| 规格 | 价格 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg | |||
| 1g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
β-lactam; cell wall synthesis
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
游离小孢子培养是在品种发育过程中快速固定F1杂种减数分裂重组产物的一种有前景的选择。清洁培养和高胚胎发生率是商业小黑麦和小麦小孢子培养的关键。因此,本研究调查了(1)分离的小孢子培养物中的污染物,(2)两种控制细菌生长的抗生素,以及(3)抗生素对增加小孢子衍生胚胎样结构(ELS)、绿色和白化植物的贡献。通过脂肪酸分析和16S核糖体RNA序列分析以及酵母,在受污染的培养物中鉴定出五种细菌(欧文氏菌、聚集泛球菌、假单胞菌属、表皮葡萄球菌和华纳氏葡萄球菌)。头孢噻肟和万古霉素的抗菌药敏试验对24株细菌分离株产生了强烈的抑制作用,头孢噻肟浓度为100mg/l,但假单胞菌属没有。其他抗生素处理至少部分抑制了细菌的生长。添加相同抗生素处理的小孢子诱导培养基成功地实现了小孢子胚胎发生和绿色植物生产。抗生素治疗首先在小黑麦中进行了测试,然后在小麦品种AC Carberry和AC Andrew中进行了验证。添加50和100mg/l头孢噻肟的诱导培养基分别显著增加了小黑麦和小麦中ELS和绿色植物的形成。顺便说一句,它也影响了所有基因型白化病的发生。我们的研究结果表明头孢噻肟具有分离小孢子培养的双重用途,最重要的是,它可以促进小黑麦和小麦基因型小孢子培养的细胞生长和成功,但也可以防止最常见细菌污染物培养物的意外损失[3]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在感染中性粒细胞减少性假单胞菌的大鼠中,羧苄青霉素(100-400 mg/kg;每 8 小时肌注一次,持续 72 小时)可显着降低死亡率 [1]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
分离物在27°C的LB培养基上在添加了不同抗生素的单独培养皿中生长48-72小时(表1),以评估菌落对抗生素的敏感性。在小黑麦和小麦基因型的分离物和分离小孢子培养物的抗生素测定中应用了以下抗生素处理:T1:对照(无抗生素);T2:万古霉素100mg/l;T3:万古霉素500mg/l;T4:头孢噻肟50mg/l;T5:头孢噻肟100mg/l;T6:万古霉素100mg/l和头孢噻肟50mg/l;T7:万古霉素500 mg/l和头孢噻肟100 mg/l。与未使用抗生素的对照组相比,分离株的生长表现为无抑制(+++)、弱抑制(++)、强抑制(+)和无生长(-)[3]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Rats made neutropenic with cyclophosphamide were infected intraperitoneally with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The challenge organism was killed synergistically in vitro by the combination of gentamicin and carbenicillin. Untreated neutropenic rats infected with 3 x 10(6)Pseudomonas died between days 2 and 7, and the overall mortality was 70%. Groups of infected neutropenic rats were treated intramuscularly with 1.5 or 6 mg of gentamicin per kg per dose, 100 or 400 mg of carbenicillin per kg per dose, or 1.5 mg of gentamicin and 100 mg of carbenicillin per kg per dose. Treatment was begun at 2 h postinfection and was continued every 8 h for about 72 h. Cultures of blood and peritoneal washings were performed in control and treated rats at 1, 4, 24, 48, and 72 h postinfection. Gentamicin at either dose level was ineffective in preventing death, but mortality was significantly reduced by high-dose carbenicillin and low-dose combination therapy. In addition, the latter regimens sterilized the peritoneal fluid and blood. Carbenicillin and gentamicin showed in vivo synergy in the treatment of neutropenic Pseudomonas-infected rats[1].
