降的抑制活性。其中,化合物1、2、4和7对藤壶沉降具有很高的抑制活性,EC50值<5μg mL-1。计算出的治疗比(LC50/EC50)大于1被认为可用于环境兼容的房颤涂料。LC50/EC50比值高于15.0的房颤化合物被认为是无毒房颤剂,LC50/EC50中比值低于5.0的化合物则被认为是有毒房颤剂。最近的意见指出,在选择候选化合物时,仍然可以考虑LC50/EC50比值较低的可降解化合物。化合物1、2、4、5、7和8的LC50/EC50比值高于5.0,表明这些化合物是抗白肋滨藜幼虫沉降的低毒AF剂。除2、3和5外,所有化合物均显示出对苔藓虫B.neritina沉降的抑制活性,EC50值<25μg mL-1,化合物8的EC50值低于5μg mL-1。所有化合物在50μg mL-1的浓度下对苦草杆菌没有显著的致死作用。 在之前的研究中,我们报道了六种常见中草药的粗提物对白肋滨藜的塞浦路斯具有AF活性,我们还从苦参中鉴定出两种AF化合物。在这项研究中,我们从另一种中草药蛇床子的果实中鉴定出了四种AF化合物(蛇床子素、欧前胡素、异戊灵、金匮酚)。这些结果进一步证明了草药作为AF药物来源的价值。蛇床子素(1)对白肋甲杆菌和苦草杆菌均表现出显著的抑制活性。此外,一些蛇床子素衍生物(5、7、8和9/Micromarin-F)也显示出既定的房颤活性。有人建议,化合物蛇床子素应被视为设计新型房颤剂的潜在先导化合物。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
官能团对抗幼虫定居活动的影响[1]
由于这九种化合物具有不同官能团的基本香豆素骨架(苯并α-吡喃环),因此可以估计官能团对抗幼虫定居活性的影响,以获得有关构效关系(SAR)的初步信息。为了讨论官能团的影响,生物测定结果的浓度单位转换为微摩尔每毫升,如图1和图2所示。 AF检测[1] 以藤壶B.albicostatus和苔藓虫B.neritina为试材,检测其天然产物和合成衍生物的AF活性。在中国福建省厦门市潮间带采集白肋滨对虾成虫。根据参考文献的方法,将I-II期无节幼体从成虫中释放出来后,收集并饲养以毛壳龟为食物来源的变态无节幼体。将变态为鲤科阶段的幼虫在5°C的黑暗中储存,直至用于生物测定。从中国福建省漳州市坡照岛附近的一个养鱼场收集了B.neritina的成虫群落。在暴露在头顶的室内光线下后,成虫释放了幼虫,这些幼虫被收获并立即使用。将测试样品溶解在EtOAc中,测量活性的方法基于参考文献。计算幼虫定居、游泳和死亡的百分比。使用Spearman-Karber方法计算化合物的EC50值(使沉降率相对于对照降低50%的浓度)和LC50值(导致50%死亡率的浓度)。采用单因素方差分析和Dunnet事后检验分析实验处理和对照之间的差异。显著性水平定义为p<0.05。 |
| 动物实验 |
AF Assay [1]
The barnacle B. albicostatus and the bryozoan B. neritina were used to test the AF activities of the natural products and synthetic derivatives. Adults of B. albicostatus were collected from the intertidal zone in Xiamen, Fujian Province, China. Based on the methods of references, after being released from the adults, the I–II stage nauplii were collected and reared to metamorphosis with Chaetoceros muelleri as food source. The larvae, which were metamorphosed to the cyprid stage, were stored in the dark at 5 °C until use for bioassays. Adult colonies of B. neritina were collected from a fish farm near Pozhao Island, Zhangzhou, Fujian Province, China. After exposure to the overhead room light, the adults released the larvae, which were harvested and immediately used. Test samples were dissolved in EtOAc and the methods for measuring activities were based on references. Percentages of larval settlement, swimming and death were calculated. The EC50 value (the concentration that reduced the settlement rate by 50% relative to the control) and LC50 value (the concentration that resulted in 50% mortality) of the compounds were calculated using the Spearman–Karber method. The differences between the experimental treatments and controls were analyzed with one-way ANOVA followed by a Dunnet post hoc test. The significance level was defined as p < 0.05. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Micromarin F has been reported in Micromelum minutum with data available.
