| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
G3BP1/2
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
FAZ-3532 (G3Ia)和G3Ib破坏RNA、G3BP1和caprin 1的体外缩合。
FAZ-3532 (G3Ia)或G3Ib预孵卵可阻止细胞中应激颗粒的形成。 FAZ-3532 (G3Ia)和G3Ib处理可快速溶解预制应力颗粒。 G3I化合物处理不影响细胞中的翻译速率。 FAZ-3532 (G3Ia)可阻止应激颗粒的形成,并可溶解人ipsc源性神经元中预先形成的应激颗粒。 FAZ-3532 (G3Ia)或G3Ib可溶解VCP致病突变体表达后形成的应激颗粒。 FAZ-3532 (G3Ia)处理导致G3BP1从响应致病FUS突变体表达而形成的应激颗粒中去除[1]。 应激颗粒的形成是由多聚体释放mrna触发的,并由rna结合蛋白G3BP1/2的作用促进。应激颗粒与多种疾病状态有关,包括癌症和神经变性。因此,限制应力颗粒形成或促进其溶解的化合物具有作为实验工具和新型治疗方法的潜力。本文中,我们描述了两个小分子,G3BP抑制剂a和b (G3Ia和G3Ib),它们被设计用于结合G3BP1/2中的特定口袋,该口袋是G3BP1/2功能的病毒抑制剂的目标。除了在体外破坏RNA、G3BP1和caprin 1的共凝聚外,这些化合物还可以抑制在应激之前或同时处理的细胞中形成应激颗粒,并溶解已有的应激颗粒。这些影响在多种细胞类型和各种初始压力源中是一致的。因此,这些化合物代表了探索应激颗粒生物学的有力工具,并有望用于调节应激颗粒形成的治疗干预。[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
突变诱导颗粒的成像及分析[1]
将敲入G3BP1-tdTomato的U2OS细胞(Yang et al., 2020)接种到96孔板中。在实验开始前24小时用ViaFect转染试剂将GFP-VCP-A232E或GFP-FUS-R495X转染到细胞中。对于化合物FAZ-3532 (G3Ia)或G3Ia’处理的样品,在实验开始前加入Hoechst(1:50 000)孵育30 min,用PBS洗涤一次,实验开始时将培养基改为100 μl FluoroBrite DMEM培养基。使用Gen5软件(版本3.11),使用Hamamatsu Orca-Flash 4.0相机,在Cytation C10旋转盘共聚焦上对板进行成像。通过Olympus Plan Apo 40× 0.6 NA干物镜进行成像,其可调环设置为0.5 μm厚度。激光自动对焦前成像的tdTomato通道被用于每张图像。仪器温度保持在37℃,细胞注入5%的CO2。在每口井的中心拍摄一张7 × 7的瓷砖,捕捉tdTomato和GFP通道(当存在Hoechst通道时)。扫描完成后,在每孔中加入100 μl含100 μM (2×) G3I化合物的FluoroBrite(涡旋5 s),孵育20 min,然后在与第一轮相同的位置开始另一轮成像。用G3Ib或G3Ib '处理的样品进行人工分析,对每个具有自发颗粒的细胞进行评分,以确定化合物处理后颗粒的存在或不存在。在转染前预处理G3I化合物的实验中,在加入转染试剂前20分钟,在U2OS细胞中加入50 μM的指定化合物或对照物。转染24 h后,用PBS洗涤细胞,4%甲醛固定细胞,实验开始前用Hoechst(1:50 000)在PBS中孵育30分钟,PBS洗涤一次,在如上所述的Cytation C10旋转盘共聚焦下进行室温成像。[1] 用FAZ-3532 (G3Ia)或G3Ia '处理的样品使用自动管道进行分析。在ilastik和Cellpose 2.0中进行分割。使用Hoechst通道的核分割和GFP和tdTomato通道中的颗粒分割通过ilastik中的像素分类进行,使用小块裁剪的部分作为每个通道的训练数据集。在Cellpose 2.0中通过输入Hoechst和G3BP1-tdTomato通道的合并RGB进行单个细胞分割。然后,Cellpose输出被侵蚀了一个像素,并在斐济设置为二进制掩模。原始的三个原始通道,来自ilastik的三个输出掩模,以及来自Cellpose的一个掩模都被输入到CellProfiler中,以生成由GFP或tdTomato定义的颗粒的每个细胞测量值。 |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
The use of FAZ-3532 (G3Ia) and G3Ib to target the NTF2L domain of G3BP1/2 has several potential applications. Primarily, these compounds will provide a tool for researchers to manipulate G3BP1/2-dependent stress granule formation and identify specific functions of stress granules in cells. Unlike many other stress granule inhibitors such as cycloheximide (Mollet et al., 2008) that lead to global inhibition of translation and are highly toxic, FAZ-3532 (G3Ia) and G3Ib are designed to be specific in their inhibition of protein binding within the NTF2L domain of G3BP1/2. FAZ-3532 (G3Ia) and G3Ib impair condensate formation in a highly tractable manner, do not appear to induce cellular toxicity or growth phenotypes (Fig. 2), and are versatile among different cell types. While NTF2L is also the dimerization domain of G3BP1/2 proteins, G3Ia and G3Ib bind to an interaction surface that is on the opposite face of the dimerization surface, thereby leaving dimerization intact (Fig. 1 D). Thus, FAZ-3532 (G3Ia) and G3Ib target only the protein–protein interaction domain of G3BP1/2 and specifically block G3BP1/2 condensate formation while leaving the dimerization and RNA-binding capabilities of G3BP1/2 unaltered. This approach also presents a significant advantage over genetic models in which G3BP1 and G3BP2 are knocked out, resulting in a complete loss of function of these proteins along with potential alterations in the expression of other stress granule proteins.
