| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Well absorbed. ABOUT 1% OF (14)C WAS RECOVERED FROM URINE, FECES & BILE AS UNCHANGED 5-NITRO-2-FURALDEHYDE SEMICARBAZONE, SUGGESTING SUBSTANTIAL METABOLISM OF THIS SUBSTANCE IN RAT /AFTER ORAL DOSAGE OF 100 MG/KG/. RATS DOSED WITH 100 MG/KG 5-NITRO-2-FURALDEHYDE SEMICARBAZONE- [FORMYL-(14)C] ... EXCRETED ABOUT 66%, 35% & 1% OF ACTIVITY IN URINE, FECES & IN RESPIRED AIR AS CO2, RESPECTIVELY, WITHIN 96 HR, & MAJORITY OF (14)C ACTIVITY WAS ELIMINATED WITHIN 48 HR. RECOVERY OF (14)C IN BILE WAS ABOUT 27% AFTER 48 HR. IN RATS DOSED WITH 100 MG/KG, PLASMA LEVELS OF 4.5 MG/L ... WERE FOUND AFTER 4 HR, 34% OF WHICH WAS BOUND TO PROTEINS. RATS DOSED WITH 200 MG/KG ... EXCRETED ABOUT 4.6% IN URINE & 0.5% IN FECES WITHIN 48 HR. ORALLY ADMIN 5-NITRO-2-FURALDEHYDE SEMICARBAZONE WAS DETECTED IN CEREBROSPINAL FLUID OF DOGS WITHIN 2 HR. Metabolism / Metabolites Nitrofurans, including nitrofural, undergo metabolic reduction at the nitro group to generate reactive species which can covalently bind to cellular macromolecules (Polnaszek et al., 1984; Kutcher & McCalla, 1984; McCalla 1979; McCalla et al., 1975). /NITROFURAZONE HAS/ BEEN SHOWN TO BE REDUCED BY ENZYMES & PREPN FROM MAMMALIAN LIVER. ... ISOLATION OF A HYDROXYLAMINE INTERMEDIATE IS NOT UNCOMMON IN IN VITRO STUDIES. The disposition of the antibiotic nitrofurazone was studied in the singlepass isolated perfused rat liver. Both the effects of the steady state level of drug and the composition of the perfusate were evaluated. The higher level (120 ug/ml) of nitrofurazone in a perfusion medium lacking the glutathione precursors, glycine, glutamic acid and cysteine, caused a marked increase in bile flow (from 1.01 + or - 0.07 to 2.33 + or - 1.07 ul/min/g), massiv biliary efflux of glutathione disulfide (from 0.55 + or - 0.07 to 60.6 + or - 25.4 nmol/min/g) and a sharp decline in the caval efflux of glutathione (to undetectable levels) and the tissue level of glutathione (from 5.74 + or - 0.20 to 2.68 + or - 0.13 umol/g). Even after the drug was discontinued, these parameters were not restored to control levels. The lower level (30 ug/ml) of nitrofurazone with or without amino acid supplementatio and the higher level with supplementation induced less dramatic effects. Using (35)S methionine, a new conjugated metabolite of nitrofurazone and glutathione was detected. The data suggest that the toxicity of the reactive oxygen species generated by the redox cycling of the nitro group and the reactive metabolites generated by further reduction of nitrofurazone can be mitigated by adequate glutathione levels, but that livers lacking sufficient glutathione to scavenge these reactive species may be damaged. Nitrofurans, including nitrofural, undergo metabolic reduction at the nitro group to generate reactive species which can covalently bind to cellular macromolecules. Half Life: 5 hours Biological Half-Life 5 hours |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
The exact mechanism of action is unknown. Nitrofurazone inhibits several bacterial enzymes, especially those involved in the aerobic and anaerobic degradation of glucose and pyruvate. This activity is believed also to affect pyruvate dehydrogenase, citrate synthetase, malate dehydrogenase, glutathione reductase, and pyruvate decarboxylase. Toxicity Data Rat LD50 = 590 mg/kg |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Nitrofurazone can cause cancer according to The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
