| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Rifamycin has a very poor absorption and thus, the generation of an oral modified-release formulation using the technology of the multi-matrix structure was required for the generation of the FDA approved product. This preparation allows the delivery of the active ingredient in the distal small bowel and colon without interfering with the flora in the upper gastrointestinal tract. The multi-matrix is made by a lipophiic matrix surrounded in a hydrophilic matrix which allows for the protection of the active ingredient from dissolution in the intestinal aqueous fluids before it arrives in the cecum. All this matrix is surrounded by a gastro-resistant polymer that only desintegrate in a pH lower than 7. All this administration-customed formulation allows for a bioavailability of <0.1% and the plasma concentrations are reported to be of <2 ng/ml in patients receiving a dose of 400 mg. This confirms that the site of action of rifamycin stays in the small intestine and colon which prevents the need for dose adjustments in special populations as well as systemic drug interactions. The reported Cmax, tmax, AUC and mean residence time after a dosage of 250 mg of rifamycin is 36 mg/L, 5 min, 11.84 mg.h/L and 0.49 h respectively. From the administered dose, 18%, 50% and 21% is recovered in feces during the first 24, 48 and 72h after administration. This will represent about 90% of the administered dose eliminated by the feces while the urinary secretion is negligible. The reported volume of distribution after measured after a dosage of 250 mg of rifamycin is 101.8 L. The reported clearance when a dose of 250 mg of rifamycin was administered is 23.3 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites When absorbed, rifamycin is mainly metabolzied in hepatocytes and intestinal microsomes to a 25-deacetyl metabolite. Biological Half-Life The reported half-life when a dose of 250 mg of rifamycin was administered is 3 h. |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In prelicensure controlled trials in patients with traveler’s diarrhea, rates of serum ALT elevations were similar in subjects treated with rifamycin compared to placebo or comparator agent (ciprofloxacin) and no participants developed clinically apparent liver injury. Since its approval, there have been no published reports of hepatotoxicity attributed to rifamycin. Because of its minimal absorption rifamycin is considered unlikely to cause liver injury. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Rifamycin is negligibly absorbed orally and used only for gastrointestinal infections. It is not likely to reach the breastmilk or bloodstream of the infant or cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants after maternal use. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding The protein binding of rifamycin is of about 80-95%. |
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Rifamycin is known to be effective against Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens and mycobacteria. It is very effective against _E. coli_ reporting a MIC90 of 64-128 mcg/ml without showing cross-resistance with other antimicrobial agents. The specific indication of rifamycin is extremely important as ther were previous reports that indicated a high risk factor in the generation of resistant _E. coli_ strains in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. In clinical trials, rifamycin was tested in a randomized clinical trial of travellers' coming from Mexico and Guatemala. In this trial, rifamycin was proven to significantly reduce the symptoms of travellers' diarrhea. |
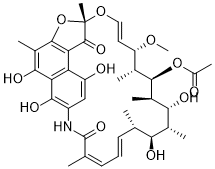
| 分子式 |
C37H47NO12
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
697.78
|
| 精确质量 |
697.31
|
| CAS号 |
6998-60-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Rifamycin sodium;14897-39-3
|
| PubChem CID |
6324616
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 熔点 |
300° (dec 140°)
|
| LogP |
4.892
|
| tPSA |
201.31
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
6
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
12
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
50
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1330
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
9
|
| SMILES |
[C@H]1(C)[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](C=CO[C@]2(OC=3C(C2=O)=C4C(C(=C(NC(C(=CC=C[C@H](C)[C@@H]([C@@H](C)[C@H]1O)O)C)=O)C=C4O)O)=C(C3C)O)C)OC)C)OC(=O)C
|
| InChi Key |
HJYYPODYNSCCOU-ODRIEIDWSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C37H47NO12/c1-16-11-10-12-17(2)36(46)38-23-15-24(40)26-27(32(23)44)31(43)21(6)34-28(26)35(45)37(8,50-34)48-14-13-25(47-9)18(3)33(49-22(7)39)20(5)30(42)19(4)29(16)41/h10-16,18-20,25,29-30,33,40-44H,1-9H3,(H,38,46)/b11-10+,14-13+,17-12-/t16-,18+,19+,20+,25-,29-,30+,33+,37-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
[(7S,9E,11S,12R,13S,14R,15R,16R,17S,18S,19E,21Z)-2,15,17,27,29-pentahydroxy-11-methoxy-3,7,12,14,16,18,22-heptamethyl-6,23-dioxo-8,30-dioxa-24-azatetracyclo[23.3.1.14,7.05,28]triaconta-1(29),2,4,9,19,21,25,27-octaen-13-yl] acetate
|
| 别名 |
Rifamycin Rifocin CB0111Rifocin RifocynAemcolo CB-0111NSC-133100CB-01-11 CB01-11 CB 01-11 CB 0111 NSC 133100Rifamicine SV Rifamycin SV Rifomycin SV
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.4331 mL | 7.1656 mL | 14.3312 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2866 mL | 1.4331 mL | 2.8662 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1433 mL | 0.7166 mL | 1.4331 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。