In the search for new environmental friendly antifouling (AF) agents, four coumarins were isolated from the herbal plant Cnidium monnieri, known as osthole (1), imperatorin (2), isopimpinellin (3) and auraptenol (4). Furthermore, five coumarin derivatives, namely 8-epoxypentylcoumarin (5), meranzin hydrate (6), 2′-deoxymetranzin hydrate (7), 8-methylbutenalcoumarin (8), and micromarin-F (9) were synthesized from osthole. Compounds 1, 2, 4, 7 showed high inhibitory activities against larval settlement of Balanus albicostatus with EC50 values of 4.64, 3.39, 3.38, 4.67 μg mL−1. Compound 8 could significantly inhibit larval settlement of Bugula neritina with an EC50 value of 3.87 μg mL−1. The impact of functional groups on anti-larval settlement activities suggested that the groups on C-5′ and C-2′/C-3′ of isoamylene chian could affect the AF activities. In conclusion, four coumarins were isolated from the herb C. monnieri, five other coumarins were prepared by chemical synthesis from osthol. All compounds were identified and tested for AF activities; most of them showed inhibitory activities against barnacle or bryozoan settlement. Among these compounds, osthole could be considered as a good lead compound in AF agent discovery, since it was present in a high quantity, was of simple structure and had substantial AF activities against both B. albicostatus and B. neritina. Furthermore, some preliminary information about the structure-activity relationship of these coumarins was given and the results showed that the groups on C-5′ and C-2′/C-3′ of the isoamylene chain could affect the AF activities.[1] |
| 分子式 |
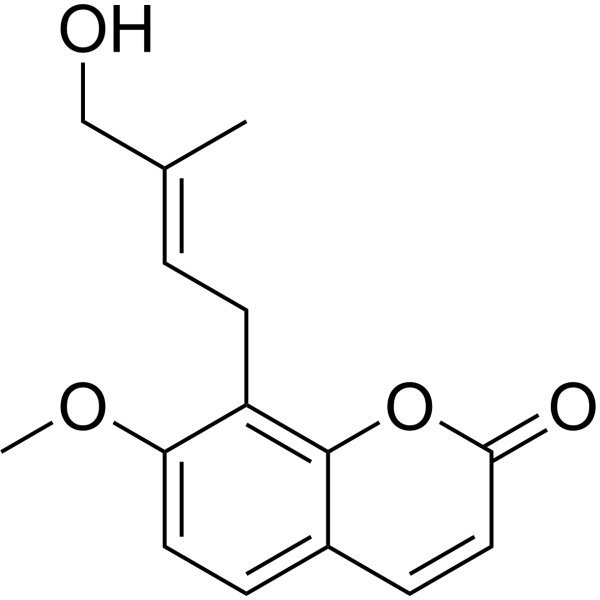
C15H16O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
260.29
|
| 精确质量 |
413.184
|
| CAS号 |
7336-40-5
|
| PubChem CID |
23758
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.24g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
683.2ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
367ºC
|
| 折射率 |
1.583
|
| LogP |
2.6
|
| tPSA |
55.8 Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
19
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
386
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
C/C(=C\CC1=C(C=CC2=C1OC(=O)C=C2)OC)/CO
|
| InChi Key |
NYBDJZVNEBTWCZ-XCVCLJGOSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H16O4/c1-10(9-16)3-6-12-13(18-2)7-4-11-5-8-14(17)19-15(11)12/h3-5,7-8,16H,6,9H2,1-2H3/b10-3+
|
| 化学名 |
8-[(E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl]-7-methoxychromen-2-one
|
| 别名 |
Micromarin F; 73292-93-0; 8-(4-Hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-7-methoxy-2H-chromen-2-one; 1443627-08-4; 8-((E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl)-7-methoxychromen-2-one; 8-[(E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl]-7-methoxychromen-2-one;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.8419 mL | 19.2093 mL | 38.4187 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7684 mL | 3.8419 mL | 7.6837 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3842 mL | 1.9209 mL | 3.8419 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。