| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Quinolone
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
奥泽诺沙星 (OZN) 的 MIC 范围为 0.008 至 4 mg/L,对临床分离的革兰氏阳性微生物表现出强大的抗菌活性。对于 gyrA 和 grlA (parC) 基因有两个、三个或四个突变的 MRSA、MSSA、MSSE 和 MRSE 菌株,奥泽诺沙星表现出良好的活性[1]。 MSSA 和无乳链球菌菌株受 Ozenoxacin 抑制,耐药率分别 >10−10 和 5.3 × 10−10。泽诺沙星对突变株的最大 MIC 值为 8 mg/L[2]。
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Four studies were performed in which varying strengths of ozenoxacin cream, up to 2% (twice the concentration of the marketed formulation), were administered to 110 patients. Three of the studies examined systemic absorption in healthy subjects and in subjects having impetigo. The studies were performed with either single or repeated application of up to 1 g ozenoxacin cream to intact or abraded skin (up to 200 cm squared surface area). No systemic absorption was seen in 84 of 86 subjects, and negligible systemic absorption was seen at the level of detection (0.489 ng/mL) in 2 subjects. Studies regarding elimination and excretion have not yet been investigated in humans due to the negligible systemic absorption observed in clinical studies. Ozenoxacin undergoes negligible systemic absorption after its topical administration. Subsequently, since negligible systemic absorption of ozenoxacin was observed in clinical studies, tissue distribution has not been investigated in humans either. Ozenoxacin undergoes negligible systemic absorption after its topical administration. Metabolism / Metabolites Studies have demonstrated that ozenoxacin is not metabolized in the presence of fresh human skin discs and is minimally metabolized in human hepatocytes. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on ozenoxacin cream during breastfeeding. Because ozenoxacin is poorly absorbed after topical application, it is not likely to reach the bloodstream of the infant or cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants after maternal application away from the breast. Although quinolones are generally acceptable for systemic use, ozenoxacin should be avoided on the nipple because the infant could ingest the drug via licking. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding The plasma protein binding of [14 C]-ozenoxacin is moderate at ~80-85% and does not appear to be dependent on concentration. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Ozenoxacin is a member of quinolines.
To date, ozenoxacin has been used in trials studying the treatment of impetigo. As of December 11, 2017 the FDA approved Ferrer Internacional S.A.'s Xepi (ozenoxacin 1%) as a topically applied cream indicated for the treatment of impetigo caused by *Staphylococccus aureus* or *Streptococcus pyogenes* in adult and pediatric patients 2 months of age and older. Despite being a common and highly contagious bacerial skin infection that affects millions of children and adults in the United States each year, ozenoxacin cream is a novel, non-fluorinated quinolone that has demonstrated safe and effective therapy in both the adult and pediatric population. Ozenoxacin is a Quinolone Antimicrobial. Drug Indication Ozenoxacin cream is indicated for the topical treatment of impetigo caused by *Staphylococcus aureus* or *Streptococcus pyogenes* in patients aged 2 months of age and older. FDA Label Treatment of impetigo Mechanism of Action Ozenoxacin is a quinolone antibiotic drug. And, like most quinolones, ozenoxacin predominately executes its mechanism of action by entering into bacterial cells and acting to inhibit the bacterial DNA replication enzymes DNA gyrase A and topoisomerase IV. As DNA gyrase A and topoisomerase IV are essential to bacterial DNA replication activities including supercoiling, supercoil relaxation, chromosomal condensation, chromosomal decatenation and more, their inhibition is the principal action of ozenoxacin's mechanism and it has been demonstrated to be bactericidal against *S. aureus* and *S. pyogenes* organisms. Pharmacodynamics Although the exposure response relationship for ozenoxacin after it has been applied topically has not yet been studied, a formal relationship is unlikely because systemic exposure of ozenoxacin following its topical application has been measured to be negligible. |
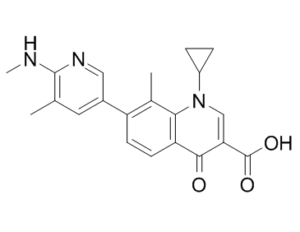
| 分子式 |
C21H21N3O3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
363.42
|
| 精确质量 |
363.158
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 69.41; H, 5.82; N, 11.56; O, 13.21
|
| CAS号 |
245765-41-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Ozenoxacin-d3
|
| PubChem CID |
9863827
|
| 外观&性状 |
Solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
573.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
300.7±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.694
|
| LogP |
3.41
|
| tPSA |
87.45
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
27
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
645
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C(C1=CN(C2CC2)C3=C(C=CC(C4=CC(C)=C(NC)N=C4)=C3C)C1=O)O
|
| InChi Key |
XPIJWUTXQAGSLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H21N3O3/c1-11-8-13(9-23-20(11)22-3)15-6-7-16-18(12(15)2)24(14-4-5-14)10-17(19(16)25)21(26)27/h6-10,14H,4-5H2,1-3H3,(H,22,23)(H,26,27)
|
| 化学名 |
1-cyclopropyl-8-methyl-7-(5-methyl-6-(methylamino)pyridin-3-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid
|
| 别名 |
GF-001001-00; M 5120; GF-001001-00; M-5120; M-5120; GF001001-00; M5120; GF-001001 00; T-3912; GF-00100100; Ozenoxacin; trade name: Xepi
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : 2.86 ~5 mg/mL (7.87~ 13.75 mM )
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7516 mL | 13.7582 mL | 27.5164 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5503 mL | 2.7516 mL | 5.5033 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2752 mL | 1.3758 mL | 2.7516 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。