| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
多佐胺以剂量依赖性方式阻断组分 A,该组分 A 由 CO2 流入和 CA-II 水合产生,在 50% 抑制浓度下,IC50 为 2.4 μM(95% 置信区间:0.5-10.85 μM)[2]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 EAC 实体瘤模型中,多佐胺(3、10 或 30 mg/kg/天,腹腔注射)与丝裂霉素 C 联合使用时具有抗癌功效。计算出的比率(相对值 57.3±1、25.5±1.8 和 24.3±0.7) %)随着多佐胺剂量的增加而下降[3]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Female Swiss albino mouse (EAC solid tumor) [3].
Doses: 3, 10 or 30 mg/kg/day (with mitomycin C). Doses: IP, one time/day for 3 weeks. Experimental Results: TXNIP and p53 were up-regulated, and bcl-2 was down-regulated. Effectively delays the growth of EAC in mice. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Dorzolamide readily penetrated into the eye in animal studies. Upon ophthalmic administration, dorzolamide is absorbed via the cornea and stroma. Dorzolamide is reported to be absorbed systematically following topical administration. The systemic exposure of dorzolamide following long-term administration was assessed in healthy subjects receiving an oral dose of 2 mg dorzolamide twice daily, which equates to the ophthalmic dose of 2% dorzolamide three times daily. In these subjects receiving the treatment for 20 weeks, the steady-state was reached within 8 weeks. Dorzolamide is primarily excreted unchanged in the urine; however, N-desethyldorzolamide is also detected in the urine. There is limited information on the volume of distribution of dorzolamide; however, the plasma concentrations of dorzolamide and its main metabolite are generally below the assay limit of quantitation, which is 15nM. Dorzolamide accumulates in red blood cells following chronic administration as a result of binding to CA-II, which is contained in peripheral red blood cells (RBCs). There is limited information on the clearance rate of dorzolamide. Metabolism / Metabolites Dorzolamide is slowly metabolised to N-desethyldorzolamide, which has a less potent pharmacological activity on CA-II and some inhibitory effect on CA-I. Like the parent drug, N-desethyldorzolamide is also stored in RBCs, where it binds to CA-I. The findings of an _in vitro_ study using liver microsomes from Sprague-Dawley rats suggest the involvement of CYP2B1, CYP2E1, and CYP3A2 in the metabolism of dorzolamide in rat liver. Biological Half-Life As the drug administration is stopped, dorzolamide stored in RBCs is washed out of RBCs in a non-linear fashion, with the terminal elimination half-life of ≥120 days in RBCs. This initial rapid decline in drug concentrations is followed by the slow elimination phase, where the elimination half-life of the drug is about >4 months. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Limited experience with the use of ophthalmic dorzolamide indicate that it is unlikely to adversely affect the breastfed infant. French guidelines recommend ophthalmic carbonic anhydrase inhibitor drops as a preferred therapy for glaucoma during breastfeeding. To substantially diminish the amount of drug that reaches the breastmilk after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A newborn infant was breastfed during maternal therapy with various combinations of ocular timolol, dipivifrin, dorzolamide, brimonidine and several doses of acetazolamide. Ultimately, the mother was treated with timolol gel-forming solution 0.5% and dorzolamide 2% drops. The drugs were given immediately following breastfeeding with punctal occlusion and no apnea or bradycardia was observed in the infant. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Dorzolamide is approximately 33% bound to plasma proteins. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
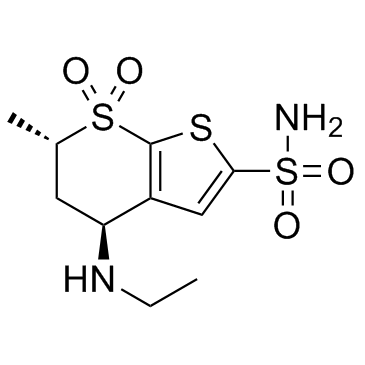
Dorzolamide is 5,6-Dihydro-4H-thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-2-sulfonamide 7,7-dioxide in which hydrogens at the 4 and 6 positions are substituted by ethylamino and methyl groups, respectively (4S, trans-configuration). A carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, it is used as the hydrochloride in ophthalmic solutions to lower increased intraocular pressure in the treatment of open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. It has a role as an EC 4.2.1.1 (carbonic anhydrase) inhibitor, an antihypertensive agent and an antiglaucoma drug. It is a sulfonamide and a member of thiophenes.
