| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Anti-ocular hypertension; BK channels
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
H2O2 处理前一小时,用乌诺前列酮(0.01、0.1 和 1 μM)进行预处理,以浓度依赖性方式抑制 H2O2 诱导的细胞死亡率,在 0.1 μM 和 1 μM 浓度下显示出最大效果 [1]。用 0.1 至 3 μM 剂量的乌诺前列酮预处理,以浓度依赖性方式抑制光诱导的细胞凋亡;在浓度为 1 和 3 μM 时,影响显着。乌诺前列酮可减少形态改变,并显着防止光照射引起的线粒体膜电位低和细胞死亡 [1]。乌诺前列酮的 Ki 值为 3.86 μM,表现出与前列腺素 F2α 受体 (FP) 的结合亲和力 [2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
乌诺前列酮(0.06%、0.12%;局部滴注;3 µl)以剂量依赖性方式降低小鼠眼内压 (IOP) [3]。
WT和FPKO小鼠的基线眼压(平均+/-SEM)白天分别为15.0+/-0.2和15.0+/-0.3 mm Hg,晚上分别为18.9+/-0.4和19.2+/-0.4 mm Hg。在WT小鼠中,拉坦前列素分别在施用后2至6小时和1至6小时显著降低了白天和夜间的眼压。在药物滴注后3小时,无论是白天(10.9+/-1.8%)还是晚上(23.2+/-1.1%),眼压都出现了最大程度的降低。滴注后3小时,拉坦前列素(白天和夜间分别为10.9+/-1.8%和23.2+/-1.1%)、曲伏前列素(15.9+/-1.4%和26.1+/-1.2%)和比马前列素(8.8+/-2.0和19.8+/-1.5%)显著降低了WT小鼠白天和晚上的眼压;异丙基乌诺前列酮在夜间显著降低了眼压(13.7+/-1.9%),但在白天没有降低(5.3+/-3.2%)。在FPKO小鼠中,拉坦前列素、曲伏前列素、比马前列素和乌诺前列酮没有显示出明显的降眼压作用。Bunazosin显著降低了WT(22.1+/-1.6%)和FPKO小鼠(22.2+/-2.1%)的眼压。 结论:单次应用拉坦前列素、曲伏前列素、比马前列素或乌诺前列素对推测具有功能性葡萄膜巩膜流出途径的FPKO小鼠的眼压没有影响。前列腺素FP受体在所有市售前列腺素类似物早期降低眼压的机制中起着至关重要的作用[3]。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[1]
细胞类型: H2O2 诱导的感光细胞 测试浓度: 0.01、0.1、1 μM 孵育持续时间: H2O2 处理前 1 小时 实验结果: 以浓度依赖性方式防止 H2O2 诱导的细胞死亡。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male mice (6 weeks old) [3]
Doses: 0.06%, 0.12% Route of Administration: local infusion; 3 µl Experimental Results: Reduce IOP in mice in a dose-dependent manner. FPKO and wild-type (WT) mice were bred and acclimatized under a 12-hour light-dark cycle. IOP was measured under general anesthesia by a microneedle. Method: To evaluate the effects of each drug, a single drop (3 muL) of each drug solution was topically applied in a masked manner to a randomly selected eye. IOP reduction was evaluated by the difference in IOP between the treated eye and the untreated contralateral eye in the same mouse. First, the diurnal variation and baseline IOP in WT and FPKO mice were measured. Then, to determine the window feasible for demonstrating the most marked ocular hypotensive effect, 0.005% latanoprost was applied to WT mice during the day or at night. The time when the ocular hypotensive effect was larger was selected for further studies to evaluate the effects of latanoprost (0.005%), travoprost (0.004%), bimatoprost (0.03%), and unoprostone (0.12%). In addition, bunazosin (0.1%) was also applied to demonstrate functional uveoscleral outflow in FPKO mice. All experiments were conducted under a masked study design.[3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
After application to the eye, unoprostone isopropyl is absorbed through the cornea and conjunctival epithelium where it is hydrolyzed by esterases to unoprostone free acid. mean peak unoprostone free acid plasma concentration was <1.5 ng/mL and dro pped below the lower limit of quantitation (<0.250 ng/mL) 1 hour following instillation, indicating low systemic absorption and rapid plasma excretion. Elimination of unoprostone free acid from human plasma is rapid. Plasma levels of unoprostone free acid dropped below the lower limit of quantitation ( < 0.25 ng/mL) 1 hour following ocular instillation. Urinary elimination is the predominant elimination route. Intended for local use only, very low systemic absorption. Intended for local use only, very low systemic absorption. Metabolism / Metabolites After ocular application, unoprostone isopropyl is hydrolyzed by esterases in the cornea to its biological active metabolite, unoprostone free acid. Unoprostone free acid is then metabolized to several inactive metabolites with lower molecular weight and increased polarity via ε- or β-oxidation. No secondary conjugation is found and no significant effect on hepatic microsomal enzyme activity has been observed. Biological Half-Life Half-life of Unoprostone is 14 minutes. