| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Doxorubicin prodrug; Topoisomerase
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在这项研究中,研究人员合成了异基因DOX作为生物正交前药(补充图23-26)。阿霉素(DOX)在临床上用于癌症治疗;它通过结合DNA并引发酶介导的链断裂来起作用。通过将伯胺与烯丙基氨基甲酸酯基团封合,如荧光滴定法所示(图4a、b和补充图27,Kalloc-DOX和KDOX分别表示异基因DOX和DOX与ctDNA相互作用的结合常数),异基因DOX(Kalloc-DOX=7.96×104 M-1)对小牛胸腺DNA的结合亲和力远低于DOX(KDOX=9.36×105 M-1)。异基因DOX的这种较弱的DNA结合能力是因为柔红霉素部分正电荷的减少使DNA-药物嵌入复合物的稳定性降低。同时,高效液相色谱(HPLC)分析证明了溶液中Pd-TNS催化的合金DOX的衰变(补充图28)。这种掩蔽策略可以提供活性较低的前药,同时允许通过生物正交催化进行恢复。[1]
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
同时,通过测量小鼠的体重变化并与DOX治疗的小鼠进行比较,确定了异基因DOX的体内毒性(补充图36)。每三天腹腔注射高达150mg kg-1的异基因DOX,导致体重减轻约7.7%;同时,当剂量超过10mg/kg-1时,DOX会导致严重的体重减轻和死亡,这表明前药在体内毒性较低。根据毒性耐受数据,为了强调前药毒性较小的特点,同时避免过高剂量的意外副作用,在以下抗肿瘤研究中应用了等毒性剂量的异基因DOX(100 mg kg–1)和DOX(5 mg kg–l),差异为20倍。[2]
接下来,将携带B16-F10肿瘤的小鼠随机分为五组,每三天用同种异体DOX/PT-MN组合、DOX、同种异体DOX、PT-MNs或PBS治疗一次。DOX、异基因DOX和PBS通过腹腔注射给药。在注射前药之前,将PT-MNs从表面皮肤插入肿瘤部位并固定一小时,以使针头彻底膨胀。记录生物发光成像和肿瘤体积,以观察肿瘤生长并评估治疗效率(图5a)。如图5a-c所示,与用PBS治疗的对照组一样,单独用同种异体DOX或PT-MNs治疗的组没有观察到延迟的肿瘤生长,表明前药和单独的催化装置都没有抗肿瘤作用。在DOX治疗组中观察到中度抑制结果,但在停止DOX给药后肿瘤生长迅速。相比之下,同种异体DOX/PT-MN组合更好地抑制了肿瘤生长,导致小鼠在四次治疗后肿瘤最小。此外,各组小鼠的体重均未出现明显波动(图5d),表明前药和PT-MN装置的副作用较低。重要的是,TUNEL检测仅在用同种异体DOX/PT-MNs和DOX治疗的组中验证了凋亡信号,这暗示了类似的肿瘤细胞杀伤机制(图5e)。[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
DOX或alloc-DOX与ctDNA的相互作用[2]
进行荧光滴定以研究ctDNA与DOX或alloc-DOX之间的相互作用。溶液在波长λEx=490 nm下激发,在25°C下收集520至720 nm的光谱。滴定是通过将越来越多的ctDNA直接加入含有2µM DOX或alloc-DOX溶液的试管中进行的。在平衡过程中,避免了光照。所有样品均在pH 7.5、含有1mM乙二胺四乙酸二钠的10mM Tris缓冲液中制备。[2] Pd-TNS激活前药[2] 与同种异体RH 110激活过程类似,首先将Pd TNS(1 mg)分散在0.9 ml PBS缓冲液中,然后与100µl在DMSO(1 mM)中制备的alloc-DOX储备溶液混合。在37°C下在黑暗中搅拌混合物。在指定的时间点,取出5µl反应介质并与50µl甲醇混合。在21100g下离心5分钟后,通过HPLC分析上层溶液。HPLC分析在Waters Alliance e2695系统上进行,使用Kromasil C18 HPLC柱(粒径,5μm;孔径300Å;长度与内径之比为250 mm×4.6 mm),流速为1.0 ml min-1,柱温为40°C。流动相由水/乙腈(68:32)和0.1%三氟乙酸组成。通过测量波长λ=254 nm的紫外吸收记录所有色谱图。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞毒性试验[2]
将三种细胞系,即B16-F10、4T1和Hep G2细胞,以每孔200µl培养基中10000个细胞的密度接种在96孔板中。孵育24小时后,用不同浓度的DOX和同种异体DOX处理细胞,一式三份。对于alloc-DOX/PT-MN组合组,将带有阵列的PT-MN切成足够大的小块,覆盖一个孔,每个小块约58针浸入培养基中。培养基的体积约为每孔350µl。孵育48小时后,向每个孔中加入20µl 3-(4,5-二甲基噻唑-2-基)-2,5-二苯基溴化四唑(MTT)溶液,并将平板再孵育4小时。之后,通过加入100µl DMSO裂解细胞。在微孔板读数器中,以660nm为参考波长,在570nm处测量吸光度。对于流式细胞术的凋亡研究,根据制造商的说明,使用凋亡检测试剂盒(Invitrogen,Thermal Fisher Scientific)进行Annexin V-APC(别藻蓝蛋白)和SYTOX Green双重染色。对于不同处理后DNA断裂的激光扫描共聚焦显微镜分析,根据制造商的说明进行TUNEL分析;同时,用Hoechst 33342对细胞核进行共定位染色。为了证明DOX在细胞外空间的产生,取出培养基并与甲醇/氯仿(3:2)充分混合。在21100g下离心30分钟后,分离有机相并在氮气下干燥。将残余物重新溶解在乙腈中,并通过HPLC进行分析。为了分析潜在的催化剂泄漏,将上层培养基移至试管中,同时用150µl浓硝酸消化底部的细胞。收集每个孔的所有溶液,与1ml王水混合并进一步消化。在21100g下离心30分钟后,稀释上清液并通过电感耦合等离子体质谱法进行分析。 |
| 动物实验 |
Toxicity of DOX and alloc-DOX in vivo[2]
The solutions of alloc-DOX and DOX were prepared by dissolving alloc-DOX in PBS buffer with the assistance of Tween 80 (2%). To decide the dose that could be used for antitumour studies, the toxicity of alloc-DOX was determined by measuring the weight loss of mice after i.p. injection every three days. The body changes of mice treated with DOX were also measured for comparison. Reversible weight change within 10% was considered safe.