| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Dermal absorption of RH-287 was examined in male Crl:CD:BR rats. There were six experimental groups of 4 rats each. Two concentrations of RH-287 were employed, 3% and 0.045%. Dermal application was made to a shaved 2 x 2 cm area on the interscapular region of the back, which was fitted with a contoured glass ring secured with cyanoacrylate glue and a porous top secured with rubber bands after application of the test substance in a dose aliquot of 60 uL. Two groups (A and B) received either 3% of 0.045% RH287 and urine and feces samples obtained at 10 hours post-dose, at which time the animals were killed and analysis for radioactivity performed in whole blood, plasma, and remaining carcass. Two additional groups (C and D) received either 3% or 0.045% RH-287 and were subjected to the same procedures as groups A and B, except exposure duration was 24 hours. The last two groups (E and F) received either 3% or 0.045 % RH-287, and urine and feces samples taken at 0, 10, 24, 48, and 72 hours post-dose. Animals in this group were sacrificed at 72 hours post-dose and analysis for radioactivity performed as for the other groups. Results of this study showed that at a dose of 0.045% RH-287, 44-50% of the dose was absorbed after a 10 hour exposure, and 70% after a 24 hour exposure. Administration of 3% RH-287 resulted in 31-34% absorption after 10 hours of exposure, and 52% absorption after 24 hours exposure. |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: 4,5-Dichloro-2-octyl-3-isothiazolone (DCOIT) is a solid. It is used as a marine antifoulant. HUMAN STUDIES: An outbreak of occupational contact dermatitis occurred due to the biocide DCOIT. Eight of 19 persons, six females, 20 to 63 years old, employed in a Japanese textile finishing factory developed edematous reddish eruptions on their forearms, upper arms, face, or neck. The subjects have been sensitized to DCOIT without apparent cross sensitization to DCOIT. ANIMAL STUDIES: In dogs decreased body weight and food consumption, hematologic and clinical chemistry parameter changes observed at 1500 ppm. After inhalation in rats at concentrations of 0.02, 0.63, and 6.72 mg/cu m for 6 hours per day, 5 days per week, for thirteen weeks, treatment-related microscopic lesions in the nose, larynx, and lungs were observed in mid- and high-dose treated rats. Minimal or mild subacute inflammation of the nose was observed in increased incidence, as was transitional respiratory epithelial hyperplasia and goblet cell hyperplasia. In the epiglottis, hyperplasia of the squamous and cuboidal epithelium was observed in mid- and high dose rats, as was chronic-active inflammation of the epiglottis. Goblet cell hyperplasia and acute inflammation was observed in increased incidence in the lungs of high dose rats. In the developmental study in rabbits, there were no treatment-related external, visceral, or skeletal malformations or variations. In rats, fetuses at 100 mg/kg/day showed an increase in the number of fetuses with wavy ribs, along with an increase in number of litters with this effect as well as the severity of the effect. It was not mutagenic in Salmonella strains TA1535, TA1537, TA98, TA100 with or without metabolic activation. It induced clastogenic response in Chinese hamster ovary in vitro cytogenetic assays in the presence or absence of metabolic activation. ECOTOXICITY STUDIES: In marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) gene transcription analysis showed that DCOIT had positive regulatory effects mainly in male of the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonadal-liver axis with lesser extent in females. The stimulated steroidogenic activities resulted in increased concentrations of steroid hormones, including estradiol (E2), testosterone (T), and 11-KT-testosterone (11-KT), in the plasma of both sexes, leading to an imbalance in hormone homeostasis and increased E2/T ratio. The relatively estrogenic intracellular environment in both sexes induced the hepatic synthesis and increased the liver and plasma content of vitellogenin (VTG) or choriogenin. Furthermore, parental exposure to DCOIT transgenerationally impaired the viability of offspring, as supported by a decrease in hatching and swimming activity. DCOIT induced differential expression of 26 proteins in male brains and of 27 proteins in female brains of the marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) after a 28-day exposure to environmentally-realistic concentration at 2.55 ug/L. Interactions The toxicity of three antifoulants (Sea-Nine, Irgarol, and TBT) was determined individually and in mixtures in two tests with microalgae. Effects on periphyton community photosynthesis and reproduction of the unicellular green algae Scenedesmus vacuolatus were investigated. The tested antifoulants were highly toxic in both tests. Observed mixture toxicities were compared with predictions derived from two concepts: Independent Action (IA), assumed to be more relevant for the tested mixtures that were composed of dissimilarly acting substances, and Concentration Addition (CA), regarded as a reasonable worst-case approach in predictive mixture hazard assessment. Despite the corresponding mechanistic basis, IA failed to provide accurate predictions of the observed mixture toxicities. Results show the same pattern in both assays. Mixture effects at high concentrations were slightly overestimated and effects at low concentrations were slightly underestimated. Maximum observed deviations between observed and IA-predicted concentrations amount to a factor of 4. The suggested worst-case approach using CA was protective only in effect regions above 20%. Nevertheless, the application of any concept that accounts for possible mixture effects is more realistic than the present chemical-by-chemical assessment. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
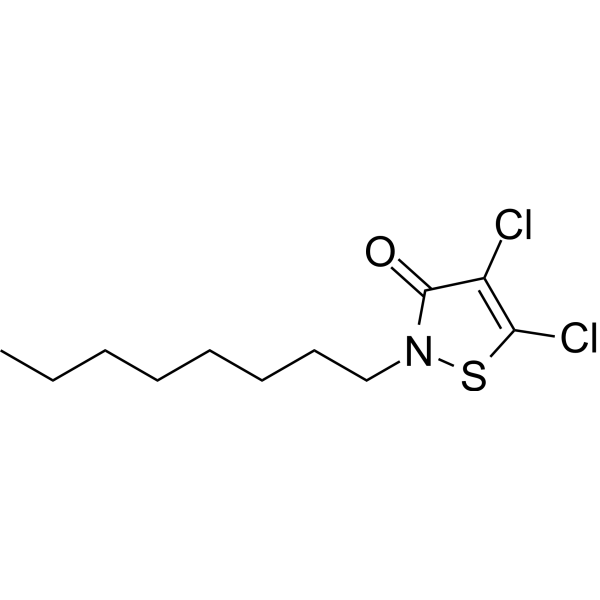
4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-3(2H)-isothiazolone is a 1,2-thiazole that is 1,2-thiazol-3(2H)-one substituted by chloro groups at positions 4 and 5 and an octyl group at position 2. It is used as a fungicide. It has a role as an environmental contaminant, a xenobiotic and a fungicide. It is an organochlorine compound and a member of 1,2-thiazoles.
|
| 分子式 |
C11H17CL2NOS
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
282.23
|
| 精确质量 |
281.04
|
| CAS号 |
64359-81-5
|
| PubChem CID |
91688
|
| 外观&性状 |
Crystals from hexane
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
322.6±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
36-40ºC
|
| 闪点 |
148.9±30.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.552
|
| LogP |
4.34
|
| tPSA |
50.24
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
16
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
281
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
ClC1=C(SN(C1=O)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])Cl
|
| InChi Key |
PORQOHRXAJJKGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C11H17Cl2NOS/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-14-11(15)9(12)10(13)16-14/h2-8H2,1H3
|
| 化学名 |
4,5-dichloro-2-octyl-1,2-thiazol-3-one
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
Typically soluble in DMSO (e.g. 10 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5432 mL | 17.7160 mL | 35.4321 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7086 mL | 3.5432 mL | 7.0864 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3543 mL | 1.7716 mL | 3.5432 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。