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of unoprostone during breastfeeding. Because of its short half-life it is not likely to reach the bloodstream of the infant or cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. Professional guidelines consider prostaglandin eye drops acceptable during breastfeeding. To substantially diminish the amount of drug that reaches the breastmilk after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Intended for local use only, very low systemic absorption. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
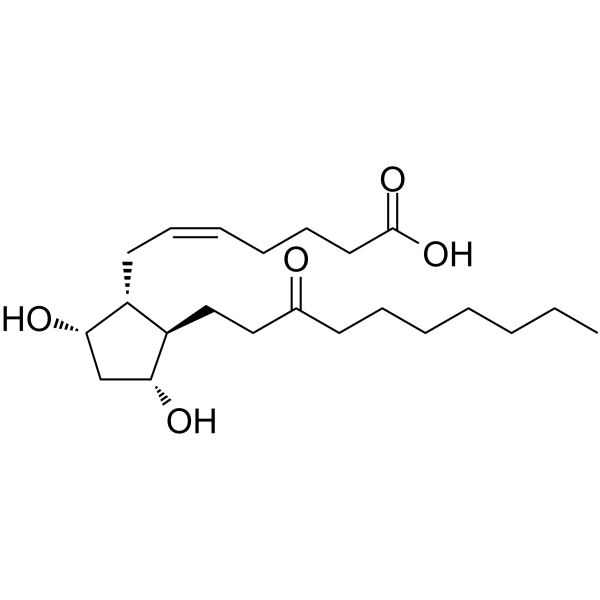
Unoprostone is an oxo monocarboxylic acid, a prostaglandins Falpha and a ketone. It has a role as an antiglaucoma drug and an antihypertensive agent.
Unoprostone isopropyl is a prostaglandin analogue. Ophthalmic Solution 0.15% is a synthetic docosanoid. Unoprostone isopropyl has the chemical name isopropyl (+)-(Z)-7-[(1R,2R,3R,5S)-3,5 dihydroxy-2-(3-oxodecyl)cyclopentyl]-5-heptenoate. The main indication of Unoprostane is treatment of glucoma. Unoprostone is a Prostaglandin Analog. Drug Indication For the lowering of intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension who are intolerant of other intraocular pressure lowering medications or insufficiently responsive (failed to achieve target IOP determined after multiple measurements over time) to another intraocular pressure lowering medication. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Unoprostone is believed to reduce elevated intraocular pressure (IOP), by increasing the outflow of aqueous humor. The mechanism of action for the IOP-lowering effect of unoprostone is controversial. Early studies showed that unoprostone increases aqueous humor outflow through the uveoscleral pathway similar to the 20-carbon prostaglandin analogs, such as latanoprost.8 More recent evidence, however, shows that it may work, at least in part, through stimulation of Ca2+-activated BK and CIC-2 type channels, leading to increased trabecular meshwork outflow. Pharmacodynamics Unoprostone will begin to reduce IOP 30 minutes after ocular instillation. |
| 分子式 |
C22H38O5
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
382.53412
|
| 精确质量 |
382.271
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 69.08; H, 10.01; O, 20.91
|
| CAS号 |
120373-36-6
|
| PubChem CID |
5311236
|
| 外观&性状 |
Colorless to light yellow liquids
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
562.9±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
308.3±23.8 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.5 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.509
|
| LogP |
3.19
|
| tPSA |
94.83
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
15
|
| 重原子数目 |
27
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
460
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
| SMILES |
CCCCCCCC(CC[C@H]1C(O)CC(O)C1C/C=C/CCCC(=O)O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
TVHAZVBUYQMHBC-SNHXEXRGSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H38O5/c1-2-3-4-5-8-11-17(23)14-15-19-18(20(24)16-21(19)25)12-9-6-7-10-13-22(26)27/h6,9,18-21,24-25H,2-5,7-8,10-16H2,1H3,(H,26,27)/b9-6-/t18-,19-,20+,21-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(Z)-7-[(1R,2R,3R,5S)-3,5-dihydroxy-2-(3-oxodecyl)cyclopentyl]hept-5-enoic acid
|
| 别名 |
Unoprostone; 120373-36-6; Unoprostone [MI]; Unoprostone [INN]; 13,14-dihydro-15-keto-20-ethyl PGF2alpha; Unoprostane; CHEBI:39455; 6X4F561V3W;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6142 mL | 13.0709 mL | 26.1417 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5228 mL | 2.6142 mL | 5.2283 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2614 mL | 1.3071 mL | 2.6142 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。