| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
米加司他抑制人溶酶体 a-Gal A 的 IC50 和 Ki 值为 0.04 μM [1]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
α-半乳糖苷酶 A 活性缺陷是导致法布里病(一种 X 连锁隐性遗传病)的原因 [2]。在表达人类突变体 α-Gal A (TgM) 的转基因小鼠中,米加司他(口服灌胃,每天 3 mg/kg,持续 4 周)可增强心脏、肾脏、脾脏和肝脏中的 α-Gal A 活性,并显示剂量和时间依赖效应。 )[2]。在治疗的前两周,Migasalstat 在 TgM 的所有关键问题上表现出半衰期不到一天 [2]。在转基因小鼠中,migastat(口服灌胃,每天 100 mg/kg,持续 28 天)使肾脏、心脏和皮肤中的 lyso-Gb3 水平依次降低了 64%、59% 和 81% [3]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定 [4]
细胞类型: EHK 细胞突变 α-Gal A 测试浓度: 10 μM 孵育时间: 9天 实验结果:Gb3积累和溶酶体体积减少。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male non-transgenic (Non-Tg) C57BL/6 mice; transgenic mice expressing human mutant R301Q α-Gal A (TgM), α-Gal A knockout mice (KO), in null background Mice expressing human R301Q α-Gal A (TgM/KO) [2]
Doses: 3 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); one time/day for 4 weeks Experimental Results: Triacylceramide (Gb3) in mouse kidneys Storage is Dramatically diminished. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
With absorption occurring largely in the gut, the absolute bioavailability (AUC) for a single oral 150 mg migalastat hydrochloride dose or a single 2-hour 150 mg intravenous infusion was approximately 75% and Tmax was approximately 3 hours. Plasma migalastat exposure (AUC0-∞) and Cmax demonstrated dose-proportional increases at migalastat hydrochloride oral doses from 50 mg to 1,250 mg (doses from 0.5 to 8.3-fold of the approved recommended dosage). Migalastat administered with a high-fat meal (850 calories; 56% from fat), or 1 hour before a high-fat or light meal (507 calories; 30% from fat), or 1 hour after a light meal, resulted in significant reductions of 37% to 42% in mean total migalastat exposure (AUC0-∞) and reductions of 15% to 39% in mean peak migalastat exposure (Cmax) compared with the fasting state. In a mass balance study in healthy male subjects, following oral administration of 123 mg [14C]-migalastat, approximately 77% of the total radiolabeled dose was recovered in urine and 20% of the total radiolabeled dose was recovered in feces with an overall total recovery of 98% within 96 hours post-dose. In urine, unchanged migalastat accounted for 80% of the radioactivity, which equates to 62% of the administered dose. In feces, unchanged migalastat was the only drug-related component. In plasma, unchanged migalastat accounted for approximately 77% of the plasma radioactivity, and three dehydrogenated O-glucuronide conjugated metabolites, M1 to M3, together accounted for approximately 13% of the plasma radioactivity, none of which comprised more than 6% of the radiolabeled dose. Approximately 9% of the total radioactivity in plasma was unassigned. In healthy volunteers, the volume of distribution (Vz/F) of migalastat following ascending single oral doses (25-675 mg migalastat HCl) ranged from 77 to 133 L, indicating it is well distributed into tissues and greater than total body water (42 liters). Following ascending single oral doses (25-675 mg migalastat hydrochloride), no trends were found for clearance (CL/F). At the 150 mg dose, CL/F was approximately 11 to 14 L/hr, while at 123 mg, the apparent clearance was calculated to be 12.5 L/hr. Metabolism / Metabolites Based upon in vivo data, migalastat is a substrate for uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (otherwise known as UGT or UDPGT), being a minor elimination pathway. Biological Half-Life The mean elimination half-life (t1/2) of migalastat ranges from approximately 3 to 5 hours for a single oral dose of 150 mg. For the dose of 123 mg, the mean elimination half-life was estimated to be 4 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In placebo-controlled trials, liver test abnormalities were rare and no more common with migalastat than with placebo treatment. What abnormalities occurred were mild and resolved spontaneously without need for dose interruption. During these premarketing clinical trials and since its more widespread clinical availability, no instances of acute liver injury with jaundice have been reported attributable to migalastat. However, the total clinical experience with its use has been limited. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of migalastat during breastfeeding. Because no information is available on the use of migalastat during breastfeeding caution should be used, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding There was no detectable plasma protein binding following administration of [14C]-migalastat hydrochloride in the concentration range between 1 and 100 µM. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Asano N, et al. In vitro inhibition and intracellular enhancement of lysosomal alpha-galactosidase A activity in Fabry lymphoblasts by 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin and its derivatives. Eur J Biochem. 2000 Jul;267(13):4179-86.
[2]. Ishii S, et al. Preclinical efficacy and safety of 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin in mice for Fabry disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Mar;328(3):723-31. [3]. Young-Gqamana B, et al. Migalastat HCl reduces globotriaosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb3) in Fabry transgenic mice and in the plasma of Fabry patients. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57631. [4]. Welford RWD, et al. Glucosylceramide synthase inhibition with lucerastat lowers globotriaosylceramide and lysosome staining in cultured fibroblasts from Fabry patients with different mutation types. Hum Mol Genet. 2018 Oct. 27(19):3392-3403. |
| 其他信息 |
Migalastat is a member of piperidines.
