| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
BTK (IC50 = 37.9 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Evobrutinib 能够阻断 BTK 活性并阻止 BCR 信号通路被激活。它通过 GSH 结合、O-脱烷基化、羟基化、水解和葡萄糖醛酸化进行分解[2]。
Evobrutinib是一种新型、高选择性、不可逆的BTK抑制剂,可有效阻断Fc和BCR受体介导的信号传导。Evobrutinib具有阻断BTK活性和阻止BCR信号通路被激活的能力。它通过谷胱甘肽偶联、o -脱烷基、羟基化、水解和葡萄糖醛酸化分解[2]。
Evobrutinib是一种新型、高选择性、不可逆的BTK抑制剂,可有效抑制BCR-和Fc受体介导的信号传导,从而抑制人类B细胞和先天免疫细胞(如单核细胞和嗜碱性细胞)的后续激活和功能。[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在这项研究中,研究人员在RA和SLE的临床前模型中评估了Evobrutinib/依沃鲁替尼,并描述了BTK占用与疾病活性抑制之间的关系。在类风湿性关节炎和SLE小鼠模型中,口服Evobrutinib显示出强大的疗效,证明了疾病严重程度和组织学损伤的降低。在SLE模型中,Evobrutinib抑制B细胞活化,降低自身抗体产生和浆细胞数量,并使B细胞和T细胞亚群正常化。在RA模型中,尽管未能降低自身抗体,但仍能达到疗效。药代动力学/药效学模型显示,在RA和SLE小鼠模型中,血细胞中BTK的平均占用率为80%与近乎完全的疾病抑制有关。此外,Evobrutinib在被动皮肤过敏反应模型中抑制肥大细胞活化。因此,Evobrutinib通过同时作用于B细胞和先天免疫细胞来达到疗效。综上所述,我们的数据表明,Evobrutinib是一种很有前途的分子,可用于B细胞驱动的自身免疫性疾病的慢性治疗。
|
| 酶活实验 |
激酶检测[3]
利用纯化的全长重组BTK测定依沃鲁替尼对BTK的效价。BTK蛋白用75 μM ATP和1 μM KinKDR肽FITC-AHA-EEPLYWSFPAKKK-NH2在缓冲液中稀释至终浓度0.05 ng/μl。不同浓度的依伏鲁替尼也包括在内。在25°C下反应90分钟,加入含有0.5 M EDTA的停止溶液停止反应。然后在Caliper LabChip 3000上读取板,并将数据加载到Genedata Screener中生成IC50曲线。为了比较evobrutinib或ibrutinib对野生型(WT) BTK与C481S BTK的抑制作用,我们使用了覆盖激酶结构域的重组蛋白(BTK WT 328-659或BTK C481S 328-659)。跳跃稀释实验,将含有100倍标准生化试验浓度BTK (0.63 nM)的20 μl实验缓冲液加入到200 nl依沃鲁替尼或RN486中,最终浓度为10倍IC50或阴性对照(DMSO)。室温孵育90 min后,将1 μl的混合溶液稀释到含有底物肽(序列FITC-AHA-EEPLYWSFPAKKK-NH2, 1 μM)和ATP (75 μM)的99 μl实验缓冲液中。将微孔板放置在Caliper Life Sciences LabChip 3000中,重复取样112分钟。在KinaseProfiler筛选板(EMD Millipore, Billerica, MA)中确定evobrutinib和ibrutinib的激酶选择性,测试化合物在1 μM下对267种激酶的抑制活性。[3] Ramos细胞BTK磷酸化/BTK phosphorylation in Ramos cells[3] 在Ramos B细胞中测定依维鲁替尼对BCR激活后BTK磷酸化的影响。Ramos Burkitt淋巴瘤细胞系从美国类型培养收集中获得,并在含有青霉素/链霉素,2mm l-谷氨酰胺和10%胎牛血清的RPMI 1640培养基中维持。将Ramos细胞接种于96孔组织培养板中,每孔8 × 106个细胞。用溶解在DMSO中的BTK抑制剂evobrutinib在37℃下预处理细胞30分钟。复合处理后,用浓度为5 μg/ml的抗igm抗体F(ab’)2 ab (SouthernBiotech, Birmingham, AL)刺激细胞激活BCR。细胞与抗igm在37℃下孵育5 min。处理后,收集细胞,500 × g离心5 min,抽吸培养基,加入150 μl含有Thermo Scientific Halt蛋白酶/磷酸酶抑制剂混合物的冰凉Thermo Scientific Pierce M-PER裂解缓冲液。将细胞重悬于裂解缓冲液中,裂解物冷冻至- 80°C,用于后续测量BTK磷酸化。根据制造商的说明,使用自动Wes仪器进行蛋白印迹分析BTK磷酸化。Western blot检测中,使用6 μl裂解液,用1:3000稀释的一抗BTK p-Y551 或1:50稀释的抗BTK p-Y223检测磷酸化的BTK。 |
| 细胞实验 |
外周血和全血中B细胞的活化[3]
Evobrutinib阻断BCR信号的能力是用全血B细胞或纯化的PBMCs来测定的。用柠檬酸盐作为抗凝血剂采集人血。对于PBMC实验,通过Ficoll梯度分离PBMC,每孔2.5 × 105个细胞接种到96孔板中。全血测定时,每孔90 μl的血直接转移到96孔板上。细胞在37℃用依沃鲁替尼稀释液预处理60 min,然后用山羊抗人IgM F(ab’)2 (Dianova)活化,加入终浓度为20 μg/ml, 37℃孵育过夜。活化后,细胞用抗cd69 - allophycocyanin和抗cd19 - percp - cy5.5染色45分钟,然后用FACS裂解液裂解,在PBS中重悬,然后进行FACS分析。在FACSCanto II仪器上进行FACS分析。首先对细胞进行CD19门控,并测定CD19阳性细胞的百分比。 B细胞增殖、细胞因子释放和质母细胞分化的研究[3] 使用B细胞纯化试剂盒II,按照制造商的说明,通过阴性选择从健康志愿者的外周血中分离CD19+ B细胞。纯化后的B细胞用evobrutinib孵育1 h,用10 μg/ml山羊F(ab’)2抗igm和10 ng/ml重组人IL-4刺激4 d,最后18 h加入[3H]胸腺嘧啶微孔孵育1 h。使用多板β计数器测量增殖。在细胞因子释放实验中,将健康志愿者外周血中分离的CD19+ B细胞与依维鲁替尼孵育1小时,然后用10 μg/ml兔抗人IgA + IgG + IgM (h +L)、3 μg/ml CpG寡脱氧核苷酸2006和8000 IU/ml重组人IFN-α刺激48小时,用细胞计数头阵列试剂盒检测上清中的细胞因子。为了产生Ig,分离的B细胞分别用20 U/ml IL-2、100 ng/ml IL-10、10 μg/ml灭活的金黄色葡萄球菌Cowan和不同浓度的依维鲁替尼刺激。培养10 d后,ELISA检测上清液中IgG和IgM水平。 fc - γ - r信号的抑制作用[3] U937 NF -κB-Luc报告细胞在二氧化碳调节的组织培养箱中37°C保持贴壁培养。实验当天,收集细胞,计数,并在96孔组织板中镀。Evobrutinib以5 nM ~ 10 μM的浓度加入。细胞与evobrutinib在37°C组织培养箱中孵育30分钟。然后将细胞转移到涂有抗cd64的新鲜板上并刺激4小时。使用EnVision板阅读器测量细胞裂解物中的荧光素酶活性。 嗜碱性粒细胞抑制试验[3] Evobrutinib阻断Fc受体信号的能力通过全血嗜碱性粒细胞测定。用柠檬酸盐作为抗凝剂收集人血,并转移到96孔板上。37℃用依维鲁替尼稀释液预处理30 min后,抗ige活化,加入终浓度2 μg/ml, 37℃孵育5 min。活化后,细胞用抗cd63 - fitc染色15 min,然后加入PBS-EDTA (20 mM),再加入固定/裂解缓冲液。在FACS分析之前,将细胞固定在甲醛中。使用FACSCanto II仪器对CD123+HLA-DR -细胞进行首次门联后,测定CD63表达的平均荧光强度(MFI)。[3] BioMAP分析[3] Evobrutinib和ibrutinib的生物选择性在体外使用原代人细胞和BioSeek的BioMAP分析进行评估。根据先前发表的详细方法,在12种不同的原代细胞共培养系统中,使用370 nM-10 μM的浓度范围对化合物的活性进行了评估。 |
| 动物实验 |
DBA/1J female mice
