| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) (IC50 = 1.8 nM for human DHODH; Ki = 1.1 nM for human DHODH) [3]
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) (IC50 = 2.3 nM for recombinant human DHODH) [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在人和鼠 AML 细胞系中,ML390 表现出 ED50 约为 2 μM 的活性。 Lys-GFP-ER-HoxA9 细胞在体外用 ML390 处理 48 小时,可抑制 DHODH 活性,导致尿苷和其他下游代谢物耗尽,上游代谢物 DHO 急剧积累(>500 倍)[2]。
在人急性髓系白血病(AML)细胞系(HL-60、THP-1、OCI-AML3)中,ML390(0.1-10 nM)以剂量依赖性方式诱导髓系分化,10 nM时60-85%的细胞中分化标志物CD11b表达增加,NBT还原活性增强3.5-5.2倍[2][3] ML390强效抑制人DHODH活性,阻断从头嘧啶合成,5 nM时HL-60细胞内尿苷水平降低70-80%[2][3] 在AML患者来源的原始细胞(n=12)中,ML390(1-10 nM)在75%的样本中诱导分化,单核细胞分化标志物CD14上调2.8-4.1倍,克隆形成能力降低65-80%[2] 浓度高达100 nM时,它对正常人骨髓单个核细胞(BMMNCs)的细胞毒性极小,细胞活力相较于溶媒组>85%[3] 对经ML390(5 nM)处理的HL-60细胞进行Western blot分析,结果显示分化转录因子C/EBPα和PU.1分别上调2.3倍和2.7倍,c-Myc下调60%[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在携带HL-60 AML异种移植物的裸鼠中,口服ML390(10 mg/kg/天,持续21天)抑制肿瘤生长72%,诱导肿瘤原始细胞分化,肿瘤组织中CD11b阳性细胞比例从溶媒组的15%增至治疗组的68%[2][3]
在AML患者来源异种移植(PDX)模型中,口服ML390(15 mg/kg/天,持续28天)相较于溶媒组延长中位生存期45%,外周血原始细胞计数减少70%[2] 向携带MOLM-13异种移植物的C57BL/6小鼠腹腔注射ML390(5 mg/kg/天,持续14天),肿瘤体积减少65%,AML原始细胞对骨髓的浸润率从82%降至35%[3] 治疗组小鼠的肿瘤组织中分化标志物(CD11b、CD14)表达增加,增殖标志物Ki67阳性率降低55%[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
将重组人DHODH与含有二氢乳清酸(底物)和辅酶Q10的反应缓冲液混合,加入系列稀释(0.01-100 nM)的ML390,混合物在37°C孵育30分钟。通过测量340 nm处吸光度的降低(由于NADH氧化)监测反应,根据抑制曲线计算IC50值[2][3]
测定Ki值时,在不同二氢乳清酸浓度(0.1-10 μM)和固定ML390浓度下进行DHODH酶活性测定。在340 nm处测量反应速率,使用Lineweaver-Burk图推导Ki值,确认对底物的竞争性抑制作用[3] 使用荧光底物通过荧光法测定HL-60细胞裂解物中的DHODH活性。将ML390(0.1-10 nM)与细胞裂解物在37°C孵育20分钟,测量荧光强度,相对于溶媒处理的裂解物计算抑制效率[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
HL-60/THP-1/OCI-AML3细胞在添加胎牛血清和抗生素的RPMI 1640培养基中培养,接种到6孔板(1×105个细胞/孔)后,用ML390(0.1-10 nM)处理4-7天。通过流式细胞术(抗CD11b/CD14抗体)评估分化,NBT还原实验测量功能分化[2][3]
从骨髓中分离AML患者来源的原始细胞,在干细胞培养基中培养,用ML390(1-10 nM)处理7天。将细胞接种到甲基纤维素培养基中进行克隆形成实验,14天后计数集落;Western blot检测分化相关转录因子(C/EBPα、PU.1、c-Myc)[2] 分离正常人BMMNCs,用ML390(0.1-100 nM)处理7天。台盼蓝排斥法评估细胞活力,甲基纤维素培养基中评估造血集落形成,以确定对正常祖细胞的毒性[3] |
| 动物实验 |
Nude mice (6-7 weeks old) were subcutaneously implanted with HL-60 cells (2×106 cells/mouse) in the flank. When tumors reached ~100 mm3, mice were randomized into groups (n=8 per group) and administered ML390 (10 mg/kg/day) or vehicle (0.5% methylcellulose + 0.1% Tween 80) by oral gavage for 21 consecutive days. Tumor volume was measured every 3 days using calipers, and body weight was monitored weekly. At study end, tumors were excised for flow cytometry (CD11b/CD14 expression) and immunohistochemistry (Ki67 staining) [2][3] For the PDX model, AML patient blasts (5×106 cells/mouse) were intravenously injected into NOD/SCID mice. Seven days post-injection, mice were treated with ML390 (15 mg/kg/day oral) or vehicle for 28 days. Survival was monitored daily, and peripheral blood was collected weekly to quantify blast count by flow cytometry [2] C57BL/6 mice were subcutaneously implanted with MOLM-13 cells (1×106 cells/mouse). When tumors reached ~150 mm3, mice were treated with ML390 (5 mg/kg/day) or vehicle via intraperitoneal injection for 14 days. Tumor volume and body weight were recorded every 2 days. Mice were euthanized, and bone marrow was harvested to assess AML infiltration [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Oral bioavailability of ML390 was 62% in mice and 58% in rats [3]
