| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 50g |
|
||
| 100g |
|
||
| 200g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Surfactant
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
分别采用膜水合法和反溶剂法制备了负载厚朴酚的混合胶束(MMs)和厚朴酚纳米混悬剂(MNs)。最佳的MMs和MNs制剂分别以1:12:5和2:1:1的比例使用厚朴酚、Soluplus®和泊洛沙姆188制备。MMs的平均粒径为111.8±14.6,MNs的平均粒度为78.53±5.4nm。MMs的包封率和载药率分别为89.58±2.54%和5.46±0.65%。MNs的载药效率为42.50±1.57%。在体外释放研究中,MMs表现出缓慢的药物释放,而MNs表现出快速的药物释放。Caco-2跨细胞转运研究的结果表明,MMs和MNs都增加了厚朴酚的渗透。如药代动力学研究所示,MMs和MNs分别显著促进胃肠道药物吸收2.85倍和2.27倍 [1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
创伤性脑损伤(TBI)是全球发病率和死亡率的主要原因,可破坏血管内皮系统的细胞膜完整性,危及血脑屏障功能并威胁细胞生存。对血管内皮系统的保护可能会增强TBI后的临床结果。泊洛沙姆188(P188)已被证明可改善缺血/再灌注(I/R)损伤后和TBI后神经元功能。我们旨在建立一种体外压缩型TBI模型,比较轻度、中度和重度损伤,以观察P188对小鼠脑微血管内皮细胞(MBEC)的直接影响。将汇合的MBEC暴露于常氧或缺氧条件下5或15小时(小时)。加入压缩1小时,并在2小时复氧期间给予P188。通过评估细胞数量/活力、细胞毒性/膜损伤、代谢活性和总一氧化氮生成(tNOp)来测试P188对MBEC的直接影响。虽然P188增强了细胞数量/活力、代谢活性和tOp,但阻止了轻度至中度损伤后细胞毒性/膜损伤的增加。在严重损伤的MBEC中,P188仅改善代谢活性。P188在复氧过程中存在,直接影响模拟I/R和压缩型TBI中的MBEC功能[2]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
代谢活性[2]
使用CellTiter 96 AQueous单溶液细胞增殖测定法测定代谢活性。四唑化合物(3-(4,5-二甲基噻唑-2-基)-5-(3-羧甲氧基苯基)-2-(4-磺基苯基)-2H-四唑鎓,内盐;MTS)被代谢活性细胞生物还原,形成可溶于培养基中的有色甲zan产物。在20–25°C下解冻90分钟后,将20µL CellTiter 96 AQueous One Solution Reagent添加到每个含有100µL培养基的孔中(达到约16.67%的浓度)。将平板在37°C的细胞培养箱中,在含5%CO2的加湿空气中培养1-4小时。在板读数器中在490nm处读取abs。最后,从总腹肌中减去空白腹肌。[2] NO总生成量[2] tOp使用开曼硝酸盐/亚硝酸盐比色测定试剂盒进行测定。一氧化氮(NO)是一种高活性、短命的自由基,在生物系统中由NO合酶(NOS)家族的酶合成,包括内皮型NOS(eNOS)、神经元型NOS(nNOS)和诱导型NOS(iNOS)。不同的细胞类型可以产生NO,包括内皮细胞。NO的主要作用是鸟苷酸环化酶的旁分泌激活,这导致细胞内环状鸟苷单磷酸的增加,导致平滑肌细胞放松。该测定通过添加亚硝酸盐(NO2−)和硝酸盐(NO3−)来测量NO的总产量,这两种物质都代表NO的最终产物。首先,NO3−暴露于NO3−还原酶,将其转化为NO2−。在第二步中,Griess试剂用于将NO2−转化为偶氮发色团。测量所得abs可以确定NO2−浓度。制备试剂和样品,并按照测定方案中的指示进行测定。简言之,将10µL的酶辅因子混合物和硝酸还原酶混合物添加到多达80µL的样品中(所得浓度:10%的酶辅剂混合物、10%的硝酸还原酶混合物、80%的样品)。在所需的孵育时间后,补充50µL Griess试剂R1和50µL Griess试剂R2(每个结果的浓度为25%)。使用平板读数器在540nm处测量abs。每当进行测定时,按照测定方案中的说明制备标准曲线。 |
| 细胞实验 |
皮尔斯乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)细胞毒性测定试剂盒(Thermo Fisher Scientific;Waltham,MA,USA)用于测定细胞毒性/膜损伤。在健康细胞中,LDH是一种胞浆酶。在质膜损伤之后,LDH被释放到培养基中。我们使用比色法,通过使用偶联酶反应测量细胞外LDH来量化细胞毒性。LDH催化乳酸盐到丙酮酸盐的反应,导致烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸从其氧化态(NAD+)还原为其还原态(NADH)。四唑盐碘硝基四唑鎓通过黄递酶使用NADH还原为红色甲酰胺产物。甲酰胺的形成与LDH的释放量成正比。这可用于指示细胞毒性/膜破坏的水平。按照制造商的说明制备和储存试剂。简言之,将含有基质混合物(冻干物)的小瓶用11.4mL超纯水稀释。将测定缓冲液解冻,同时遮光。反应混合物由0.6 mL测定缓冲液(5%)和11.4 mL底物混合物(95%)组成。首先,将每个孔的50µL介质转移到未预涂的透明96孔板上。之后,加入50µL反应混合物(达到50%反应混合物的浓度),轻轻拍打板,并使用铝箔保护板不受光照。将平板在室温下孵育。30分钟后,加入50µL停止溶液(浓度约33%)。然后,10分钟后,使用平板读数器(Synergy H1,BioTek Instruments股份有限公司)在490nm处测量培养基内的吸光度。在第二步中,将5µL裂解缓冲液(10X)加入到含有细胞和50µL残余培养基的原始平板中。将平板在37°C下孵育60分钟,并如上所述进行测定。计算吸光度(abs):
abs(培养基)/(abs[培养基]+abs[裂解的细胞])[2]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: TourniquetInduced Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats [2]
Doses: 150 mg/kg Route of Administration: intravenous/i.v. Experimental Results: dramatically decreased the elevated TBARS but not to control levels and SOD activity was at control levels. Male Sprague-Dawley rats underwent 180 minutes of tourniquet-induced ischemia. Five minutes before tourniquet release, rats received either a bolus of (1) Poloxamer-188 (P-188) (150 mg/kg; P-188 group) or (2) vehicle (Vehicle group) via a jugular catheter (n=10 per group). After 240 minutes reperfusion, both groups received a second bolus of either Poloxamer-188 (P-188) or vehicle (Vehicle) via a tail vein catheter. Sixteen hours later, rats were killed; muscle weights were determined, infarct size (2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride method), and blinded histologic analysis (hematoxylin and eosin) were