| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
PAR4 (Protease-Activated Receptor 4)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
BMS-986120 (BMS) 在体外可显着抑制人和猴血液中 PAR4-AP 诱导的 PA(IC50 分别为 9.5±2.7 和 2.1±0.4 nM)[1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在猴子中,BMS-986120对 PAR4-AP 的 log PA 剂量反应产生平行右移,而不影响最大反应,表明可克服的拮抗作用。 BMS (1 mg/kg) 不会抑制 PAR1-AP、ADP 和胶原蛋白诱导的 PA,支持选择性。 BMS(0.2、0.5、1 mg/kg)分别使 TW 降低 35±5、49±4 和 83±4%。 KBT 和 MBT 的最大增幅分别仅为 2.2 倍和 1.8 倍。 ASA 最大抗血小板剂量(4 mg/kg/h,n=8)使 TW 略微降低 12±2%,并使 KBT 和 MBT 分别增加 2.2 倍和 2.7 倍。 ASA 和 BMS(0.5 或 1 mg/kg)共同给药使 TW 分别降低 54±3 和 95±2%,KBT 分别增加 3.1 和 3.6 倍,MBT 分别增加 2.6 和 3.3 倍( n=8/组)。在伴侣猴研究中,单独使用氯吡格雷(0.3 mg/kg/天,n=6)可使 TW 降低 49±6%,但使 KBT 和 MBT 分别增加 7.3 倍和 8.1 倍[1]。
BMS对PAR4-AP诱导的体外人、猴血PA均有明显抑制作用(ic50分别为9.5±2.7 nM和2.1±0.4 nM)。在猴子中,BMS使对数PA剂量对PAR4-AP的反应平行向右移动,而不影响最大反应,表明可克服的拮抗作用。BMS (1 mg/kg)对PAR1-AP、ADP和胶原诱导的PA无抑制作用,具有选择性。BMS(0.2、0.5、1 mg/kg)分别使TW减少35±5%、49±4%和83±4%。KBT和MBT的最大增幅分别只有2.2倍和1.8倍。ASA最大抗血小板剂量(4 mg/kg/h, n=8)可使TW略微降低12±2%,使KBT和MBT分别增加2.2倍和2.7倍。ASA和BMS(0.5或1 mg/kg)联合给药可使TW分别降低54±3%和95±2%,使KBT分别提高3.1和3.6倍,使MBT分别提高2.6和3.3倍(n=8/组)。在同伴猴子研究中,氯吡格雷(0.3 mg/kg/天,n=6)单独使用可使TW降低49±6%,但使KBT和MBT分别增加7.3倍和8.1倍。 结论:在猴子中,BMS单独或联合ASA可预防闭塞性颈动脉血栓形成,但对BT的影响有限,与标准护理抗血小板药物阿司匹林和氯吡格雷相比,[1] 在食蟹猴动脉血栓形成模型中,BMS-986120显示出强大而高效的抗血栓活性。与标准抗血小板药物氯吡格雷相比,BMS-986120在相同的非人灵长类动物模型中也表现出低出血倾向和明显更宽的治疗窗口。这些临床前发现确定了PAR4在介导血小板聚集中的生物学作用。此外,它们表明靶向PAR4是一种有吸引力的抗血小板策略,与目前的护理标准相比,它有可能治疗动脉粥样硬化血栓形成高风险患者,并且具有更高的安全性。[3] 40名健康志愿者完成了1期平行组PROBE试验(前瞻性随机开放标签盲法终点)。在(1)口服BMS-986120 (60 mg)或(2)口服阿司匹林(600 mg)后(18小时)口服阿司匹林(600 mg)和口服氯吡格雷(600 mg)后0,2和24小时测量体外血小板活化,血小板聚集和血栓形成。BMS-986120对PAR4激动剂肽(100 μM)刺激的P-选择素表达、血小板单核细胞聚集和血小板聚集具有高度选择性和可逆性的抑制作用(P<0.001)。与预处理相比,高剪切时总血栓面积(μm2/mm)减少29.2%(95%可信区间,18.3% ~ 38.7%;P<0.001)和21.4% (9.3% ~ 32.0%;P=0.002)。血栓形成减少是由富血小板血栓沉积减少引起的:34.8% (19.3%-47.3%;P<0.001), 23.3% (5.1% ~ 38.0%;P=0.016)。与阿司匹林单独使用或与氯吡格雷联合使用相比,BMS-986120对低剪切血栓形成无影响(P=无统计学意义)。BMS-986120给药与凝血时间增加或严重不良事件无关。 结论:BMS-986120是一种高选择性和可逆性口服PAR4拮抗剂,可在高剪切应力条件下显著减少富含血小板的血栓形成。我们的研究结果表明PAR4拮抗剂作为抗血小板治疗策略具有很大的潜力。[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
BMS-986120对血小板活化和聚集[2]
的影响 BMS-986120对PAR4激动剂肽(AP;100 μM)刺激的血小板活化和聚集(P<0.001)。与预处理相比,PAR4 ap刺激的血小板P-选择素表达(%)、血小板单核细胞聚集(%)和血小板聚集(%)的增加在2小时降低了91.7%(95%置信区间[CI], 81.0-102.4)、80.6% (95% CI, 68.6%-92.6%)和85.0% (95% CI, 82.0-88.1),在24小时降低了53.9% (95% CI, 43.2%-64.7%)、41.1% (95% CI, 28.9%-53.2%)和6.0% (95% CI, 2.9%-9.0%)(所有P<0.001;图2)BMS-986120血浆浓度与p -选择素表达(ρ=−0.87)、血小板-单核细胞聚集(ρ=−0.88)和血小板聚集(ρ=−0.82;P<0.001;图III(仅在线数据补充)。对PAR1、AP、ADP或花生四烯酸血小板反应均无影响(P=无统计学意义[ns]);图2)。 BMS-986120对体外血栓形成的影响 BMS-986120在高剪切时减少血栓形成总量(P<0.001),但在低剪切时没有减少血栓形成总量(P=ns;图3)与预处理相比,高剪切时总血栓面积(μm2/mm)减少29.2% (95% CI, 18.3%-38.7%;P<0.001)和21.4% (95% CI, 9.3%-32.0%;P=0.002)。血浆BMS-986120浓度与高剪切时血栓形成总量相关(ρ= - 0.47;P<0.001),但在低剪切(ρ= - 0.18;P = ns;图III(仅在线数据补充)。 |
| 动物实验 |
