| 规格 | 价格 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg | |||
| 1g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
ETA receptor
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Ambrisentan钠是一种内皮素A型受体拮抗剂[1]。 Nrf2 被 ambrisentan 钠激活。与媒介物对照相比,安立生坦减少了缺氧引起的 BMEC 渗漏,并且 BMEC 单层的内皮通透性在暴露于缺氧 24 小时后增加。当在治疗前用靶向 Nrf2 的 siRNA 转染 BMEC 时,这些结果发生了逆转 [2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Ambrisentan 组的肝脏羟脯氨酸浓度显着低于对照组(分别为 18.0 μg/g±6.1 μg/g 和 33.9 μg/g±13.5 μg/g 肝脏,P=0.014)。通过天狼星红染色测定,安立生坦组的肝纤维化和 α-平滑肌肌动蛋白阳性区域均显着减少,这表明肝星状细胞活化(分别为 0.46% ± 0.18% 和 1.11% ± 0.28%,P =0.0003;和 0.12%±0.08% vs 0.25%±0.11%,分别,P=0.047)。此外,Ambrisentan 组的前胶原-1 和金属蛋白酶组织抑制剂-1 (TIMP-1) 的肝脏 RNA 表达水平分别显着降低 60% 和 45%。在肝脏中,各组之间的脂肪变性、炎症或内皮素相关 mRNA 表达没有明显差异。通过降低 proollagen-1 和 TIMP-1 基因表达并阻止肝星状细胞的活化,ambrisentanodium 可以减缓肝纤维化的发展。安布里生坦钠不影响脂肪变性和炎症[1]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
除非另有说明,每次 BMEC 实验的细胞被随机分配到四组:(1)常氧载体对照(Nx-CTRL); (2)常氧处理; (3)缺氧(24 h)对照(Hx-CTRL); (4)缺氧(24小时)处理。如前所述,在任何缺氧暴露前 24 小时添加 Nrf2 激活剂。 Protandim (100 μg/mL)、醋甲唑胺 (125 μg/mL)、硝苯地平 (7 μg/mL) 或 ambrisentan (40 μg/mL) 是细胞处理剂。此外,Nrf2 siRNA 还应用于一部分细胞。在这些测试中,在给药前 24 小时添加 siRNA。 BMEC 24小时缺氧暴露的目的是保证细胞在24小时缺氧暴露和药物预处理(常氧24小时)期间维持其siRNA转染。在不同的三天 (n=9),从至少三种不同的细胞培养制剂中收集数据 [2]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Mice: The experimental group consists of thirteen male FLS-ob/ob mice, weighing 42.88 g±1.74 g and aged 8 weeks. Male FLS-ob/ob mice are randomized at random to either the control (n = 5) or Ambrisentan (n = 8) group at 12 weeks or older. When a conscious animal has a gastric tube that is the right size, intragastric gavage is administered. Through the use of a gastric tube, ambrisentan (2.5 mg/kg daily) is given orally as a bolus every afternoon for four weeks. The group under control receives water treatment. The fourth week involves fasting the animals for four hours, drawing blood from the tail vein, and testing their blood glucose levels. Blood is extracted from the right ventricle and the animals are put to death after four weeks by injection with pentobarbital anesthesia. Plasma samples are kept at -80°C in a frozen state. The fat from the liver and viscera is then weighed, liquid nitrogen-snap frozen, and kept at -80°C for storage. Further liver specimens are embedded in paraffin and fixed in 10% buffered formalin for histological examination.
