| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
醋丁洛尔是一种β受体阻滞剂,用于治疗心律失常和高血压。在大鼠中,醋丁洛尔(10 mg/kg)的血浆清除率为61.9 mL/min/kg,分布容积为9.6 L/kg,消除半衰期为1.8小时。在大鼠中,醋丁洛尔(50 mg/kg)的血浆清除率为46.5 mL/min/kg,分布容积为9.5 L/kg,消除半衰期为2.3小时[1]。在 Sprague-Dawley 大鼠中,在 1 分钟和 10 分钟测量后,醋丁洛尔 (30 mg/kg) 的心输出量分别减少了 65% 和 31%。与 Sprague-Dawley 大鼠的基线值相比,醋丁洛尔 (30 mg/kg) 显着降低了 1 或 10 分钟时测量的大多数器官的局部血流量 (RBF)。
|
|---|---|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Well absorbed from the Gl tract with an absolute bioavailability of approximately 40% for the parent compound. Elimination via renal excretion is approximately 30% to 40% and by non-renal mechanisms 50% to 60%, which includes excretion into the bile and direct passage through the intestinal wall. Metabolism / Metabolites Subject to extensive first-pass hepatic biotransformation (primarily to diacetolol). Biological Half-Life The plasma elimination half-life is approximately 3 to 4 hours. The half-life of its metabolite, diacetolol, is 8 to 13 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Acebutolol is associated with a low rate of mild-to-moderate elevations of serum aminotransferase levels during treatment. These enzyme elevations are usually asymptomatic and transient and resolve even with continuation of therapy. There have been few documented cases of clinically apparent, acute liver injury attributed to acebutolol. The time to onset of injury was typically between 1 and 6 weeks of starting. The pattern of liver enzyme elevations was usually hepatocellular with an acute hepatitis-like presentation, although some cases present with a mixed pattern of enzymes. Fever commonly accompanied the liver injury, but usually without rash and eosinophia. Acebutolol is known to induce autoantibodies such as antinuclear antibody in 10% to 30% of patients, some of whom develop a lupus-like syndrome with fatigue, skin rash and arthralgias. Serum enzyme elevations may accompany this syndrome, but jaundice and symptoms of liver injury are uncommon. The published cases of hepatotoxicity due to acebutolol were relatively mild, self-limited and recovery was rapid upon stopping. Rechallenge resulted in rapid recurrence of injury. Likelihood score: C (probable cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because of the relatively extensive excretion of acebutolol and its active metabolite diacetolol into breastmilk and some possible reports of adverse reactions in breastfed infants, other agents are preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A study of mothers taking beta-blockers during nursing found a numerically, but not statistically significant increased number of adverse reactions in those taking any beta-blocker. Although the ages of infants were matched to control infants, the ages of the affected infants were not stated. One mother reported no adverse effects in her breastfed infant (age unstated) during acebutolol use. Hypotension, bradycardia, and transient tachypnea occurred in a newborn infant, probably because of acebutolol and diacetolol in breastmilk. The mother was taking 400 mg daily of acebutolol and had renal impairment. Two other neonates in this report who were breastfed had no adverse reactions noted. A mother with essential hypertension had been taking acebutolol for several years. She continued the drug during her first pregnancy and while breastfeeding. Her infant was generally healthy, but seemed to have decreased muscle tone. She stopped the drug, but the infant continued to have stridor and possible sleep apnea. She was also taking acebutolol during her second pregnancy, but her blood pressure was uncontrolled and a cesarean section was performed. The infant did well in the NICU, except for decreased tone including lying with extremities extended, an incomplete Moro response and marked head lag. The infant was not breastfed. It is possible that the late postpartum adverse effects in the first infant were caused by acebutolol and diacetolol in breastmilk, but no measurements of infant plasma drug levels were made. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information on the effects of beta-blockade or acebutolol during normal lactation was not found as of the revision date. A study in 6 patients with hyperprolactinemia and galactorrhea found no changes in serum prolactin levels following beta-adrenergic blockade with propranolol. Protein Binding 26% |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Piquette-Miller, M. and F. Jamali, Pharmacokinetics and multiple peaking of acebutolol enantiomers in rats. Biopharm Drug Dispos, 1997. 18(6): p. 543-56.