Individual anesthetized monkeys were given orally of BMS (0.2, 0.5,1 mg/kg) or vehicle (n=8/group) 2 hour before a combination of thrombosis, BT and ex vivo biomarker experiments. Aspirin alone (ASA, 4 mg/kg/h IV) or in combination with BMS (0.5, 1 mg/kg) was also studied (n=8/group). Thrombus weight (TW) reduction, BT increase over vehicle in kidney (KBT) and mesenteric artery (MBT), and platelet aggregation (PA) inhibition were determined. Peak PA responses to activation peptides selective for PAR4 (PAR4-AP, 12.5 μM) and PAR1 (PAR1-AP, 18 μM), ADP (20 μM), and collagen (5 μg/ml) were determined by whole blood aggregometry.[1]
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Pharmacokinetic Profile of Oral BMS-986120 [2]
BMS-986120 was rapidly absorbed with peak plasma concentrations occurring at 2 hours (255±136 ng/mL; Figure 1). Plasma concentrations of BMS-986120 were halved by 4 hours (133±100 ng/mL) and <10% of the peak concentration by 24 hours (21±9 ng/mL). |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
In conclusion, we have demonstrated that PAR4 antagonism with BMS-986120—a highly selective and reversible oral PAR4 antagonist—substantially reduces ex vivo thrombus formation in healthy volunteers under conditions of high shear stress. BMS-986120 was well tolerated with no change in coagulation assays or serious adverse events. Given the potential hemostatic sparing effects of PAR4 antagonism, our results suggest that BMS-986120 has major potential as a novel antiplatelet agent and that further investigation in clinical trials is warranted. [2]
BMS-986120 (BMS) is a novel orally-active antagonist of protease-activated receptor-4 (PAR4), a human platelet thrombin receptor, and is in phase I clinical trial. The antithrombotic potential of BMS was studied in models of electrically-mediated carotid artery thrombosis and bleeding time (BT) in cynomolgus monkeys, which have platelet thrombin receptors similar to human.[1] Antiplatelet agents are proven efficacious treatments for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. However, the existing drugs are compromised by unwanted and sometimes life-threatening bleeding that limits drug usage or dosage. There is a substantial unmet medical need for an antiplatelet drug with strong efficacy and low bleeding risk. Thrombin is a potent platelet agonist that directly induces platelet activation via the G protein (heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding protein)-coupled protease-activated receptors PAR1 and PAR4. A PAR1 antagonist is approved for clinical use, but its use is limited by a substantial bleeding risk. Conversely, the potential of PAR4 as an antiplatelet target has not been well characterized. Using anti-PAR4 antibodies, we demonstrated a low bleeding risk and an effective antithrombotic profile with PAR4 inhibition in guinea pigs. Subsequently, high-throughput screening and an extensive medicinal chemistry effort resulted in the discovery of