| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
NA/neuraminidase(IC50 = 0.9-4.3 nM); IKK-α;STAT3;ERK1;ERK2
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
对于巨噬细胞,帕拉米韦(0.3125–40 μM,4 小时)是无毒的。在 LPS 诱导的 hPBMC 中,帕拉米韦(2–10 μM,6–12 小时)抑制细胞因子的释放[1]。
细胞培养中的抗病毒活性[5] 使用0.32至100μM的剂量联合评估了奥司他韦羧酸盐和帕拉米韦对MDCK细胞培养中病毒产量的抑制作用(表1)。单独使用奥司他韦羧酸盐在100μM时将病毒产量降低了4.4log10。32和100μM的培拉米韦使病毒产量比检测限低≥5 log10。在三种特定条件下,当10μM奥司他韦羧酸盐与3.2或10μM帕拉米韦联合使用,并使用每种抑制剂3.2μM的组合时,发现病毒滴度比预期抑制了10倍以上。图1显示了显示高于和低于预期值的数据的三维MacSynergy图。1至10μM奥司他韦和1至10微米帕拉米韦之间存在明显的协同作用区域,协同作用体积为9.1。当0.32μM帕拉米韦与3.2-32μM奥司他韦羧酸盐联合使用时,出现了轻微拮抗区域,计算出的拮抗体积为-1.7。整个表面的净效应为7.4的协同体积。 病毒神经氨酸酶抑制研究[5] 表2列出了奥司他韦羧酸盐和帕拉米韦组合对神经氨酸酶活性的影响。在10nM奥司他韦羧酸盐治疗或1-10nM帕拉米韦治疗的情况下,神经氨酸酶活性最低。大多数低剂量组合(0.01至3.2 nM奥司他韦羧酸盐与0.01至0.32 nM帕拉米韦组合)比单独使用任何一种化合物都能产生更大的抑制作用。组合使用的每种抑制剂的浓度较高(0.32至10 nM)导致的抑制作用比预期的要小。这是在一个单独使用帕拉米韦对酶活性具有高度抑制作用的区域,药物组合进一步抑制的潜力不大。数据的三维MacSynergy图如图2所示。组合的增加或减少百分比很小。低剂量组合区域的协同作用体积为86(中度协同作用),而高剂量联合区域的拮抗作用体积为-65(中度拮抗作用),整个表面的净效应为21(无差异)。 |
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
帕拉米韦(20–60 mg/kg,腹腔注射,单剂量)可减轻急性肺损伤,预防 LPS 诱导的细胞因子风暴,并延长细胞因子风暴综合征模型小鼠的生存时间[1]。
在免疫功能低下的小鼠模型中针对乙型流感病毒感染,帕拉米韦(75 mg/kg,肌肉注射,每天一次,持续 7 天)使 BALB scid 小鼠免于 BR/08 的致命攻击[2]。 |
||
| 酶活实验 |
病毒神经氨酸酶抑制试验[5]
按照制造商的说明,使用市售试剂盒在96孔实心白色微孔板中测定化合物对病毒神经氨酸酶活性的影响,如前所述(Smee等人,2010)。将半对数稀释增量的化合物与病毒(作为神经氨酸酶的来源)一起孵育。每个微孔中A/NWS/33(H1N1)流感病毒的量约为500细胞培养感染剂量。在加入化学发光底物之前,将板在37°C下预孵育10分钟。加入底物后,将平板在37°C下孵育30分钟。在加入NA Star®加速剂溶液后,立即使用Centro LB 960光度计(Berthold Technologies,Oak Ridge,TN)评估神经氨酸酶活性0.5秒。每种化合物浓度下的化学发光计数百分比基于在未处理条件下归一化为100%的计数。 |
||
| 细胞实验 |
细胞培养抗病毒研究[5]
在MDCK细胞的融合培养中测定了羧酸奥司他韦和帕拉米韦的抗病毒活性。通过在培养三天后量化病毒产量,在感染了约50%细胞培养感染剂量(CCID50)病毒的96孔微孔板中进行了检测。样品板在-80°C下冷冻。随后,将两个微孔中的培养基合并,用于制备滴定样品。每种抑制剂浓度下的病毒产量是通过终点稀释法(Reed和Muench,1938)在96孔微孔板中的新鲜MDCK细胞单层上滴定样品(以10倍稀释增量)来确定的,每次稀释使用4个微孔。在感染后3天和6天检查微孔板是否存在病毒细胞病理学。病毒滴度表示为log10CCID50/0.1ml。 |
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
The post-exposure therapeutic efficacy of peramivir was also evaluated in outbred animals (ferrets), as pharmacokinetic analysis of peramivir in ferrets showed rapid uptake into the circulation following i.m. inoculation.
