| 规格 | 价格 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg | |||
| 1g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
CBFβ SMMHC-RUNX1
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
为了开发CBFβ-SMMHC功能的靶向抑制剂,我们使用先前描述的荧光共振能量转移(FRET)测定法,用Venus-CBFβ-SSMHC代替Venus-CBFb(图S1),以筛选美国国立癌症研究所,NIH,Diversity Set中抑制CBFβ/SMMHC与RUNX1 Runt结构域结合的化合物。该筛选确定了活性化合物AI-4-577,其50%抑制浓度(IC50)为22μM,而缺乏甲氧基官能团的衍生物AI-4-88是无活性的(表1)。小分子结合后,蛋白质核磁共振(NMR)光谱中化学位移的变化是确认与蛋白质结合的有力方法。我们记录了具有CBFβ和Runt结构域的AI-4-57的二维2D 15N-1H异核单量子相干(HSQC)光谱和1D饱和转移差(STD)NMR实验。Runt结构域没有观察到相互作用,但我们可以证明,在添加AI-4-57后,CBFβ的HSQC光谱发生了化学位移扰动(图1A),在添加无活性衍生物AI-4-88后没有变化(图S2),这表明该化合物与CBFβ结合。骨架和两个芳香侧链[位置113(W113)的色氨酸和位置96(Y96)的酪氨酸]中的化学位移扰动表明,该化合物在空间上靠近CBFβ的位点结合,但不在CBFβ上的蛋白质相互作用表面上结合,也就是说,它以变构方式抑制结合[1]。
CBFβ-RUNX结合小分子抑制剂与CBFβ结合的初步研究[2] 我们最近报道了2-吡啶基苯并咪唑AI-4-57作为一种化合物,它与CBFβ-SMMHC融合蛋白的CBFβ部分结合,并抑制其与RUNX蛋白Runt结构域的结合(Illundula等人,2015)。使用我们之前描述的用于CBFβ氨基酸1-141部分与Runt结构域结合的FRET测定法(Gorczynski等人,2007),我们表明该化合物也是野生型CBFβ与RUNX1 Runt结构区结合的适度效力抑制剂(见图1,表3)。为了开发更有效的类似物用作探针RUNX和CBFβ蛋白功能的工具化合物,我们合成了一个AI-4-57类似物库,并对其活性进行了表征。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
对AI-4-57的药代动力学特性的分析表明,该化合物在小鼠血浆中的半衰期较短(t½=37分钟)(图S5),甲氧基官能团的甲基损失是主要代谢产物。三氟甲氧基(CF3O)取代已被证明反应性较低,因此我们用这种取代合成了AI-10-47。FRET测量表明,这种取代实际上增强了单价化合物的活性(表1)。肝微粒体稳定性的测量表明,AI-10-47降低了代谢责任,因此证明了二价衍生物AI-10-49的合成是合理的(表1)。AI-10-49是强效的(FRET IC50=260nM)(表1)[等温滴定量热法(ITC)测量得出解离常数(KD)=168 nM](图S6),改善了体内药代动力学特性(t½=380min)(图S5),与母体质子化二价化合物AI-4-83(IC50约为3μM)相比,对ME-1细胞生长的抑制活性增强(IC50=0.6 mM)(图1F)(图1E)。请注意,AI-10-49在正常人骨髓细胞中显示出可忽略的活性(IC50>25μM)(图1G),这表明了一个强大的潜在治疗窗口。在11种人类白血病细胞系中,ME-1细胞是唯一对AI-10-49高度敏感的细胞系[1]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
Docking[2]
在网格生成中,在对接选项卡下,我们将该位点用作蛋白质中结合位点残基的质心。通过蛋白质与AI-4-57结合的15N-1H和13C-1H HSQC NMR实验中的化学位移扰动来确定活性位点残基。选择以下残基进行网格生成:V86、L88、R90、E91、Y96、K98、A99、K111、G112、W113、M122、G123、C124。对接是使用虚拟筛选工作流框架进行的。所有化合物都灵活对接,对接后,100%具有所有良好状态的最佳化合物由MM-GBSA评分。 CBFβ突变蛋白[2] 野生型CBFβ(1-141)和CBFβ突变体R90E、K98E和K111E在15N标记的最低培养基中于15°C下表达。使用Ni-NTA柱纯化蛋白质,用rTev蛋白酶消化过夜,然后进行尺寸排阻色谱以去除亲和标签和杂质。将150μM的蛋白质样品透析,插入核磁共振缓冲液中,用600μM AI-4-57滴定。所有15N-1H HSQC都记录在配备有冷冻探针的布鲁克800 MHz NMR光谱仪上。 核磁共振波谱[2] 所有基于NMR的实验都是使用CBFβ(1-141)溶液在含有50 mM KPi、0.1 mM EDTA、1 mM DTT、0.01%(w/v)叠氮化钠、5%(v/v)DMSO和5%(v/v)D2O的缓冲液中获得的,最终pH值为7.5。所有实验均在配备CryoProbe™的Bruker 18.8 T光谱仪上记录在25°C下浓缩至0.5 mM的均匀标记的15N CBFβ样品上。所有NMR数据均使用NMRPipe进行处理。通过在100%DMSO中加入AI-4-57以产生等摩尔蛋白质化合物溶液来制备含有化合物的样品。 15N和13C化学位移扰动分别由在AI-4-57存在和不存在的情况下收集的15N-和13C-HSQC实验确定。使用先前已知的共振来分配峰,并使用CcpNMR软件套件叠加和比较光谱(Vranken等人,2005)。如袁等人(2002)所述,通过使用方程式∆15N+1HN)=| \8710》δHN|+(|∇δN|/4.69)计算加权化学位移变化(百万分之几)。0.1 ppm或更大的共振偏移被认为是显著的。 所有15N弛豫测量都是用CBFβ+AI-4-57和单独的CBFβ样品进行的。使用10、180、300、500、1300、1800和2300 ms的弛豫延迟进行15N T1实验。15N T2实验使用10、25、50、75、100、150、200、225和250 ms的弛弛豫延迟。峰值强度符合y=Ae-Bx,其中B是弛豫速率(R),使用CcpNMR确定T1和T2弛豫时间。R1和R2弛豫率是T1和T2的倒数,用于计算蛋白质与化合物和蛋白质与DMSO单独的R1*R2和R2/R1值。计算CBFβ+AI-4-57单独CBFβ样品的R1、R2、R1*R2和R2/R1值之间的差异。R1*R2变化大于两个标准差的残基,高于或低于由60%数据中位数组成的修剪平均值,被认为存在显著差异。 饱和转移差异NMR样品由200μM CBFβ、2 mM AI-4-57、10%D2O和5%DMSO组成,溶于50 mM KPi、1 mM DTT、0.1 mM EDTA、001%w/v NaN3、pH 7.5,最终体积为200μl。所有STD实验均使用600 MHz Bruker NMR光谱仪在25°C下进行,饱和时间为500、750、1000、1500和2000 ms。样品在0.4 ppm(蛋白质)和30 ppm(非共振对照)下照射,并使用MestReNova计算差谱。 |
| 动物实验 |
Pharmacokinetic Studies [1]