Nitrofurazone appears as odorless pale yellow needles or yellow powder. pH (saturated aqueous solution) 6.0 - 6.5. Alkaline solutions are dark orange. (NTP, 1992) Nitrofurazone is a semicarbazone resulting from the formal condensation of semicarbazide with 5-nitrofuraldehyde. A broad spectrum antibacterial drug, although with little activity against Pseudomonas species, it is used as a local application for burns, ulcers, wounds and skin infections. It has a role as an antibacterial drug. It is a semicarbazone and a nitrofuran antibiotic. Nitrofural or nitrofurazone is a topical anti-infective agent effective against gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. It is used for superficial wounds, burns, ulcers, and skin infections. Nitrofural has also been administered orally in the treatment of trypanosomiasis. Except for topical drug products formulated for dermatologic application, the FDA withdrew its approval for the use of drug products containing nitrofurazone. A topical anti-infective agent effective against gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. It is used for superficial wounds, burns, ulcers, and skin infections. Nitrofurazone has also been administered orally in the treatment of trypanosomiasis. A topical anti-infective agent effective against gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. It is used for superficial WOUNDS AND INJURIES and skin infections. Nitrofurazone has also been administered orally in the treatment of TRYPANOSOMIASIS. See also: Butacaine Sulfate; Nitrofurazone (component of) ... View More ... Drug Indication For the treatment of bacterial skin infections including pyodermas, infected dermatoses and infections of cuts, wounds, burns and ulcers due to susceptible organisms. Mechanism of Action The exact mechanism of action is unknown. Nitrofurazone inhibits several bacterial enzymes, especially those involved in the aerobic and anaerobic degradation of glucose and pyruvate. This activity is believed also to affect pyruvate dehydrogenase, citrate synthetase, malate dehydrogenase, glutathione reductase, and pyruvate decarboxylase. MECHANISM OF ANTIBACTERIAL ACTION OF FURAN DERIV IS UNKNOWN, BUT IT IS PRESUMED THAT THE COMPD INTERFERES WITH ENZYMATIC PROCESSES ESSENTIAL TO BACTERIAL GROWTH. /FURAN DERIV/ The exact mechanism of action of nitrofurazone is not known. It appears, howeverthat the drug acts by inhibiting bacterial enzymes involved in carbohydrage metabolism. Oragnic matter (eg, blood pus, serum) and aminobenzoic acid (p-aminobenzoic acid) inhibit the antibacterial action of nitrofurazone. Therapeutic Uses Anti-Infective Agents, Local; Anti-Infective Agents, Urinary; Trypanocidal Agents /NITROFURAZONE/ IS BACTERICIDAL FOR MANY GRAM POSITIVE & GRAM NEGATIVE ORGANISMS PRESENT IN SURFACE INFECTIONS ... IT HAS BEEN USED TOPICALLY TO TREAT INFECTIONS OF SKIN & MUCOUS MEMBRANES. NITROFURAZONE MAY BE TRIED IN ... /LATE-STAGE TRYPANOSOMIASIS/ WITH SOME CHANCE OF SUCCESS. SINGLE COURSE OF TREATMENT ... AT 6 HR INTERVALS FOR 1 WK. 3 COURSES MAY BE GIVEN