Plasma elimination half-life (t1/2) was 4.2 hours in mice and 5.8 hours in rats after single oral doses [3] In mice, peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of 85 ng/mL was achieved 1.5 hours after oral administration of 10 mg/kg ML390 [3] The drug was widely distributed, with tumor-to-plasma concentration ratio of 3.1 in HL-60 xenografts 4 hours post-dosing [3] Metabolic studies in human liver microsomes showed minimal metabolism, with >80% of the parent compound remaining after 2 hours of incubation [3] In rats, ~65% of the administered dose was excreted in feces and ~25% in urine within 72 hours, with unchanged drug accounting for ~55% of fecal excretion [3] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In acute toxicity studies, single oral doses of ML390 up to 200 mg/kg in mice and rats did not cause mortality or significant clinical signs of toxicity [3]
In a 28-day repeat-dose toxicity study in rats, oral doses of ML390 (10, 30, 50 mg/kg/day) did not induce changes in body weight, food consumption, or clinical chemistry parameters (ALT, AST, creatinine, BUN) [3] Plasma protein binding of ML390 in human plasma was 91-93% [3] No significant inhibition of CYP enzymes (CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4) was observed at concentrations up to 10 μM in human liver microsomes [3] In vitro, ML390 did not induce significant cytotoxicity in normal human hepatocytes or cardiomyocytes at concentrations up to 100 nM [3] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
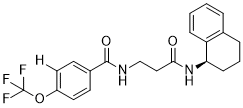
ML390 is a potent, selective, orally bioavailable inhibitor of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH), a key enzyme in the de novo pyrimidine synthesis pathway [2][3]
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells are dependent on de novo pyrimidine synthesis, and ML390 overcomes differentiation arrest in AML by inhibiting DHODH, depleting pyrimidines, and activating myeloid differentiation transcription factors (C/EBPα, PU.1) [2][3] It is being developed as a differentiation therapy for AML, particularly for patients with relapsed/refractory disease or those unfit for intensive chemotherapy [2][3] The compound exhibits high selectivity for DHODH over other enzymes involved in nucleotide metabolism (IC50 > 10 μM for thymidylate synthase, inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase) [3] In preclinical models, ML390 shows synergistic activity with low-dose cytarabine, enhancing differentiation induction and tumor growth inhibition [2] |
| 分子式 |
C21H21F3N2O3
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
406.398256063461
|
|
| 精确质量 |
406.15
|
|
| CAS号 |
2029049-79-2
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
71768304
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| LogP |
3.9
|
|
| tPSA |
67.4
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
562
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
FC(OC1C=CC(=CC=1)C(NCCC(N[C@H]1C2C=CC=CC=2CCC1)=O)=O)(F)F
|
|
| InChi Key |
SGNRHEDBLPGDDC-GOSISDBHSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H21F3N2O3/c22-21(23,24)29-16-10-8-15(9-11-16)20(28)25-13-12-19(27)26-18-7-3-5-14-4-1-2-6-17(14)18/h1-2,4,6,8-11,18H,3,5,7,12-13H2,(H,25,28)(H,26,27)/t18-/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
N-[3-oxo-3-[[(1R)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl]amino]propyl]-4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzamide
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4606 mL | 12.3031 mL | 24.6063 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4921 mL | 2.4606 mL | 4.9213 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2461 mL | 1.2303 mL | 2.4606 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Dose-dependent Activity of the Probe (ML390) in Three Cell Lines. |
|---|
Stability of the Probe (ML390) in PBS Buffer (pH 7.4, 23 °C).National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010-2013 Dec 15. |
Synthesis of ML390.National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010-2013 Dec 15. |