| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Little information is available on the distribution of carbamates in the various organs and tissues in mammals following exposure by inhalation or the oral route. The organs in which residues have been reported are the liver, kidneys, brain, fat, and muscle.The half-life in the rat is of the order of 3 - 8 hr. It seems that the excretion of carbamates via urine is also rapid in man, and that the metabolic pathways in man are the same as those in the rat. /Carbamate pesticides/ The pharmacokinetics of furathiocarb were studied in vivo in male Sprague-Dawley rats following dermal treatment. HPLC and post-column derivatization were used for the analysis of furathiocarb and its metabolites (carbofuran, 3-hydroxycarbofuran and 3-ketocarbofuran). Carbofuran and 3-hydroxycarbofuran were detected in plasma and urine rather than furathiocarb. 3-Ketocarbofuran, another potential metabolite, was not observed in any sample. The concentration of carbofuran was higher than that of 3-hydroxycarbofuran in plasma, but the reverse was the case in urine. The corresponding area under the plasma concentration-time curve, Tmax, and Cmax values of carbofuran and 3-hydroxycarbofuran for 1,500 mg/kg doses were 2.4-8.0 mg equiv/ml, 12 hr and 0.1-0.4 mg equiv/ml, respectively. T1/2 was calculated only for 3-hydroxycarbofuran (28 hr). Two metabolites were excreted in a dose-dependent manner without saturation. Metabolism / Metabolites Metabolic transformation in rats proceeds via rapid and complete hydrolysis, followed by oxidation and conjugation. Excretion occurs mainly via kidney. The first step in the metabolism of carbamates is hydrolysis to carbamic acid, which decomposes to carbon dioxide (CO2) and the corresponding amine. The mechanism of hydrolysis is different for N -methyl and N-dimethyl derivatives. The N-methyl carbamates pass through an isocyanate intermediate, whereas in the hydrolysis of N-dimethylcarbamates, an addition product with a hydroxyl ion is formed yielding the alcohol and N-dimethyl substituted acid. The rate of hydrolysis by esterases is faster in mammals than in plants and insects. Apart from hydrolysis, oxidation also takes place including: hydroxylation of the aromatic ring, O-dealkylation, N -methyl hydroxylation, N-dealkylation, oxidation of aliphatic side chains, and sulfoxidation to the corresponding sulfone. Oxidation is associated with the mixed-function oxidase (MFO) enzymes. Conjugation leads to the formation of O- and N- glucuronides, sulfates, and mercapturic acid derivatives in mammals. Glycosides and phosphates are conjugation products more common in plants. /Carbamate Pesticides/ The pharmacokinetics of furathiocarb were studied in vivo in male Sprague-Dawley rats following dermal treatment. HPLC and post-column derivatization were used for the analysis of furathiocarb and its metabolites (carbofuran, 3-hydroxycarbofuran and 3-ketocarbofuran). Carbofuran and 3-hydroxycarbofuran were detected in plasma and urine rather than furathiocarb. 3-Ketocarbofuran, another potential metabolite, was not observed in any sample. ... The carbamates are hydrolyzed enzymatically by the liver; degradation products are excreted by the kidneys and the liver. (L793) Biological Half-Life The half-life in the rat is of the order of 3-8 hr. /Carbamate pesticides/ |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Furathiocarb is a cholinesterase or acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. Carbamates form unstable complexes with chlolinesterases by carbamoylation of the active sites of the enzymes. This inhibition is reversible. A cholinesterase inhibitor suppresses the action of acetylcholine esterase. Because of its essential function, chemicals that interfere with the action of acetylcholine esterase are potent neurotoxins, causing excessive salivation and eye-watering in low doses. Headache, salivation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea are often prominent at higher levels of exposure. Acetylcholine esterase breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is released at nerve and muscle junctions, in order to allow the muscle or organ to relax. The result of acetylcholine esterase inhibition is that acetylcholine builds up and continues to act so that any nerve impulses are continually transmitted and muscle contractions do not stop. Toxicity Data LC50 (rat) = 214 mg/m3/4h Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat oral 53 mg/kg LD50 Mouse oral 327 mg/kg LD50 Rat percutaneous >2,000 mg/kg LC50 Rat inhalation 0.214 mg/l air/4 hr |
| 参考文献 |
Anal. Chem., 80, 9450 (2008)
|
| 其他信息 |
Furathiocarb is a carbamate ester and a member of 1-benzofurans. It has a role as an EC 3.1.1.7 (acetylcholinesterase) inhibitor, a carbamate insecticide and an agrochemical.
Furathiocarb is a carbamate pesticide. Carbamate pesticides are derived from carbamic acid and kill insects in a similar fashion as organophosphate insecticides. They are widely used in homes, gardens and agriculture. The first carbamate, carbaryl, was introduced in 1956 and more of it has been used throughout the world than all other carbamates combined. Because of carbaryl's relatively low mammalian oral and dermal toxicity and broad control spectrum, it has had wide use in lawn and garden settings. Most of the carbamates are extremely toxic to Hymenoptera, and precautions must be taken to avoid exposure to foraging bees or parasitic wasps. Some of the carbamates are translocated within plants, making them an effective systemic treatment. (L795) Mechanism of Action Carbamates are effective insecticides by virtue of their ability to inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in the nervous system. They also inhibit other esterases. The carbamylation of the enzyme is unstable, and the regeneration of AChE is relatively rapid compared with that from a phosphorylated enzyme. Thus, carbamate pesticides are less dangerous with regard to human exposure than organophosphorus pesticides. The ratio between the dose required to produce death and the dose required to produce minimum symptoms of poisoning is substantially larger for carbamate compounds than for organophosphorus compounds. /Carbamate pesticides/ |
| 分子式 |
C18H26N2O5S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
382.47
|
| 精确质量 |
382.156
|
| CAS号 |
65907-30-4
|
| PubChem CID |
47759
|
| 外观&性状 |
Yellow, viscous liquid.
|
| 密度 |
1.208g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
460ºC
|
| 折射率 |
1.551
|
| LogP |
4.262
|
| tPSA |
93.61
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
26
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
502
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
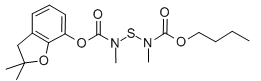
CCCCOC(=O)N(C)SN(C)C(=O)OC1=CC=CC2=C1OC(C)(C)C2
|
| InChi Key |
HAWJXYBZNNRMNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H26N2O5S/c1-6-7-11-23-16(21)19(4)26-20(5)17(22)24-14-10-8-9-13-12-18(2,3)25-15(13)14/h8-10H,6-7,11-12H2,1-5H3
|
| 化学名 |
(2,2-dimethyl-3H-1-benzofuran-7-yl) N-[butoxycarbonyl(methyl)amino]sulfanyl-N-methylcarbamate
|
| 别名 |
CGA 73102; Deltanet; Promet; Promet 666SCO; 2,4-Dimethyl-5-oxo-6-oxa-3-thia-2,4-diazadecanoic Acid 2,3-Dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-7-benzofuranyl Ester
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6146 mL | 13.0729 mL | 26.1458 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5229 mL | 2.6146 mL | 5.2292 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2615 mL | 1.3073 mL | 2.6146 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。