12 mg/kg o.g. Ex vivo B cell stimulation in mouse whole blood[3] Evobrutinib was administered by oral gavage to female C57BL/6 mice (five per group) at indicated doses and time points before heparinized whole blood was obtained and divided into two aliquots. One aliquot was incubated with anti-IgD as stimulation and another with PBS as basal control. CD69 MFI on the B cell surface was measured by flow cytometry. The difference between stimulated and basal levels of MFI was calculated and expressed as Δ MFI. Percent inhibition was calculated according to the following formula: percent inhibition = (1− [Δ MFIevobrutinib/Δ MFIvehicle]) × 100.[3] PK/PD model and occupancy assay for whole blood[3] To build a PK/PD relationship for evobrutinib, DBA/1J female mice aged 11–12 wk were dosed with the compound. BTK occupancy in the blood and plasma concentrations were measured over time. Evobrutinib was formulated in a vehicle solution of 20% kleptose and 50 mM citrate, pH 3, and mice were administered the compound via oral gavage. At various time points after dosing, mice were euthanized, and blood was collected into heparinized tubes via the vena cava. For determination of BTK occupancy, a previously described method that uses a biotinylated BTK-binding probe and a streptavidin-capture ELISA was used. Plasma samples were analyzed by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for determination of evobrutinib concentrations.[3] Passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in mice[3] C57BL/6 mice were sensitized intradermally in the back with 250 ng of anti-DNP IgE or anti-OVA IgE. Twenty-four hours later, all mice were challenged i.v. with 0.5 mg of DNP–human serum albumin in the presence of 0.5% Evans blue. Mice were sacrificed 30 min after challenge, back skin was harvested, and the Evans blue was extracted in formamide for 24 h at 55°C. OD was measured at 620 nm and compared with a standard curve of known Evans blue concentrations. The results are expressed as nanograms of dye per milligram of tissue.[3] Collagen-induced arthritis in mice[3] All mouse collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) studies were performed at Bolder BioPATH. DBA/1OlaHsd mice (12–15 animals per group) were anesthetized with isoflurane, shaved at the base of the tail, and injected intradermally with 150 μl of CFA (Sigma) containing bovine type II collagen (2 mg/ml) at the base of the tail on day 0 and again on day 21. On study day 18, mice were randomized by body weight into treatment groups. Treatment was initiated after enrollment and continued daily (once daily at 24-h intervals) through study day 33. Animals were dosed by the oral route with vehicle (20% hydroxy-propyl-β cyclodextrin in H2O) or evobrutinib at various doses or the reference compound methotrexate (MTX; 0.5 mg/kg). On study day 34, the studies were terminated. Daily clinical scores were given for each of the paws (right front, left front, right rear, and left rear) on arthritis days 18–34 using the following criteria: 0 = normal; 1 = one hind or forepaw joint affected or minimal diffuse erythema and swelling; 2 = two hind or forepaw joints affected or mild diffuse erythema and swelling; 3 = three hind or forepaw joints affected or moderate diffuse erythema and swelling; 4 = four hind or forepaw joints affected or marked diffuse erythema and swelling; and 5 = entire paw affected, severe diffuse erythema and severe swelling, and unable to flex digits. Histopathological scoring was performed on forepaws, hind paws, and knees from mice. Inflammation, pannus formation, cartilage damage, and bone resorption were scored separately. Scores for all four parameters were added for each individual ankle or knee. Mean scores for all six tissues were calculated for each animal, and mean scores for each group are shown.