| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
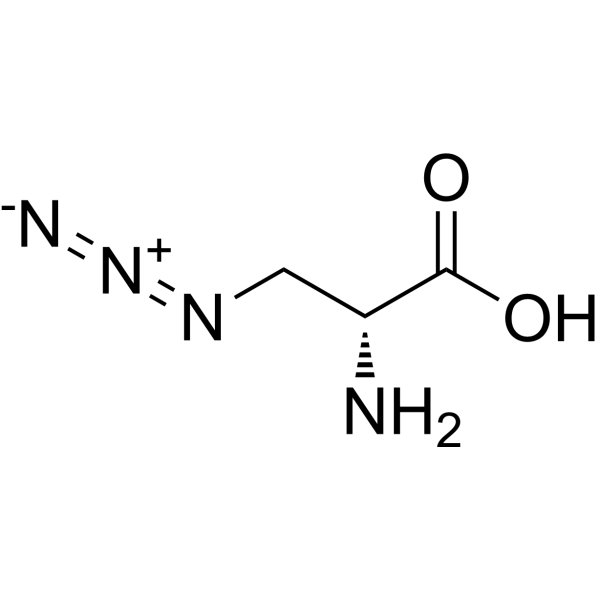
Azido-modified D-alanine for click chemistry labeling
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
磺酸基-DBCO-ICG与3-叠氮-d-丙氨酸/D-AzAla标记细菌的结合特性表征[1]
通过将磺酸基-DBCO-ICG与3-azido-d-alanine/d-AzAla标记细菌进行共价偶联,我们采用共聚焦激光扫描显微镜(CLSM)、流式细胞术等实验验证了磺酸基-DBCO-ICG在3-叠氮-d-丙氨酸/d-AzAla标记细菌表面的有效包被。如图2A所示,CLSM检测到磺酸基-DBCO-ICG-细菌复合物具有ICG荧光信号。流式细胞术分析进一步证实该结果,与未标记ICG的空白细菌组(无ICG荧光)相比,磺酸基-DBCO-ICG-细菌组显示出强ICG荧光信号(图2B)。紫外-可见吸收光谱显示(图2C),d-AzAla标记细菌表面包被的磺酸基-DBCO-ICG吸收峰从779nm红移至795nm,这主要归因于磺酸基-DBCO-ICG与细菌表面叠氮基团的相互作用。 ICG在808nm近红外光照射下可产热导致细菌光热裂解。在808nm激光照射下,空白细菌组温度仅升至26.7°C,而ICG-细菌组90秒内最高温度达57.2°C(图2D)。通过ATP检测仪验证发现(图2E),近红外照射后,d-AzAla标记的ICG-细菌组释放大量ATP,而其他组因缺乏ICG介导的光热效应仅释放微量ATP。透射电镜(TEM)和扫描电镜(SEM)观察显示(图2F-G):经808nm照射后,磺酸基-DBCO-ICG-细菌组(b)发生明显形态改变和裂解;而未偶联DBCO-ICG的细菌组(a)无论是否接受照射均保持完整形态,间接证明单纯808nm红外激光对细菌形态影响极微。上述结果共同表明:磺酸基-DBCO-ICG能有效包被d-AzAla标记细菌,并在808nm近红外光照射下通过产热作用裂解释放ATP。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
靶向能力评估通过体内成像实验进行验证。在靶向验证实验中,采用四组处理MRSA感染的小鼠伤口:PBS组、游离ICG+3-叠氮-d-丙氨酸/d-AzAla组、DBCO-ICG组、以及DBCO-ICG+d-AzAla组。静脉注射不同ICG制剂后0.5、3和6小时,使用动物活体成像仪观察各组靶向效果。如图5D-E所示,在各时间点DBCO-ICG+d-AzAla组在MRSA感染皮肤的荧光分布强度均显著高于游离ICG+d-AzAla组,其中3小时时间点的荧光强度达到峰值(**p=0.0036)。同时发现游离ICG不仅缺乏靶向性且代谢迅速(与文献Lim等2014年报道一致),而DBCO-ICG在给药6小时后仍能在感染伤口周围检测到荧光,表明DBCO基团的引入不仅使ICG能与d-AzAla发生点击化学反应,还延长了ICG的体内代谢时间。
给药3小时后对MRSA感染模型进行近红外照射,检测产热效果。如图5F所示,DBCO-ICG+d-AzAla组经180秒照射后,小鼠背部感染皮肤温度可达46°C(该温度可有效裂解细菌,参见Yang等2019和Shen等2020研究),而其他组仅升温至38°C左右。上述结果证实DBCO-ICG能精准靶向MRSA感染伤口,并在808nm近红外照射下达到杀菌温度。 体内抗菌与生物相容性[1] 在验证靶向性和光热效应后,我们评估了DBCO-ICG对MRSA感染伤口的治疗效果。小鼠背部创面分别采用PBS+NIR、DBCO-ICG(D-ICG)+NIR、游离ICG+3-叠氮-d-丙氨酸(F-ICG+d)+NIR、DBCO-ICG+d-3-azido-d-alanine/AzAla(D-ICG+d)+NIR处理(造模流程见图6A)。通过两周后伤口愈合情况和细菌载量评价疗效。 如图6B-C所示,虽然各组伤口均出现愈合,但D-ICG+d治疗组的瘢痕面积显著小于其他组,表明该组能显著加速伤口愈合并具有最佳杀菌效果。F-ICG+d组与D-ICG组的治疗效果无显著差异,且均逊于D-ICG+d组,说明游离ICG缺乏体内靶向性,无法与细菌表面氨基酸发生叠氮反应;单独DBCO-ICG的抗菌效果也有限。只有通过无铜点击化学反应使DBCO-ICG与d-AzAla修饰的细菌结合,才能实现ICG包被细菌的荧光双检测和光热抗菌治疗(PTAT)。 第14天采用平板稀释法检测伤口组织细菌载量(图6D-E),D-ICG+d组能清除约95%的MRSA(***p<0.001)。H&E染色显示(图6F),其他组可见大量炎症细胞(中性粒细胞,红色箭头),而D-ICG+d组的炎症细胞极少,与正常皮肤组织相似,证实该组具有优异的抗菌和促愈合能力。 通过主要器官H&E染色评估系统性生物安全性(附图S3),与PBS组相比,各给药组均未观察到明显组织损伤或形态学改变,表明DBCO-ICG无显著生物毒性。上述结果证明DBCO-ICG在MRSA感染模型中具有高效抗菌作用且未诱发明显毒副作用。 |
| 细胞实验 |
磺酸基-DBCO-ICG标记细菌的共聚焦激光扫描显微镜与流式细胞术分析 [1]
将细菌悬浮液稀释至1×106-1×107 CFU/mL浓度范围。取250 μL细菌悬液与40 μL 1 mg/mL DBCO-ICG溶液及100 μL 3-叠氮-d-丙氨酸/d-AzAla在1.5 mL离心管中混合,37℃避光孵育1小时获得DBCO-ICG-细菌复合物。取10 μL染色菌液滴加于18 mm方形盖玻片,通过共聚焦激光扫描显微镜观察。同法制备的DBCO-ICG-细菌复合物经4%多聚甲醛固定后,使用LSRFortessa流式细胞仪检测(激发/发射波长780-810 nm),数据通过FlowJo v9.9.8软件分析。 基于ATP生物发光的光热裂解细菌检测 [1] 取200 μL细菌悬液依次与3-叠氮-d-丙氨酸/d-AzAla和DBCO-ICG混合,室温孵育30分钟后,采用808 nm激光(1.0 W/cm2)照射90秒。立即将处理液与荧光素酶溶液混合,30秒内在酶标仪上完成生物发光信号检测。 |
| 动物实验 |