[2]. Bristow MR, et al. Treatment of chronic heart failure with β-adrenergic receptor antagonists: a convergence of receptor pharmacology and clinical cardiology. Circ Res. 2011 Oct 28;109(10):1176-94. [3]. Mostafavi, S., R. Lewanczuk, and R. Foster, Influence of acebutolol and metoprolol on cardiac output and regional blood flow in rats. Biopharm Drug Dispos, 2000. 21(4): p. 121-8. |
| 其他信息 |
Acebutolol is an ether that is the 2-acetyl-4-(butanoylamino)phenyl ether of the primary hydroxy group of 3-(propan-2-ylamino)propane-1,2-diol. It has a role as a beta-adrenergic antagonist, an anti-arrhythmia drug, an antihypertensive agent and a sympathomimetic agent. It is a member of ethanolamines, a propanolamine, a secondary amino compound, an ether, a monocarboxylic acid amide and an aromatic amide. It is a conjugate base of an acebutolol(1+).
A cardioselective beta-adrenergic antagonist with little effect on the bronchial receptors. The drug has stabilizing and quinidine-like effects on cardiac rhythm as well as weak inherent sympathomimetic action. Acebutolol is a beta-Adrenergic Blocker. The mechanism of action of acebutolol is as an Adrenergic beta-Antagonist. Acebutolol is a cardioselective beta-blocker used in the treatment of hypertension, angina pectoris and cardiac arrhythmias. Acebutolol has been linked to several instances of clinically apparent drug induced liver injury. Acebutolol is a synthetic butyranilide derivative with hypotensive and antiarrhythmic activity. Acebutolol acts as a cardioselective beta-adrenergic antagonist with little effect on bronchial receptors and has intrinsic sympathomimetic properties. Having stabilizing and quinidine-like effects on cardiac rhythm, Acebutolol is used in ventricular arrhythmias. Other indications include hypertension, alone or in combinations with other agents. A cardioselective beta-1 adrenergic antagonist with little effect on the bronchial receptors. The drug has stabilizing and quinidine-like effects on cardiac rhythm, as well as weak inherent sympathomimetic action. See also: Acebutolol Hydrochloride (has salt form); Diacetolol (has subclass); Secradex (is active moiety of). Drug Indication For the management of hypertension and ventricular premature beats in adults. Mechanism of Action Acebutolol is a selective β1-receptor antagonist. Activation of β1-receptors by epinephrine increases the heart rate and the blood pressure, and the heart consumes more oxygen. Acebutolol blocks these receptors, lowering the heart rate and blood pressure. This drug then has the reverse effect of epinephrine. In addition, beta blockers prevent the release of renin, which is a hormone produced by the kidneys which leads to constriction of blood vessels. Pharmacodynamics Acebutolol is a cardioselective, beta-adrenoreceptor blocking agent, which possesses mild intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA) in its therapeutically effective dose range. In general, beta-blockers reduce the work the heart has to do and allow it to beat more regularly. Acebutolol has less antagonistic effects on peripheral vascular ß2-receptors at rest and after epinephrine stimulation than nonselective beta-antagonists. Low doses of acebutolol produce less evidence of bronchoconstriction than nonselective agents like propranolol but more than atenolol. |
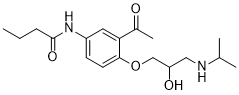
| 分子式 |
C18H28N2O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
336.43
|
| 精确质量 |
336.204
|
| CAS号 |
37517-30-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Acebutolol hydrochloride;34381-68-5;Acebutolol-d7;Acebutolol-d5;1189500-68-2
|
| PubChem CID |
1978
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
564.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
119-123ºC
|
| 闪点 |
295.0±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.543
|
| LogP |
1.95
|
| tPSA |
87.66
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
10
|
| 重原子数目 |
24
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
401
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CCCC(NC1=CC(C(C)=O)=C(OCC(O)CNC(C)C)C=C1)=O
|
| InChi Key |
GOEMGAFJFRBGGG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H28N2O4/c1-5-6-18(23)20-14-7-8-17(16(9-14)13(4)21)24-11-15(22)10-19-12(2)3/h7-9,12,15,19,22H,5-6,10-11H2,1-4H3,(H,20,23)
|
| 化学名 |
N-[3-acetyl-4-[2-hydroxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propoxy]phenyl]butanamide
|
| 别名 |
Acetobutolol Neptal Acebutolol Sectral Dl-Acebutolol Prent
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9724 mL | 14.8619 mL | 29.7239 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5945 mL | 2.9724 mL | 5.9448 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2972 mL | 1.4862 mL | 2.9724 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。