[3] SLE model[3] Ten-week-old female NZB/W F1 mice were given two i.v. injections on day 0 and day 1 of 1 × 108 IU/100 μl of adenovirus with mmIfna5_v1 insert in saline or left untreated (sham). Drug treatments were initiated at 2 wk after delivery of adenovirus with mmIfna5_v1 insert and continued until the end of the experiment (at 10 wk). Mice (10 per group) were treated once daily with evobrutinib at indicated doses or mycophenolate mofetil at 300 mg/kg by oral gavage. Serum and urine samples were collected for anti-dsDNA Ab determination (by ELISA) and urinary protein creatinine ratio (UPCR; measured on ADVIA 1800) determination, respectively, on the days indicated. Proteinuria was defined as UPCR > 3. In addition, serum was analyzed for clinical chemistry parameters including urea nitrogen, albumin, total protein, and cholesterol on an ADVIA1800 chemistry analyzer on the final day of the experiment. Hematological analysis was performed on whole blood on the final day using a Sysmex XT-2000iV analyzer. Spleen cells were analyzed for B and T cell subsets on the final day using flow cytometry. The gating strategy is shown in Fig. 9. BTK occupancy in splenocytes was measured as described by Honigberg and colleagues |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
PK/PD modeling of BTK occupancy in mice[3]
In this study, researchers established a relationship between exposure, target occupancy, and efficacy in preclinical disease models. PK parameters were estimated from a two-compartment model with first-order absorption for male DBA/1OlaHsd and for female NZB/W mice, which were used in the RA and SLE models, respectively. Strain-specific PK parameters may be found in Supplemental Table II. The corresponding exposure data are shown in Supplemental Fig. 1F and 1G. Once evobrutinib has engaged BTK, the PD effect depends largely on the resynthesis and degradation rates of BTK in vivo rather than the systemic exposure of evobrutinib. This is due to the covalent binding of evobrutinib to BTK and illustrated in Fig. 12A. BTK occupancy PK/PD modeling was performed for male DBA/1OlaHsd mice using the BTK occupancy and exposure data shown in Fig. 4C and and4D.4D. PK parameters from this strain were used to parameterize the second-order rate constant kirrev, which describes binding of evobrutinib to BTK. The plasma concentration and BTK occupancy time course following oral administration of evobrutinib were fit to a PK/PD model adapted from Abelö et al. and shown schematically in Fig. 12A. The selected PD model consisted of an indirect response model that describes both the second-order rate constant describing the irreversible binding of evobrutinib to BTK (kirrev) and the mouse degradation rate of the BTK protein (kdeg). The estimated PK/PD parameters in mouse WBCs are reported in Supplemental Table II, and the occupancy dose–response time course is shown in Fig. 12B. These drug (kirrev) and system (kdeg) parameters were integrated into a model describing fluctuation of BTK occupancy at steady state after daily dosing. As shown in Fig. 12C, this model predicts that daily dosing with 1 mg/kg of evobrutinib in mice results in a maximum BTK occupancy of 70% and a minimum occupancy of 50% at steady state. A daily dose of 5 mg/kg results in maximum and minimum BTK occupancy of 97 and 70%, respectively. Higher doses of evobrutinib are predicted to have a marginal effect on the BTK occupancy time course in mice. This is in line with the PD effect being entirely driven by the turnover of BTK protein in vivo rather than exposure with evobrutinib. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Evobrutinib is under investigation in clinical trial NCT03934502 (Effect of Meal Composition and Timing on Evobrutinib Bioavailability).