Pharmacokinetic analysis indicated that the parenteral formulation of peramivir was rapidly introduced into the circulation of these mice following intramuscular inoculation. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2680697/
|
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Despite widespread use, there is little evidence that peramivir, when given as recommended as a single intravenous infusion, is associated with liver injury, either in the form of serum enzyme elevations or clinically apparent liver disease. A proportion of patients with influenza may have minor serum enzyme elevations during the acute illness, but these appear to be independent of therapy and are not exacerbated by peramivir. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because peramivir is poorly absorbed orally, it is not likely to reach the bloodstream of the infant in clinically important amounts. However, because no information is available on the use of peramivir breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. |
||
| 参考文献 | |||
| 其他信息 |
Peramivir is a member of the class of guanidines that is used (as its trihydrate) for the treatment of acute uncomplicated influenza in patients 18 years and older who have been symptomatic for no more than two days. It has a role as an antiviral drug and an EC 3.2.1.18 (exo-alpha-sialidase) inhibitor. It is a member of cyclopentanols, a member of acetamides, a member of guanidines and a 3-hydroxy monocarboxylic acid. It contains a peramivir hydrate.
Peramivir is an antiviral agent developed by Biocryst Pharmaceuticals to treat influenza A/B. The development of peramivir has been supported by the US Department of Health and Human Services as part of the government's effort to prepare for a flu pandemic. Being an influenza virus neuraminidase inhibitor, peramivir works by preventing new viruses from emerging from infected cells. Due to the poor oral bioavailability, the oral formulation of the drug was previously abandoned by Johnson and Johnson Company. The injectable intravenous formulation of peramivir was approved by the FDA in September 2017 for the treatment of acute uncomplicated influenza to pediatric patients 2 years and older who have been symptomatic for no more than two days. Peramivir is an inhibitor of the influenza neuraminidase enzyme and is used as therapy of acute symptomatic influenza A and B. Peramivir has not been associated with serum enzyme elevations during therapy or with clinically apparent liver injury. Peramivir is a cyclopentane derivative with activity against influenza A and B viruses. Peramivir is a neuraminidase inhibitor which prevents normal processing of virus particles such that virus particles are not released from infected cells. Drug Indication Peramivir is indicated for the treatment of acute uncomplicated influenza in patients six months and older who have been symptomatic for no more than two days. FDA Label Alpivab is indicated for the treatment of uncomplicated influenza in adults and children from the age of 2 years. Treatment of influenza Mechanism of Action Peramivir is an inhibitor of influenza neuraminidase, preventing new virus particles from leaving infected cells. |
| 分子式 |
C15H28N4O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
328.41
|
| 精确质量 |
328.211
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 54.86; H, 8.59; N, 17.06; O, 19.49
|
| CAS号 |
330600-85-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Peramivir trihydrate;1041434-82-5
|
| PubChem CID |
154234
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 折射率 |
1.614
|
| LogP |
-1.37
|
| tPSA |
151.03
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
5
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
23
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
460
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
5
|
| SMILES |
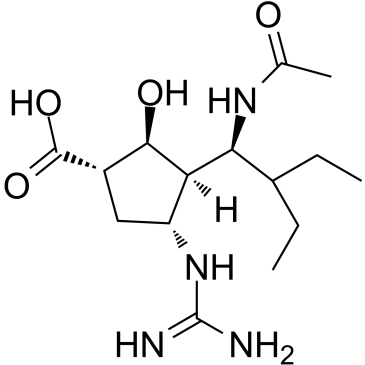
O[C@H]1[C@]([C@H](C(CC)CC)NC(C)=O)([H])[C@H](NC(N)=N)C[C@@H]1C(O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
XRQDFNLINLXZLB-CKIKVBCHSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H28N4O4/c1-4-8(5-2)12(18-7(3)20)11-10(19-15(16)17)6-9(13(11)21)14(22)23/h8-13,21H,4-6H2,1-3H3,(H,18,20)(H,22,23)(H4,16,17,19)/t9-,10+,11+,12-,13+/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(1S,2S,3R,4R)-3-((S)-1-acetamido-2-ethylbutyl)-4-guanidino-2-hydroxycyclopentanecarboxylic acid
|
| 别名 |
RWJ 270201; RWJ270201; BCX-1812; Rapiacta; 229614-55-5; Peramivir anhydrous; RAPIVAB; Brand name: Rapivab; Rapiacta and Peramiflu; BCX1812; BCX1812; BCX 1812; RWJ270201;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0450 mL | 15.2249 mL | 30.4497 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6090 mL | 3.0450 mL | 6.0899 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3045 mL | 1.5225 mL | 3.0450 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00957996 | COMPLETEDWITH RESULTS | Drug: Peramivir Drug: Peramivir |
Cough Fatigue Headache Myalgia |
BioCryst Pharmaceuticals | 2009-10 | Phase 3 |
| NCT02635724 | COMPLETEDWITH RESULTS | Drug: Peramivir | Influenza | BioCryst Pharmaceuticals | 2015-12 | Phase 3 |
| NCT02665351 | COMPLETED | Drug: Peramivir | Influenza | Chinese University of Hong Kong | 2011-02 | Phase 2 Phase 3 |
| NCT01063933 | WITHDRAWN | Drug: Peramivir | Influenza | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) | 2011-08 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT00297050 | COMPLETED | Drug: Peramivir | Influenza | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) | 2006-02-23 | Phase 1 |
|
|
|