[2] Antitumour activity mediated by the bioorthogonal catalysis in vivo[2] The 1 × 106 luciferase-tagged B16-F10 melanoma tumour cells were subcutaneously injected into the right flank of C57BL/6J mice. When the tumour sizes reached about 50–100 mm3, the mice were randomly divided into different groups, and respectively treated with the alloc-DOX (100 mg kg–1)/PT-MN combination, DOX (5 mg kg–1), alloc-DOX (100 mg kg–1), PT-MNs or PBS, once every three days, for four times total. The drug, prodrug and PBS were administered by i.p. injection. For groups treated with PT-MNs, the size of PT-MNs was adjusted to cover the tumour area, and the PT-MNs were inserted into the tumour sites one hour before prodrug administration and fixed with Liquivet Rapid Tissue Adhesive to allow the thorough swelling of the needles. Tumour growth was monitored by bioluminescence signals after i.p. injection of luciferin (150 mg kg–1, catalogue no. LUCK-100, Gold Biotechnology), and images were obtained using an IVIS Lumina imaging system. The changes in tumour size were measured by a digital caliper, and the tumour volume (mm3) was calculated by the following equation: long diameter × short diameter2 × 0.5. If the mice showed signs of impaired health, or once the volume of the tumour exceeded 1,500 mm3, the mice were euthanized with CO2. To assess the potential toxicities, changes in mice body weight were measured, and histological analysis using hematoxylin and eosin staining was conducted on the tumour and major organs (that is, heart, liver, spleen, lung and kidney) at the end of the treatment. For apoptosis analysis, the fixed tumour sections were stained by TUNEL Assay Kit BrdU-Red according to the manufacturer’s protocol and the cell nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342. The stained tumour slides were then imaged by a Zeiss LSM 880 confocal microscope. For the groups treated with DOX-MNs or intratumourally injected DOX, the doses of DOX given were similar to the average amount of DOX generated in the group treated with alloc-DOX/PT-MNs at each corresponding treatment time point, which was determined by collecting all the DOX measured in the tumour, blood and major organs.[2] Analysis of DOX, alloc-DOX and Pd distribution in plasma and tissues[2] After i.p. injection of DOX or alloc-DOX into mice bearing tumours with a size around 200 mm3, blood was collected by retro-orbital puncture using a BD microtainer capillary blood collector and BD microgard closure. Plasma was isolated by centrifugation at 1,000g for 10 min. The 50 µl plasma was withdrawn and mixed with 150 µl acetonitrile to extract DOX and alloc-DOX. All tissues (heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney and tumour) were weighed after drying the surfaces with wipers and homogenized in 200 µl acetonitrile thoroughly with Cole-Parmer Tissue Tearor 985370-07 homogenizer. After shaking all the samples for 24 h at room temperature in the dark, the tubes containing plasma or homogenized tissues were centrifugated at 21,100g for 30 min. Then 30 µl of the upper solution was taken out, mixed with a known amount of DOX and alloc-DOX internal standard and then analysed by HPLC using the same protocol described above. A similar procedure was conducted for groups treated with DOX-MNs or intratumour injection of DOX. To analyse the Pd content in plasma and tissues, plasma (50 µl) and homogenized tissues were first dissolved in 500 µl concentrated nitric acid for 1 day. Then, 500 µl aqua regia was added to each sample, and the mixtures were incubated for another day. After removing the tissue debris by centrifugation (21,100g, 30 min), the supernatants were withdrawn, and the Pd contents were measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Palladium catalysts have been widely adopted for organic synthesis and diverse industrial applications given their efficacy and safety, yet their biological in vivo use has been limited to date. Here we show that nanoencapsulated palladium is an effective means to target