Establishment of MRSA-Infected Mouse Models [1]
On day 4 before the infection, the mice were administered one dose of CTX. 150 mg CTX per kg mouse body weight (150 mg kg−1) was injected i. p. This treatment fostered a more vulnerable environment in the mice to infection. The mice were anesthetized using a standard anesthesia procedure, and then the dorsal region of the mice was shaved to prepare for surgery. Then one round wound of 80 mm in diameter was made using a puncher on the left back of mice weighing 30–40 g with 5 ICR male mice in each group. After 6 h, 50 μl of MRSA (1 × 108 CFU ml−1) was slowly added to each wound. In Vivo Antimicrobial Assay [1] After the establishment of MRSA-infected mouse models, the infection sites were treated with drugs and the same volume of PBS via the tail vein. PTAT treatment was conducted by irradiating the infection sites with laser irradiation (808 nm, 1.0 W cm−2) for 180 s. The infection sites were treated with PTAT solutions every 2 days. The regeneration process of wounds was studied through wound area monitoring and histomorphological determination. In wound size measurement, the mice in each group were anesthetized, and the wound size was determined by tracing the boundaries of wounds on days 3, 7, 11, and 14. For histomorphological evaluation, wound tissue of day 14 was collected for biochemical analysis. The samples were made into 0.5 cm2 square shape and immersed in standard formalin solution. Then tissue samples were conducted with H&E staining and prepared into a wax section for observation. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Bacterial infection is one of the most serious physiological conditions threatening human health. There is an increasing demand for more effective bacterial diagnosis and treatment through non-invasive approaches. Among current antibacterial strategies of non-invasive approaches, photothermal antibacterial therapy (PTAT) has pronounced advantages with properties of minor damage to normal tissue and little chance to trigger antimicrobial resistance. Therefore, we developed a fast and simple strategy that integrated the sensitive detection and photothermal therapy of bacteria by measuring adenosine triphosphate (ATP) bioluminescence following targeted photothermal lysis. First, 3-azido-d-alanine (d-AzAla) is selectively integrated into the cell walls of bacteria, photosensitizer dibenzocyclooctyne, and double sulfonic acid-modified indocyanine green (sulfo-DBCO-ICG) are subsequently designed to react with the modified bacteria through in vivo click chemistry. Next, the sulfo-DBCO-ICG modified bacteria under irradiation of 808 nm near-infrared laser was immediately detected by ATP bioluminescence following targeted