Fabry disease is a rare, progressive genetic disorder characterized by a defective GLA gene that causes a deficiency in the enzyme alpha-Galactosidase A (alpha-Gal A). This enzyme is responsible for breaking down glycosphingolipid substrate that, when deficient in patients with Fabry disease, builds up in the blood vessels, the kidneys, the nerves, the heart, and other organs. In the U.S., it is estimated that more than 3,000 people are living with Fabry disease, and an estimated more than 50 percent of these diagnosed patients are currently untreated. Migalastat (approved and sold under Amicus Therapeutics' brand name Galafold) is subsequently an oral pharmacological chaperone of alpha-Gal A for the treatment of Fabry disease in adults who have amenable GLA variants. In these patients, migalastat works by stabilizing the body’s dysfunctional alpha-Gal A enzyme so that it can clear the accumulation of glycosphingolipid disease substrate. Globally, it is estimated that approximately 35 to 50 percent of Fabry patients may have amenable GLA variants that are treatable with migalastat. Given the rarity of Fabry disease and the proportion of Fabry disease patients that could benefit from migalastat therapy, Amicus Therapeutics' brand name Galafold was approved using the Accelerated Approval pathway, under which the FDA may approve drugs for serious conditions where there is an unmet medical need and where a drug is shown to have certain effects that are reasonably likely to predict a clinical benefit to patients. A further study is required to verify and describe the clinical benefits of Galafold, and the sponsor will be conducting a confirmatory clinical trial of Galafold in adults with Fabry disease. Additionally, Galafold was also granted Priority Review designation, under which the FDA’s goal is to take action on an application within six months of application filing where the agency determines that the drug if approved, would provide a significant improvement in treating, diagnosing or preventing a serious condition over available therapies. Galafold also received Orphan Drug designation, which provides incentives to assist and encourage the development of drugs for rare diseases. As of August 2018, migalastat under Amicus Therapeutics' brand name Galafold is currently approved in Australia, Canada, European Union, Israel, Japan, South Korea, Switzerland, and the United States. Migalastat is pharmacologic chaperone of alpha-galactosidase the intrahepatic enzyme that is deficient in Fabry disease. Clinical experience with migalastat is limited, but it not been linked to serum enzyme elevations during therapy or to instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury. See also: Migalastat Hydrochloride (has salt form); Larazotide Acetate (annotation moved to). Drug Indication Migalastat is approved by the FDA for the treatment of adults with a confirmed diagnosis of Fabry disease and an amenable galactosidase alpha gene (GLA) variant based on in vitro assay data. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on a reduction in kidney interstitial capillary cell globotriaosylceramide (KIC GL-3) substrate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials. Migalastat is also approved by the EMA and Health Canada to treat the same disease, although it is approved for both adults and adolescents aged 16 years and older in Europe. FDA Label Galafold is indicated for long-term treatment of adults and adolescents aged 16 years and older with a confirmed diagnosis of Fabry disease (α-galactosidase A deficiency) and who have an amenable mutation. Mechanism of Action Fabry disease is a progressive X-linked lysosomal storage disorder that affects males and females. Fabry disease-causing mutations occur in the galactosidase alpha (GLA) gene and result in a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme alpha-galactosidase A (alpha-Gal A) that is required for glycosphingolipid substrate (GL-3 and lyso-Gb3) metabolism. Reduced alpha-Gal A activity is, therefore, associated with the progressive accumulation of glycosphingolipid substrate in vulnerable organs and tissues, which ultimately leads to the morbidity and mortality associated with Fabry disease. Migalastat is a pharmacological chaperone that reversibly binds to the active site of the alpha-galactosidase A (alpha-Gal A) protein (encoded by the galactosidase alpha gene, GLA), which is deficient in Fabry disease. This binding stabilizes alpha-Gal A allowing its trafficking from the endoplasmic reticulum into the lysosome where it exerts its action. In the lysosome, at a lower pH and at a higher concentration of relevant substrates, migalastat dissociates from alpha-Gal A allowing it to break down the glycosphingolipids globotriaosylceramide (GL-3) and globotriaosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb3). Certain GLA variants (mutations) causing Fabry disease result in the production of abnormally folded and less stable forms of the alpha-Gal A protein which, however, retain enzymatic activity. Those GLA variants, referred to as amenable variants, produce alpha-Gal A proteins that may be stabilized by migalastat thereby restoring their trafficking to lysosomes and their intralysosomal activity. The GLA mutations that are amenable and not amenable to treatment with migalastat are regularly maintained and updated on online sites that are readily accessible by healthcare providers. |
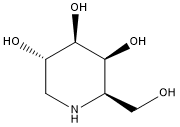
| 分子式 |
C6H13NO4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
199.63266
|
| 精确质量 |
163.084
|
| CAS号 |
108147-54-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Migalastat hydrochloride;75172-81-5
|
| PubChem CID |
176077
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.456g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
361.1ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
197.3ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
1.13E-06mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.582
|
| LogP |
-2.3
|
| tPSA |
92.95
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
5
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
11
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
132
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
| SMILES |
C1[C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@@H](CO)N1)O)O)O
|
| InChi Key |
LXBIFEVIBLOUGU-DPYQTVNSSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
1S/C6H13NO4/c8-2-3-5(10)6(11)4(9)1-7-3/h3-11H,1-2H2/t3-,4+,5+,6-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
D-Galactitol, 1,5-dideoxy-1,5-imino-
|
| 别名 |
Amigal, DDIG, Migalastat 1-Deoxygalactonojirimycin
1-Deoxygalactostatin AT1001 AT 1001 AT-1001 GR181413A GR 181413A
GR-181413A Galafold
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.0093 mL | 25.0463 mL | 50.0927 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.0019 mL | 5.0093 mL | 10.0185 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5009 mL | 2.5046 mL | 5.0093 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。