Evobrutinib is an inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon administration, evobrutinib inhibits the activity of BTK and prevents the activation of the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) signaling pathway. This prevents both B-cell activation and BTK-mediated activation of downstream survival pathways, which leads to the inhibition of the growth of malignant B-cells that overexpress BTK. BTK, a member of the Src-related BTK/Tec family of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases, is overexpressed in B-cell malignancies; it plays an important role in B-lymphocyte development, activation, signaling, proliferation and survival. Drug Indication Treatment of multiple sclerosis |
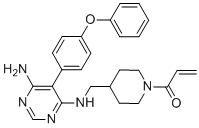
| 分子式 |
C25H27N5O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
429.5142
|
| 精确质量 |
429.216
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 69.91; H, 6.34; N, 16.31; O, 7.45
|
| CAS号 |
1415823-73-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1415823-73-2
|
| PubChem CID |
71479709
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
683.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
367.1±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.637
|
| LogP |
3.19
|
| tPSA |
93.4
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
595
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C(C([H])=C([H])[H])N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])N([H])C2C(=C(N([H])[H])N=C([H])N=2)C2C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=2[H])OC2C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=2[H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H]
|
| InChi Key |
QUIWHXQETADMGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C25H27N5O2/c1-2-22(31)30-14-12-18(13-15-30)16-27-25-23(24(26)28-17-29-25)19-8-10-21(11-9-19)32-20-6-4-3-5-7-20/h2-11,17-18H,1,12-16H2,(H3,26,27,28,29)
|
| 化学名 |
1-[4-[[[6-amino-5-(4-phenoxyphenyl)pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]methyl]piperidin-1-yl]prop-2-en-1-one
|
| 别名 |
MSC-2364447-C; MSC-2364447 C; Evobrutinib; 1415823-73-2; 1-(4-(((6-amino-5-(4-phenoxyphenyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)methyl)piperidin-1-yl)prop-2-en-1-one; Evobrutinib [INN]; M-2951; M 2951; M2951; MSC-2364447C; MSC 2364447C; MSC2364447C
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~86 mg/mL (~200.2 mM)
Ethanol: ~10 mg/mL (~23.3 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3282 mL | 11.6412 mL | 23.2823 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4656 mL | 2.3282 mL | 4.6565 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2328 mL | 1.1641 mL | 2.3282 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Study of Evobrutinib in Participants With Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis (RMS)
CTID: NCT04032158
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Termi
A Phase II, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Dose-Ranging Study To Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of M2951 in Subjects with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
CTID: null
Phase: Phase 2 Status: Completed, Prematurely Ended
Date: 2017-04-27

Figure 1. X-ray structure of BTK ligandB43bound to the BTK kinase domain.J Med Chem.2019 Aug 15. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00794. |
|---|
 Figure 2. Overlay of crystal structures ofA5andA7.
Figure 5. Crystal structure of evobrutinib bound to the BTK kinase domain.J Med Chem.2019 Aug 15. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00794. |
 Figure 3. PK/PD studies in mice.
Figure 6. Rat CIA model: rats treated with evobrutinib, MTX, or vehicle.J Med Chem.2019 Aug 15. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00794. |