WITH A WEEK'S REST BETWEEN EACH. IT FINDS USE, ESP, IN TREATMENT OF 2ND & 3RD DEGREE BURNS & IN SKIN GRAFTING IN WHICH THERE ARE COMPLICATIONS FROM BACTERIAL INFECTIONS THAT ARE REFRACTORY TO USUAL DRUGS OF CHOICE BUT IN WHICH SENSITIVITY TO NITROFURAZONE IS DEMONSTRABLE. ... NITROFURAZONE IS USED IN MGMNT OF SUSCEPTIBLE INFECTIONS OF EYE, EAR, NOSE, URETHRA & VAGINA. ... /IT/ RETAINS ITS ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY IN BLOOD, SERUM & PUS; PHAGOCYTOSIS IS NOT INHIBITED & NITROFURAZONE DOES NOT INTERFERE WITH HEALING. For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for NITROFURAZONE (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings ... /TREATMENT AS IN LATE-STAGE TRYPANOSOMIASIS/ IS UNSUITABLE FOR FEBRILE OR DEBILITATED PATIENTS. ... IT PRODUCES HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA IN PATIENTS WITH GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE DEFICIENCY. WHEN USED TOPICALLY IN EAR ... /NITROFURAZONE/ MAY PRODUCE CUTANEOUS SENSITIVITY REACTIONS. ... THIS TYPE OF REACTION ... FREQUENTLY MIMICS DISEASE BEING TREATED. ... /THIS DRUG REACTION/ CAN USUALLY BE RECOGNIZED BECAUSE THE INFLAMMATORY PROCESS BEGINS TO SPREAD TO LOBULE OF EAR & INFECTION DOES NOT RESPOND TO TREATMENT. ... STRAINS OF PSEUDOMONAS & PROTEUS ARE OFTEN RESISTANT. IT HAS NOT YET BEEN SHOWN TO BE USEFUL IN TREATMENT OF MINOR BURNS, WOUNDS, OR CUTANEOUS ULCERS WHICH ARE INFECTED. IT IS PROBABLY NOT EFFECTIVE IN TREATMENT OF PYODERMA. ... APPROX 0.5-2% OF PATIENTS BECOME SENSITIZED TO DRUG, SOMETIMES WITHIN 5 DAYS OF INITIATION OF TREATMENT. ... FOR ALL NITROFURAZONE DOSAGE FORMS, AVOID EXPOSURE AT ALL TIMES TO DIRECT SUNLIGHT, EXCESSIVE HEAT & ALKALINE MATERIALS. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for NITROFURAZONE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Nitrofurazone is a topical antibacterial agent indicated as an adjunctive therapy for second and third degree burns when resistance to other agents is a real or potential problem. Nitrofurazone is also indicated in skin grafting when bacterial contamination may cause graft rejection or donor site infection, especially in hospitals with a history of resistant bacteria. |
| 分子式 |
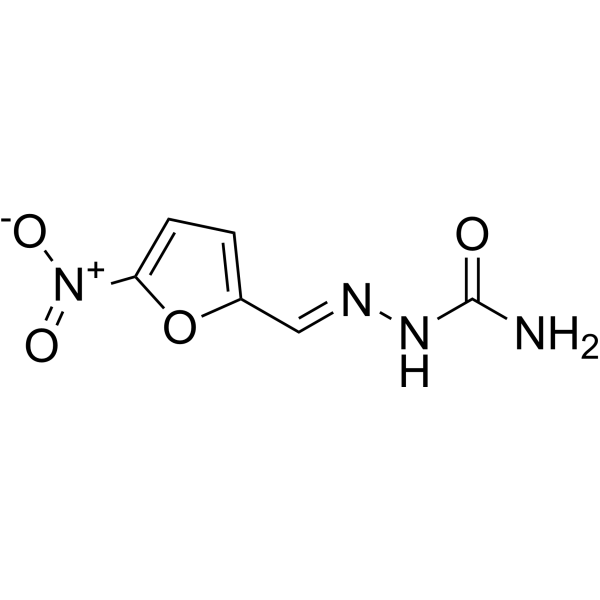
C6H6N4O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
198.14
|
| 精确质量 |
198.039
|
| CAS号 |
112574-44-4
|
| PubChem CID |
5447130
|
| 外观&性状 |
PALE YELLOW NEEDLES
LEMON-YELLOW CRYSTALLINE POWDER |
| 熔点 |
457 to 464 °F (decomposes) (NTP, 1992)
|
| LogP |
1.617
|
| tPSA |
127.43
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
14
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
261
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
C1=C(OC(=C1)[N+](=O)[O-])/C=N/NC(=O)N
|
| InChi Key |
IAIWVQXQOWNYOU-FPYGCLRLSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C6H6N4O4/c7-6(11)9-8-3-4-1-2-5(14-4)10(12)13/h1-3H,(H3,7,9,11)/b8-3+
|
| 化学名 |
[(E)-(5-nitrofuran-2-yl)methylideneamino]urea
|
| 别名 |
(E)-Nitrofural
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.0469 mL | 25.2347 mL | 50.4694 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.0094 mL | 5.0469 mL | 10.0939 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5047 mL | 2.5235 mL | 5.0469 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。