and treat disease through in vivo catalysis. Palladium nanoparticles (Pd-NPs) were created by screening different Pd compounds and then encapsulating bis[tri(2-furyl)phosphine]palladium(II) dichloride in a biocompatible poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-b-polyethyleneglycol platform. Using mouse models of cancer, the NPs efficiently accumulated in tumours, where the Pd-NP activated different model prodrugs. Longitudinal studies confirmed that prodrug activation by Pd-NP inhibits tumour growth, extends survival in tumour-bearing mice and mitigates toxicity compared to standard doxorubicin formulations. Thus, here we demonstrate safe and efficacious in vivo catalytic activity of a Pd compound in mammals.[1]
Bioorthogonal catalysis mediated by transition metals has inspired a new subfield of artificial chemistry complementary to enzymatic reactions, enabling the selective labelling of biomolecules or in situ synthesis of bioactive agents via non-natural processes. However, the effective deployment of bioorthogonal catalysis in vivo remains challenging, mired by the safety concerns of metal toxicity or complicated procedures to administer catalysts. Here, we describe a bioorthogonal catalytic device comprising a microneedle array patch integrated with Pd nanoparticles deposited on TiO2 nanosheets. This device is robust and removable, and can mediate the local conversion of caged substrates into their active states in high-level living systems. In particular, we show that such a patch can promote the activation of a prodrug at subcutaneous tumour sites, restoring its parent drug's therapeutic anticancer properties. This in situ applied device potentiates local treatment efficacy and eliminates off-target prodrug activation and dose-dependent side effects in healthy organs or distant tissues.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C31H33NO13
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
627.59
|
| 精确质量 |
627.195
|
| CAS号 |
561022-65-9
|
| PubChem CID |
171714282
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| LogP |
2.6
|
| tPSA |
218Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
6
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
13
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
9
|
| 重原子数目 |
45
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1160
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
6
|
| SMILES |
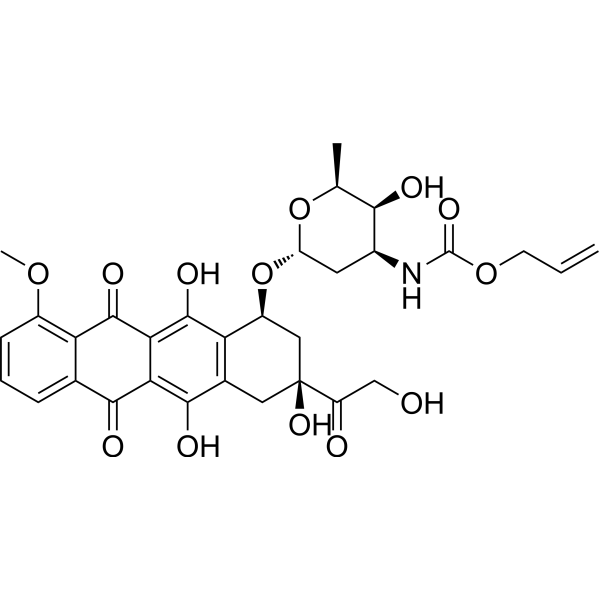
OC1=C2C(C3=CC=CC(OC)=C3C(=O)C2=C(O)C2[C@H](C[C@](O)(C(=O)CO)CC1=2)O[C@]1([H])O[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](NC(=O)OCC=C)C1)=O
|
| InChi Key |
MYTMRYOJAKUVBH-BPZXBQJLSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C31H33NO13/c1-4-8-43-30(40)32-16-9-20(44-13(2)25(16)35)45-18-11-31(41,19(34)12-33)10-15-22(18)29(39)24-23(27(15)37)26(36)14-6-5-7-17(42-3)21(14)28(24)38/h4-7,13,16,18,20,25,33,35,37,39,41H,1,8-12H2,2-3H3,(H,32,40)/t13-,16-,18-,20-,25+,31-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
prop-2-enyl N-[(2S,3S,4S,6R)-3-hydroxy-2-methyl-6-[[(1S,3S)-3,5,12-trihydroxy-3-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-10-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-2,4-dihydro-1H-tetracen-1-yl]oxy]oxan-4-yl]carbamate
|
| 别名 |
N-Alloc doxorubicin
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5934 mL | 7.9670 mL | 15.9340 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3187 mL | 1.5934 mL | 3.1868 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1593 mL | 0.7967 mL | 1.5934 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。