photothermal lysis and even the number of bacteria on the infected tissue can be significantly reduced through PTAT. This method has demonstrated the ability to detect the presence of the bacteria for ATP value in 32 clinical samples. As a result, the ATP value over of 100 confirmed the presence of bacteria in clinical samples for 22 patients undergoing craniotomy and ten otitis media patients. Overall, this study paves a brand new avenue to facile diagnosis and a treatment platform for clinical bacterial infections.[1]
In summary, our study developed a simultaneous detection and antibacterial platform for bacterial infection. It is a fast and simple strategy for the sensitive detection of bacteria by measuring ATP bioluminescence following targeted photothermal lysis. Sulfo-DBCO-ICG reacted with 3-azido-d-alanine/d-AzAla modified bacteria by copper-free click chemistry to complete a precise and rapid target. The sulfo-DBCO-ICG effectively coated on d-AzAla-bacteria and could produce heat to crack bacteria for releasing ATP below 808 nm NIR irradiation in vitro. The sulfo-DBCO-ICG could rapidly detect intracranial infections in patients after neurosurgery through ATP detection and flow cytometry. The sulfo-DBCO-ICG has targeting ability, good antibacterial effect, and biocompatibility in the MRSA-infected model. This method is faster than the clinical microbiological culture process, does not cause any drug-resistance as caused by antibiotics, and is not toxic/harmful to healthy cells. It may provide a good idea for the clinical rapid detection of bacteria.[1] |
| 分子式 |
C3H6N4O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
130.10533952713
|
| 精确质量 |
130.049
|
| CAS号 |
105928-88-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
3-Azido-D-alanine hydrochloride; 1379690-01-3
|
| PubChem CID |
55785
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| LogP |
-2.5
|
| tPSA |
77.7
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
9
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
150
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
OC(C(CN=[N+]=[N-])N)=O
|
| InChi Key |
CIFCKCQAKQRJFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C3H6N4O2/c4-2(3(8)9)1-6-7-5/h2H,1,4H2,(H,8,9)
|
| 化学名 |
2-amino-3-azidopropanoic acid
|
| 别名 |
D-Alanine, 3-azido-; 2-amino-3-azidopropanoic acid; D-Azidoalanine; DL-Azidoalanine; 3-Azidoalanine; 105928-88-9; 88192-18-1; 108342-09-2;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 7.6858 mL | 38.4290 mL | 76.8580 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.5372 mL | 7.6858 mL | 15.3716 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.7686 mL | 3.8429 mL | 7.6858 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。