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Rapidly absorbed from the small intestine following oral administration. Oral bioavailability is 30 to 40%. CARBENICILLIN IS NOT ABSORBED FROM GI TRACT &, THEREFORE MUST BE GIVEN PARENTERALLY. ... IM INJECTION OF 1 G PRODUCES PEAK PLASMA CONCN OF 15-20 UG/ML IN 1/2-2 HR... MAX PLASMA CONCN ARE ABOUT 4 TIMES HIGHER AFTER IV THAN AFTER IM ADMIN... IV INFUSION...1 G/HR RESULTS IN AVG PLASMA CONCN OF APPROX 150 UG/ML. ABOUT 50% OF ANTIBIOTIC IN PLASMA IS PROTEIN BOUND. ...CARBENICILLIN IS EXCRETED PRIMARILY BY RENAL TUBULES. ABOUT 75-80%...IS RECOVERABLE IN ACTIVE FORM IN URINE IN 9 HR. Carbenicillin is not stable in acids nor does it resist penicillinases; thus it is administered parenterally because of poor absorption following oral administration. A parenteral dose of 50-200 mg/kg is divided for administration every 4-6 hr. Although carbenicillin is eliminated from the bovine mammary gland within 72 hr posttreatment, mastitis produced by P. aeruginosa is not effectively treated; resistant organisms are recovered 24-48 hr postinfusion. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CARBENICILLIN (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Minimal. Biological Half-Life 1 hour ...T 1/2...IN INDIVIDUALS WITH NORMAL RENAL FUNCTION IS ABOUT 1 HR...PROLONGED TO ABOUT 2 HR IN PRESENCE OF HEPATIC DYSFUNCTION. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Limited information indicates that carbenicillin produces low levels in milk that are not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Occasionally disruption of the infant's gastrointestinal flora, resulting in diarrhea or thrush have been reported with penicillins, but these effects have not been adequately evaluated. Carbenicillin indanyl disodium is acceptable in nursing mothers. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding 30 to 60% Interactions Extended-spectrum penicillins are physically and/or chemically incompatible with aminoglycosides and can inactivate the drugs in vitro. The extent of in vitro inactivation of aminoglycosides by penicillins depends on the specific drugs involved and appears to be directly proportional to the penicillin concn, length of exposure, and temp ... Most in vitro studies indicate that carbenicillin ... inactivates aminoglycosides at a faster rate than mazlocillin, piperacillin, or ticarcillin. Extended-spectrum penicillins can also inactivate aminoglycosides in vivo. In patients with impaired renal function, concomitant admin of carbenicillin ... and gentamicin has resulted in decreased serum aminoglycoside concn and serum half-lives compared with admin of the aminoglycoside alone. Some in vitro studies indicate that the antibacterial activity of extended-spectrum penicillins may be additive or partially synergistic with other beta-lactam antibiotics ... . /Extended-spectrum penicillins/ In vitro studies indicate that the combination of carbenicillin ... with clavulanic acid, a beta-lactamase inhibitor, results in a synergistic bactericidal effect against many strains of beta-lactamase-producing bacteria. For more Interactions (Complete) data for CARBENICILLIN (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Scott RE, et, al. Synergistic activity of carbenicillin and gentamicin in experimental Pseudomonas bacteremia in neutropenic rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):646-51.
[2]. Neu HC, et, al. Carbenicillin and ticarcillin. Med Clin North Am. 1982 Jan;66(1):61-77. [3]. Cefotaxime prevents microbial contamination and improves microspore embryogenesis in wheat and triticale. Plant Cell Rep . 2013 Oct;32(10):1637-46. |
| 其他信息 |
Carbenicillin is a penicillin antibiotic having a 6beta-2-carboxy-2-phenylacetamido side-chain. It has a role as an antibacterial drug. It is a penicillin and a penicillin allergen. It is a conjugate acid of a carbenicillin(2-).
Broad-spectrum semisynthetic penicillin derivative used parenterally. It is susceptible to gastric juice and penicillinase and may damage platelet function. Carbenicillin is a Penicillin-class Antibacterial. Carbenicillin has been reported in Solanum lycopersicum with data available. Carbenicillin is a broad-spectrum, semi-synthetic penicillin antibiotic with bactericidal and beta-lactamase resistant activity. Carbenicillin acylates the penicillin-sensitive transpeptidase C-terminal domain by opening the lactam ring. This inactivation prevents the cross-linkage of peptidoglycan strands, thereby inhibiting the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. This leads to incomplete bacterial cell wall synthesis and eventually causes cell lysis. Broad-spectrum semisynthetic penicillin derivative used parenterally. It is susceptible to gastric juice and penicillinase and may damage platelet function. Drug Indication For the treatment of acute and chronic infections of the upper and lower urinary tract and in asymptomatic bacteriuria due to susceptible strains of bacteria. Mechanism of Action Free carbenicillin is the predominant pharmacologically active fraction of the salt. Carbenicillin exerts its antibacterial activity by interference with final cell wall synthesis of susceptible bacteria. Penicillins acylate the penicillin-sensitive transpeptidase C-terminal domain by opening the lactam ring. This inactivation of the enzyme prevents the formation of a cross-link of two linear peptidoglycan strands, inhibiting the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wall autolytic enzymes such as autolysins; it is possible