| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 25g |
|
||
| 100g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The extent of oral absorption was high (> 90%), based on urinary and biliary data, with most of the biliary component reabsorbed and excreted in urine. The biliary component increased disproportionately with increasing dose from 15 to 600 mg/kg bw. Absorption of radiolabel was rapid, with maximal blood concentrations achieved between 0.25 and 1 hour for single doses of 600 mg/kg bw and below. Quinclorac was widely distributed in the body, with highest concentrations present in the blood, plasma and kidneys. Tissue levels were generally higher (< 2-fold) in females than in males. The labelled material was rapidly excreted, primarily via urine (50-90% in 24 hours). Initial plasma half-lives were calculated to be approximately 3-4 hours. Clearance from the blood was slower following repeated dosing with 600 mg/kg bw and with single doses of 1200 mg/kg bw, resulting in non-proportionate increases in the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC). The excretion pattern and tissue distribution of radioactivity were similar across administered dose levels and when the administration of radiolabelled quinclorac was preceded by 7 or 14 days of administration of the labelled or unlabelled material. The metabolism of quinclorac ((2,3,4-(14)C)3,7-dichloro-8-quinolinecarboxylic acid) following oral administration was studied extensively in male and female CD rat. The compound was rapidly absorbed and eliminated in the urine following administration of single oral doses of (14)C quinclorac at 15 or 600 mg/kg and at 15 mg/kg after the animals were dosed with unlabeled quinclorac at 15 mg/kg/day for 14 days. Elimination in the urine 5 days after dosing accounted for 91 to 98% of the dose with only 1 to 4% eliminated in the feces. No radioactivity was detected in expired air. Biliary excretion was significant (11.5 to 14.5% of the dose) in animals receiving 600 mg/kg. However, most of this radioactivity was reabsorbed from the intestines and eliminated in the urine. Most of the radioactivity in the bile is associated with the glucuronide conjugate of quinclorac. The conjugate is apparently hydrolyzed in the intestines and reabsorbed. Almost all the radioactivity in the urine is unchanged quinclorac. Radioactive tissue residue levels 5 days after dosing were dose-dependent. Results from these and other (whole-body autoradiography and time-course) studies indicate that quinclorac may accumulate in the adrenal glands, bone marrow, thyroid, squamous epithelium of the non-fundic stomach, and ovaries. In 7-day time-course studies (oral gavage at 15 mg/kg/day or dietary at about 1,000 mg/kg/day) maximum (14)C residue levels were detected 30 minutes after the final dose; thereafter, residue levels decreased with time. Mean (14)C residues in plasma were also detected at 30 minutes in animals receiving single oral doses of 15, 100, or 600 mg/kg or 15 mg/kg/day for 7 days. Elimination was biphasic with half-lives of 3 to 4 hours for the rapid phase at the low doses and a half-life of about 13 hours at 600 mg/kg. Peak plasma levels of radioactivity in animals receiving higher doses (1200 mg/kg or 600 mg/kg/day for 7 days) were noted for 7 to 48 hours postdosing: saturation kinetics were also noted at these higher doses. Metabolism / Metabolites Samples ... extracted and analyzed for the presence of metabolites using techniques including thin-layer chromatography and mass spectroscopy. Absorbed quinclorac was metabolized to only a limited extent, with unchanged parent compound representing approximately 80% of the excreted radiolabel. The major biotransformation product was quinclorac-glucuronide conjugate, representing approximately 5% of the administered dose. The pattern of metabolism was similar across sexes, dose levels and administration of repeated doses. A number of metabolites each representing less than 5% of the administered dose were not identified. The metabolism of quinclorac is so limited that a metabolic pathway is considered unnecessary. Biological Half-Life In 7-day time-course studies (oral gavage at 15 mg/kg/day or dietary at about 1,000 mg/kg/day) maximum (14)C residue levels were detected 30 minutes after the final dose; thereafter, residue levels decreased with time. ... Elimination was biphasic with half-lives of 3 to 4 hours for the rapid phase at the low doses and a half-life of about 13 hours at 600 mg/kg. ... |
|---|---|
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Cavalheiro de Menezes C, et al. The effects of diphenyl diselenide on oxidative stress biomarkers in Cyprinus carpio exposed to herbicide quinclorac (Facet®). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2012;81:91-97.
|
| 其他信息 |
Quinclorac is a quinolinemonocarboxylic acid that is quinoline-8-carboxylic acid in which the hydrogens at positions 3 and 7 have been replaced by chlorines. It is used (particularly as its dimethylamine salt, known as quinclorac-dimethylammonium) as a (rather persistent) herbicide for the post-emergence control of weeds in rice, grass and turf. It is not approved for use within the European Union. It has a role as a herbicide, an agrochemical and a synthetic auxin. It is a quinolinemonocarboxylic acid, an organochlorine compound and a monocarboxylic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a quinclorac(1-).
Quinclorac is a selective herbicide used primarily to control weeds in rice crops, but is also used on other agricultural crops and is found in some household herbicides for lawn use. |
| 分子式 |
C10H5CL2NO2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
242.06
|
| 精确质量 |
240.969
|
| CAS号 |
84087-01-4
|
| PubChem CID |
91739
|
| 外观&性状 |
White/yellow solid
Colorless crystalline solid |
| 密度 |
1.6±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
405.4±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
274ºC
|
| 闪点 |
199.0±27.3 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.695
|
| LogP |
2.11
|
| tPSA |
50.19
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
15
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
262
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C(C1C2C(=CC(=CN=2)Cl)C=CC=1Cl)O
|
| InChi Key |
FFSSWMQPCJRCRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C10H5Cl2NO2/c11-6-3-5-1-2-7(12)8(10(14)15)9(5)13-4-6/h1-4H,(H,14,15)
|
| 化学名 |
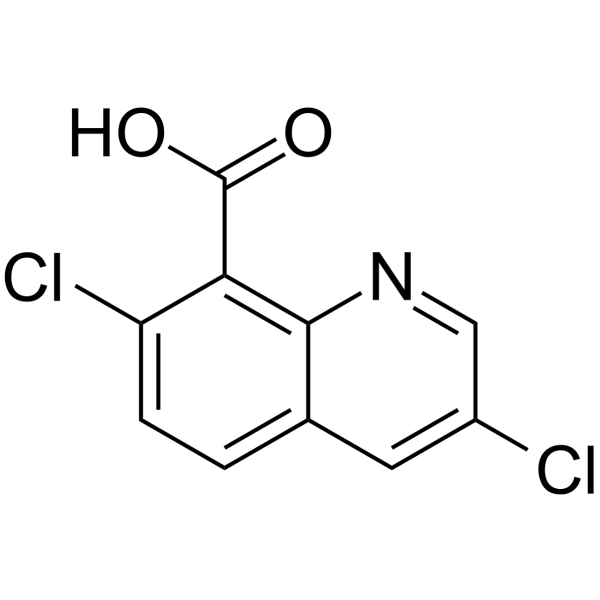
3,7-dichloroquinoline-8-carboxylic acid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: 125 mg/mL (516.40 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.1312 mL | 20.6560 mL | 41.3121 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8262 mL | 4.1312 mL | 8.2624 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4131 mL | 2.0656 mL | 4.1312 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。