Dorzolamide is a non-bacteriostatic sulfonamide derivative and topical carbonic anhydrase (CA) inhibitor that treats elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) associated with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. It works by blocking an enzyme in the ciliary process that regulates ion balance and fluid pressure in the eyes. Unlike oral CA inhibitors, dorzolamide has negligible effects of acid-base or electrolyte disturbances and other systemic adverse effects. First marketed in 1995, dorzolamide is available in ophthalmic solutions as monotherapy marketed as Trusopt or in combination with [timolol] as Cosopt PF. Dorzolamide is a Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of dorzolamide is as a Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor. Dorzolamide is an inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase, a zinc-containing enzyme that catalyzes the rapid conversion of carbon dioxide and water into carbonic acid, protons and bicarbonate ions. Distributed throughout many cells and tissues, various carbonic anhydrases play important roles in mineral and metabolic homeostasis. (NCI04) See also: Dorzolamide Hydrochloride (has salt form). Drug Indication Dorzolamide is indicated for the management of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma. It can also be used in combination with [timolol] for the same indication in patients who are insufficiently responsive to ophthalmic beta-blockers. Its pre-operative use was also investigated to prevent elevated intraocular pressure after neodynium yttrium aluminum garnet laser posterior capsulotomy. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Elevated intraocular pressure is a characteristic manifestation of ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma. The level of intraocular pressure (IOP) is governed by the balance between the production of aqueous humour (by ocular ciliary processes) and its outflow from the anterior segment of the eye via trabecular (conventional) or uveoscleral (unconventional) pathways. When there is an increase in the resistance to the trabecular outflow of aqueous humour, the intraocular pressure is elevated. Subsequently, optic nerve damage can occur from blood flow restrictions and mechanical distortion of ocular structures. Optic nerve damage can further result in optic disc cupping and progressive visual field loss (and blindness in some cases). Carbonic anhydrase (CA) is a ubiquitous enzyme that catalyzes the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate ions and dehydration of carbonic acid. In the ocular ciliary processes, the local production of bicarbonate by CAs promotes sodium and fluid transport. CA-II is a key isoenzyme found primarily in red blood cells (RBCs) that regulates aqueous humour production. Dorzolamide is a highly specific CA-II inhibitor, where it displays a 4000-fold higher affinity for carbonic anhydrase II than carbonic anhydrase I. The inhibition of CA-II in the ciliary process disrupts the formation of bicarbonate ions and reduces sodium and fluid transport, which leads to decreased aqueous humour secretion and reduced intraocular pressure. Pharmacodynamics Dorzolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor that reduces elevated intraocular pressure in open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. When used in combination with topic beta-adrenergic antagonists, dorzolamide has an additive effect of lowering intraocular pressure. The peak ocular hypotensive effect of dorzolamide is observed at about 2 hours following ophthalmic administration. |
| 分子式 |
C10H16N2O4S3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
324.44
|
| 精确质量 |
324.027
|
| CAS号 |
120279-96-1
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Dorzolamide hydrochloride;130693-82-2;Dorzolamide-d5;1227097-70-2
|
| PubChem CID |
5284549
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.53 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
575.8ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
302ºC
|
| 折射率 |
1.626
|
| LogP |
4.666
|
| tPSA |
151.33
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
19
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
534
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
O=S(C(S1)=CC2=C1S([C@@H](C)C[C@@H]2NCC)(=O)=O)(N)=O
|
| InChi Key |
IAVUPMFITXYVAF-XPUUQOCRSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C10H16N2O4S3/c1-3-12-8-4-6(2)18(13,14)10-7(8)5-9(17-10)19(11,15)16/h5-6,8,12H,3-4H2,1-2H3,(H2,11,15,16)/t6-,8-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(4S,6S)-4-(ethylamino)-6-methyl-7,7-dioxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-2-sulfonamide
|
| 别名 |
L671152MK507 L671152 MK507 Trusopt UNII-9JDX055TW1 UNII9JDX055TW1 UNII 9JDX055TW1
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0822 mL | 15.4112 mL | 30.8223 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6164 mL | 3.0822 mL | 6.1645 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3082 mL | 1.5411 mL | 3.0822 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
A Study of a Glaucoma Therapy to Treat Open-Angle Glaucoma or Ocular Hypertension
CTID: NCT00314171
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Completed
Date: 2016-11-18