Stress granules have been implicated in several disease states, including neurodegeneration and cancer (Protter and Parker, 2016). These compounds could be utilized in disease models to block stress granule formation or potentially dissolve disease-initiated granules, allowing for a better understanding of the roles of these condensates in disease initiation and progression. Consistent with this possibility, we observed that FAZ-3532 (G3Ia) and G3Ib can induce the disassembly of aberrant stress granules triggered by the expression of a pathogenic VCP A232E mutation that causes multisystem proteinopathy (Fig. 5). Additionally, G3Ia and G3Ib can be used to probe the immunological role of stress granules, as G3BP1-mediated stress granules are known to form in response to infection with numerous viral RNAs (Jayabalan et al., 2023). Finally, these compounds can be used to define whether the NTF2L domain-mediated interactions of G3BP1/2 play a role in the normal function of cells outside of their ability to drive condensation. Such studies could lead to the discovery of novel stress granule-independent functions of G3BP1, G3BP2, or their interactors in normal cell biology.
In summary, FAZ-3532 (G3Ia) and G3Ib are potent inhibitors of binding to the NTF2L domain of G3BP1/2 that are highly specific, easy to synthesize, and highly effective across multiple cell types and stressors, providing a valuable new tool in the study of condensate biology.
|
| 分子式 |
C38H56FN5O7
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
713.88
|
| 精确质量 |
713.41637
|
| PubChem CID |
170459244
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
4
|
| tPSA |
166Ų
|
| InChi Key |
OULWYQHHPPQJBM-AZWKTQJSSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C38H56FN5O7/c1-24(27-18-14-11-15-19-27)30(42-35(48)31(38(6,7)50)43-33(46)28(39)22-37(3,4)5)34(47)40-25(2)32(45)41-29(20-21-51-9)36(49)44(8)23-26-16-12-10-13-17-26/h10-19,24-25,28-31,50H,20-23H2,1-9H3,(H,40,47)(H,41,45)(H,42,48)(H,43,46)/t24-,25+,28-,29-,30-,31+/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
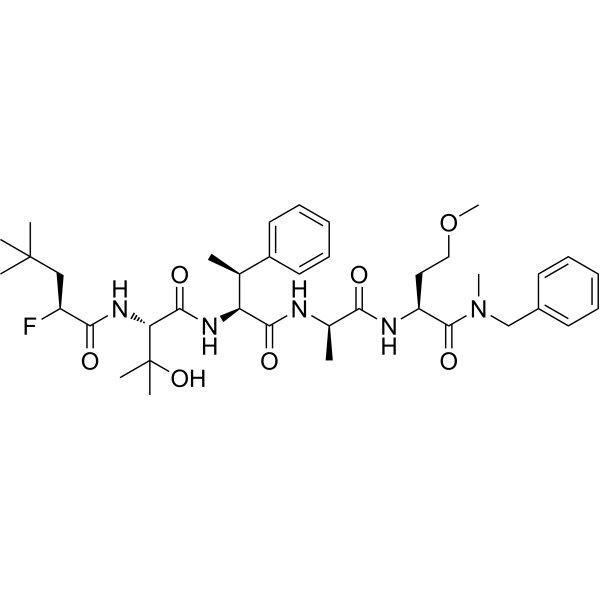
(2S)-N-[(2S)-1-[[(2S,3S)-1-[[(2R)-1-[[(2S)-1-[benzyl(methyl)amino]-4-methoxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino]-3-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]-2-fluoro-4,4-dimethylpentanamide
|
| 别名 |
FAZ-3532; FAZ3532
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
Typically soluble in DMSO (e.g. 10 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.4008 mL | 7.0040 mL | 14.0080 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2802 mL | 1.4008 mL | 2.8016 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1401 mL | 0.7004 mL | 1.4008 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。