Prior to the study, mice were fasted at least three hours and water was available ad libitum. Animals were housed on a 12-hour light/dark cycle at 72-74°C and 30-50% relative humidity. For intraperitoneal dosing 24 – 28 gm male C57BL/6 mice were manually restrained and injected in the peritoneal cavity midway between the sternum and pubis and slightly off the midline of the mouse. A 1-cc syringe with a 27-gauge needle was used for each injection. Blood was collected from the animals according to scheduled time points. Animals were anesthetized with isoflurane and blood drawn via cardiac puncture. Blood was immediately transferred to 1.5 mL heparinized microcentrifuge tubes and centrifuged at 4000 rpm for ten minutes. Plasma was then transferred to clean tubes and frozen. Due to exsanguination, the animals did not wake from the anesthesia and death was insured while under anesthesia by thoracotomy. This method is consistent with the recommendations of the AVMA Guidelines on Euthanasia for use of exsanguination as a means of euthanasia. Noncompartmental pharmacokinetic analysis of the test compound plasma concentration-time data was conducted using PK Solutions 2.0. [1] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Inhibitors With Favorable ADMET Properties
Development of a useful tool compound which can be utilized for in vivo studies requires optimization not only of the activity of the compound but also its metabolic stability in vivo. In the context of our previous work on development of small molecule inhibitors that are specific for CBFβ-SMMHC (Illendula et al., 2015), we showed that AI-4-57 has a short half-life in mice with loss of the methyl group on the methoxy functionality being the resulting metabolite. Introduction of trifluoromethoxy abrogated the metabolic liability. Introduction of a trifluoromethoxy substitution into AI-4-57 yielded a compound (AI-10-47) with improved activity in the FRET assay (see Table 1) as well as in assays of cellular activity (see below). Introduction of this substitution into 7a (Supplementary Fig. 1), yielded the inhibitor AI-10-104 with IC50 = 1.25 μM (Table 1). However, administration of AI-10-104 to mice via intraperitoneal (IP) injection of a captisol formulation at 178 mg/kg resulted in significant sedative effects within 30 s, from which the mice recovered in approximately 1 h, whereas administration of a nanoparticle formulation at 200 mg/kg was lethal in approximately ~ 3.5 h. Hypothesizing that this effect is driven by an off-target activity, we have engineered additional analogs (AI-12-126, AI-14-55, and AI-14-91, see Table 1) where we have appended morpholine ring substituents to the pyridine ring, thereby altering the structure as well as polarity of the compounds. These compounds retain similar activity in the FRET assay to the parent compounds (see Table 3). Importantly, AI-12-126 and AI-14-91, when formulated as the HCl salts with captisol and administered IP at 100 mg/kg do not induce the sedative effects seen with AI-10-104 and are well-tolerated by mice. Measurements of the pharmacokinetic properties of these compounds in mice (see Supplementary Fig. 2) showed that at a dose of 100 mg/kg, we can achieve useful concentrations of the compounds with reasonable half-lives in vivo (AI-14-91, oral gavage, t1/2 = 203 min). These derivatives are, therefore, viable options for in vivo studies of CBFβ and RUNX function.