|
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Aim: To examine the effects of the endothelin type A receptor antagonist ambrisentan on hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in a steatohepatitis mouse model.[1]
Methods: Fatty liver shionogi (FLS) FLS-ob/ob mice (male, 12 wk old) received ambrisentan (2.5 mg/kg orally per day; n = 8) or water as a control (n = 5) for 4 wk. Factors were compared between the two groups, including steatosis, fibrosis, inflammation, and endothelin-related gene expression in the liver.[1] Results: In the ambrisentan group, hepatic hydroxyproline content was significantly lower than in the control group (18.0 μg/g ± 6.1 μg/g vs 33.9 μg/g ± 13.5 μg/g liver, respectively, P = 0.014). Hepatic fibrosis estimated by Sirius red staining and areas positive for α-smooth muscle actin, indicative of activated hepatic stellate cells, were also significantly lower in the ambrisentan group (0.46% ± 0.18% vs 1.11% ± 0.28%, respectively, P = 0.0003; and 0.12% ± 0.08% vs 0.25% ± 0.11%, respectively, P = 0.047). Moreover, hepatic RNA expression levels of procollagen-1 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) were significantly lower by 60% and 45%, respectively, in the ambrisentan group. Inflammation, steatosis, and endothelin-related mRNA expression in the liver were not significantly different between the groups.[1] Conclusion: Ambrisentan attenuated the progression of hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation and reducing procollagen-1 and TIMP-1 gene expression. Ambrisentan did not affect inflammation or steatosis.[1] Reactive oxygen species (ROS) formed during acute high altitude exposure contribute to cerebral vascular leak and development of acute mountain sickness (AMS). Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a transcription factor that regulates expression of greater than 90% of antioxidant genes, but prophylactic treatment with Nrf2 activators has not yet been tested as an AMS therapy. We hypothesized that prophylactic activation of the antioxidant genome with Nrf2 activators would attenuate high-altitude-induced ROS formation and cerebral vascular leak and that some drugs currently used to treat AMS symptoms have an additional trait of Nrf2 activation. Drugs commonly used to treat AMS were screened with a luciferase reporter cell system for their effectiveness to activate Nrf2, as well as being tested for their ability to decrease high altitude cerebral vascular leak in vivo. Compounds that showed favorable results for Nrf2 activation from our screen and attenuated high altitude cerebral vascular leak in vivo were further tested in brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs) to determine if they attenuated hypoxia-induced ROS production and monolayer permeability. Of nine drugs tested, with the exception of dexamethasone, only drugs that showed the ability to activate Nrf2 (Protandim, methazolamide, nifedipine, amlodipine, ambrisentan, and sitaxentan) decreased high-altitude-induced cerebral vascular leak in vivo. In vitro, Nrf2 activation in BMECs before 24h hypoxia exposure attenuated hypoxic-induced hydrogen peroxide production and permeability. Prophylactic Nrf2 activation is effective at reducing brain vascular leak from acute high altitude exposures. Compared to acetazolamide, methazolamide may offer better protection against AMS. Nifedipine, in addition to its known vasodilatory activities in the lung and protection against high altitude pulmonary edema, may provide protection against brain vascular leak as well.[2] |
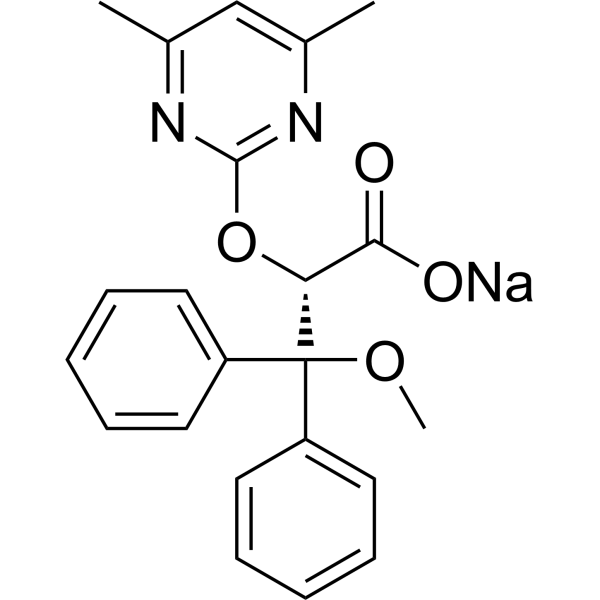
| 分子式 |
C22H23N2NAO4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
402.418796777725
|
| 精确质量 |
400.139
|
| CAS号 |
1386915-48-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Ambrisentan;177036-94-1;Ambrisentan-d10;1046116-27-1
|
| PubChem CID |
57520499
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| tPSA |
84.4Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
481
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
CC1=CC(=NC(=N1)O[C@H](C(=O)[O-])C(C2=CC=CC=C2)(C3=CC=CC=C3)OC)C.[Na+]
|
| InChi Key |
GNDMILPGCDIGHE-FSRHSHDFSA-M
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H22N2O4.Na/c1-15-14-16(2)24-21(23-15)28-19(20(25)26)22(27-3,17-10-6-4-7-11-17)18-12-8-5-9-13-18;/h4-14,19H,1-3H3,(H,25,26);/q;+1/p-1/t19-;/m1./s1
|
| 化学名 |
sodium;(2S)-2-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)oxy-3-methoxy-3,3-diphenylpropanoate
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4850 mL | 12.4248 mL | 24.8497 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4970 mL | 2.4850 mL | 4.9699 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2485 mL | 1.2425 mL | 2.4850 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。