BMS-986120, an orally active, selective, and reversible PAR4 antagonist. In a cynomolgus monkey arterial thrombosis model, BMS-986120 demonstrated potent and highly efficacious antithrombotic activity. BMS-986120 also exhibited a low bleeding liability and a markedly wider therapeutic window compared to the standard antiplatelet agent clopidogrel tested in the same nonhuman primate model. These preclinical findings define the biological role of PAR4 in mediating platelet aggregation. In addition, they indicate that targeting PAR4 is an attractive antiplatelet strategy with the potential to treat patients at a high risk of atherothrombosis with superior safety compared with the current standard of care.[3] |
| 分子式 |
C23H23N5O5S2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
513.589222192764
|
| 精确质量 |
513.11
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 53.79; H, 4.51; N, 13.64; O, 15.58; S, 12.48
|
| CAS号 |
1478712-37-6
|
| PubChem CID |
72190270
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
4.2
|
| tPSA |
153Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
11
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
35
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
724
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
MINMDCMSHDBHKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H23N5O5S2/c1-13-17(25-21(34-13)27-4-6-31-7-5-27)12-32-18-8-14(29-2)9-19-15(18)10-20(33-19)16-11-28-22(24-16)35-23(26-28)30-3/h8-11H,4-7,12H2,1-3H3
|
| 化学名 |
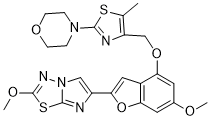
4-[4-[[6-methoxy-2-(2-methoxyimidazo[2,1-b][1,3,4]thiadiazol-6-yl)-1-benzofuran-4-yl]oxymethyl]-5-methyl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]morpholine
|
| 别名 |
BMS 986120; BMS-986120; 1478712-37-6; WDT28B7071; 4-(4-(((6-methoxy-2-(2-methoxyimidazo[2,1-b][1,3,4]thiadiazol-6-yl)benzofuran-4-yl)oxy)methyl)-5-methylthiazol-2-yl)morpholine; 4-[4-[[6-methoxy-2-(2-methoxyimidazo[2,1-b][1,3,4]thiadiazol-6-yl)-1-benzofuran-4-yl]oxymethyl]-5-methyl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]morpholine; BMS986120; compound 43 [PMID: 35729784]; 2-methoxy-6-[6-methoxy-4-[[5-methyl-2-(4-morpholinyl)-4-thiazolyl]methoxy]-2-benzofuranyl]-imidazo[2,1-b]-1,3,4-thiadiazole;
BMS986120.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~3.3 mg/mL (~6.5 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9471 mL | 9.7354 mL | 19.4708 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3894 mL | 1.9471 mL | 3.8942 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1947 mL | 0.9735 mL | 1.9471 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT02439190 | Completed | Drug: BMS-986120 Drug: Aspirin |
Thrombosis | Bristol-Myers Squibb | September 2015 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02208882 | Completed | Drug: BMS-986120 Drug: Placebo Drug: Midazolam |
Healthy Adult Volunteers | Bristol-Myers Squibb | August 2014 | Phase 1 |
|