|
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Chemical biology. A small-molecule inhibitor of the aberrant transcription factor CBFβ-SMMHC delays leukemia in mice. Science. 2015 Feb 13;347(6223):779-84.
[2]. Small Molecule Inhibitor of CBFβ-RUNX Binding for RUNX Transcription Factor Driven Cancers. EBioMedicine. 2016 Jun;8:117-131. |
| 其他信息 |
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common form of adult leukemia. The transcription factor fusion CBFβ-SMMHC (core binding factor β and the smooth-muscle myosin heavy chain), expressed in AML with the chromosome inversion inv(16)(p13q22), outcompetes wild-type CBFβ for binding to the transcription factor RUNX1, deregulates RUNX1 activity in hematopoiesis, and induces AML. Current inv(16) AML treatment with nonselective cytotoxic chemotherapy results in a good initial response but limited long-term survival. Here, we report the development of a protein-protein interaction inhibitor, AI-10-49, that selectively binds to CBFβ-SMMHC and disrupts its binding to RUNX1. AI-10-49 restores RUNX1 transcriptional activity, displays favorable pharmacokinetics, and delays leukemia progression in mice. Treatment of primary inv(16) AML patient blasts with AI-10-49 triggers selective cell death. These data suggest that direct inhibition of the oncogenic CBFβ-SMMHC fusion protein may be an effective therapeutic approach for inv(16) AML, and they provide support for transcription factor targeted therapy in other cancers. [1]
Transcription factors have traditionally been viewed with skepticism as viable drug targets, but they offer the potential for completely novel mechanisms of action that could more effectively address the stem cell like properties, such as self-renewal and chemo-resistance, that lead to the failure of traditional chemotherapy approaches. Core binding factor is a heterodimeric transcription factor comprised of one of 3 RUNX proteins (RUNX1-3) and a CBFβ binding partner. CBFβ enhances DNA binding of RUNX subunits by relieving auto-inhibition. Both RUNX1 and CBFβ are frequently mutated in human leukemia. More recently, RUNX proteins have been shown to be key players in epithelial cancers, suggesting the targeting of this pathway could have broad utility. In order to test this, we developed small molecules which bind to CBFβ and inhibit its binding to RUNX. Treatment with these inhibitors reduces binding of RUNX1 to target genes, alters the expression of RUNX1 target genes, and impacts cell survival and differentiation. These inhibitors show efficacy against leukemia cells as well as basal-like (triple-negative) breast cancer cells. These inhibitors provide effective tools to probe the utility of targeting RUNX transcription factor function in other cancers. [2] |
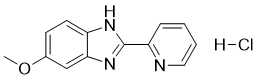
| 分子式 |
C13H12CLN3O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
261.71
|
| 精确质量 |
225.09
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 59.66; H, 4.62; Cl, 13.55; N, 16.06; O, 6.11
|
| CAS号 |
63053-14-5
|
| PubChem CID |
186762
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.268g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
459.9ºC at 760mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
164.7ºC
|
| LogP |
2.633
|
| tPSA |
50.8
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
17
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
261
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
COC1=CC2=C(C=C1)N=C(N2)C3=CC=CC=N3
|
| InChi Key |
FXXLTIFEBMOGOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C13H11N3O/c1-17-9-5-6-10-12(8-9)16-13(15-10)11-4-2-3-7-14-11/h2-8H,1H3,(H,15,16)
|
| 化学名 |
6-methoxy-2-pyridin-2-yl-1H-benzimidazole
|
| 别名 |
AI-4-57 Hydrochloride; AI457 Hydrochloride; 63053-14-5; 6-methoxy-2-pyridin-2-yl-1H-benzimidazole; 5-methoxy-2-(pyridin-2-yl)-1h-benzimidazole; 5-Methoxy-2-pyridin-2-yl-1H-benzoimidazole; MLS001208923; SMR000503813; 5-Methoxy-2-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole; 1H-Benzimidazole, 6-methoxy-2-(2-pyridinyl)-; AI 4 57 Hydrochloride; AI 4 57 HCl; AI457 HCl; AI-4-57 HCl
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.8210 mL | 19.1051 mL | 38.2102 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7642 mL | 3.8210 mL | 7.6420 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3821 mL | 1.9105 mL | 3.8210 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。