that carbenicillin interferes with an autolysin inhibitor. The penicillins and their metabolites are potent immunogens because of their ability to combine with proteins and act as haptens for acute antibody-mediated reactions. The most frequent (about 95 percent) or "major" determinant of penicillin allergy is the penicilloyl determinant produced by opening the beta-lactam ring of the penicillin. This allows linkage of the penicillin to protein at the amide group. "Minor" determinants (less frequent) are the other metabolites formed, including native penicillin and penicilloic acids. /Penicillins/ Bactericidal; inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis. Action is dependent on the ability of penicillins to reach and bind penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located on the inner membrane of the bacterial cell wall. Penicillin-binding proteins (which include transpeptidases, carboxypeptidases, and endopeptidases) are enzymes that are involved in the terminal stages of assembling the bacterial cell wall and in reshaping the cell wall during growth and division. Penicillins bind to, and inactivate, penicillin-binding proteins, resulting in the weakening of the bacterial cell wall and lysis. /Penicillins/ Therapeutic Uses Penicillins MAJOR ADVANTAGE OF THIS AGENT IS THAT IT OFTEN CURES SERIOUS INFECTIONS CAUSED BY PSEUDOMONAS SPECIES /PRC: ESP PSEUDOMONAS AEROGINOSA/, PROTEUS STRAINS RESISTANT TO AMPICILLIN, & CERTAIN OTHER GRAM-NEGATIVE MICROORGANISMS. Carbenicillin (parenteral) /is/ indicated in the treatment of bacterial pneumonia caused by susceptible organisms. /Included in US product labeling/ Carbenicillin (parenteral) /is/ indicated in the treatment of bone and joint infections caused by susceptible organisms. /Included in US product labeling/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CARBENICILLIN (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings IN FEW INSTANCES, IT IS NECESSARY TO INTERDICT FUTURE USE OF PENICILLIN BECAUSE OF RISK OF DEATH, & PT SHOULD BE SO WARNED. IT MUST AGAIN BE STRESSED THAT FATAL EPISODES OF ANAPHYLAXIS HAVE FOLLOWED THE INGESTION OF VERY SMALL DOSES OF THIS ANTIBIOTIC. /PENICILLINS/ THESE AGENTS ARE...LESS EFFECTIVE AGAINST MICROORGANISMS SUSCEPTIBLE TO PENICILLIN G, & THEY ARE NOT USEFUL AGAINST GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA, MICROORGANISMS CAN BECOME RESISTANT TO THESE DRUGS IN STEPWISE FASHION, & CROSS-RESISTANCE TO ALL PENICILLINS IS USUALLY COMPLETE /PENICILLINS/ Because of the risk of therapeutic failure from subtherapeutic drug concn, carbenicillin indanyl sodium should not be used when rapid high blood and/or urine concn are necessary or in patients with severe renal impairment (i.e., creatinine clearances less than 10 ml/min). /Carbenicillin indanyl sodium/ Penicillins are distributed into breast milk, some in low concentrations. Although significant problems in humans have not been documented, the use of penicillins by nursing mothers may lead to sensitization, diarrhea, candidiasis, and skin rash in the infant. /Penicillins/ For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CARBENICILLIN (24 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Carbenicillin is a semisynthetic penicillin. Though carbenicillin provides substantial in vitro activity against a variety of both gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms, the most important aspect of its profile is in its antipseudomonal and antiproteal activity. Because of the high urine levels obtained following administration, carbenicillin has demonstrated clinical efficacy in urinary infections due to susceptible strains of: Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Morganella morganii, Pseudomonas species, Providencia rettgeri, Enterobacter species, and Enterococci (S. faecalis). |
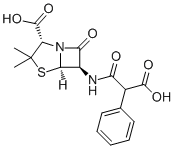
| 分子式 |
C17H18N2O6S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
378.399623394012
|
| 精确质量 |
378.089
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 53.96; H, 4.79; N, 7.40; O, 25.37; S, 8.47
|
| CAS号 |
4697-36-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Carbenicillin disodium;4800-94-6
|
| PubChem CID |
20824
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.53g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
737.8ºC at 760mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
400ºC
|
| 折射率 |
1.675
|
| LogP |
0.815
|
| tPSA |
149.31
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
26
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
645
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
3
|
| SMILES |
O=C([C@@H](C(C)(C)S[C@]1([H])[C@@H]2NC(C(C(O)=O)C3=CC=CC=C3)=O)N1C2=O)O
|
| InChi Key |
FPPNZSSZRUTDAP-UWFZAAFLSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H18N2O6S/c1-17(2)11(16(24)25)19-13(21)10(14(19)26-17)18-12(20)9(15(22)23)8-6-4-3-5-7-8/h3-7,9-11,14H,1-2H3,(H,18,20)(H,22,23)(H,24,25)/t9?,10-,11+,14-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2S,5R,6R)-6-[(2-carboxy-2-phenylacetyl)amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid
|
| 别名 |
Carboxybenzylpenicillin; 4697-36-3; alpha-Carboxybenzylpencillin; Carbenicilina; Carbenicilline; Carbenicillinum; Carboxybenzylpenicillin acid;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6427 mL | 13.2135 mL | 26.4271 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5285 mL | 2.6427 mL | 5.2854 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2643 mL | 1.3214 mL | 2.6427 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。