performed on the gastrocnemius and tibialis anterior muscles, as well as indices of antioxidant status. [3] Experimental Procedures and Monitoring [3] Rats were randomly assigned to Poloxamer-188 (P-188) (P-188 + vehicle) or Vehicle (vehicle only) groups (n = 10 per group). Rats were weighed and anesthetized using 1.5% to 2.5% isoflurane anesthesia and analgesia was administered (buprenorphine; 0.1 mg/kg intraperitoneally). Both hind limbs were shaved and animals were instrumented with a lubricated rectal temperature probe inserted 5 cm beyond the rectal sphincter. Animals were then placed supine on a warm water flow temperature-regulated bed and core temperature was maintained at 37°C ± 1°C. Blood draining of the experimental leg was performed by elevation above the level of the heart for 5 minutes before tourniquet inflation. A pneumatic tourniquet was then applied to the proximal aspect of the elevated hind limb and inflated to a pressure of 250 mm Hg. All procedures have been detailed previously.16 Tourniquets were left in place for 180 minutes. A detailed description of the experiment is shown in Figure 1, which details all procedures including periods of anesthesia, recovery, catheterizations, and administration of drug treatments. Rats were returned to their cages and allowed ad libitum access to water and food during the periods between administering anesthesia. No resuscitation fluids were administered during the experimental period. Administration of Poloxamer-188 (P-188) [3] Sterile P-188 solution contained 150 mg/mL highly purified P-188, 3.08 mg/mL sodium chloride, 2.38 mg/mL sodium citrate, and 0.366 mg/mL citric acid. The placebo solution contained the same ingredients with the exception of Poloxamer-188 (P-188). Doses consisted of 1.0 mL/kg body weight of P-188 solution or vehicle. Injections of P-188 or vehicle were administered via tail vein. Two injections were administered at (1) 5 minutes before tourniquet release and (2) 240 minutes after tourniquet release. Rats were lightly anesthetized (1.5% isoflurane) before the second injection. This administration schedule was designed to maximize the bioavailability of P-188. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Poloxamer is an epoxide.
Poloxamer is a non-ionic triblock copolymer comprised of a hydrophobic core of polyoxypropylene flanked by two hydrophilic side chains of polyoxyethylene, that may be used as a fixative and as solubilizer, emulsifier and stabilizer in drug delivery systems. See also: Poloxalene (annotation moved to); Poloxamer 188 (annotation moved to); Poloxamer 331 (annotation moved to) ... Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI), the main contributor to morbidity and mortality worldwide, can disrupt the cell membrane integrity of the vascular endothelial system, endangering blood-brain barrier function and threatening cellular subsistence. Protection of the vascular endothelial system might enhance clinical outcomes after TBI. Poloxamer 188 (P188) has been shown to improve neuronal function after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury as well as after TBI. We aimed to establish an in vitro compression-type TBI model, comparing mild-to-moderate and severe injury, to observe the direct effects of P188 on Mouse Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells (MBEC). Confluent MBEC were exposed to normoxic or hypoxic conditions for either 5 or 15 h (hours). 1 h compression was added, and P188 was administered during 2 h reoxygenation. A direct effect of P188 on MBEC was tested by assessing cell number/viability, cytotoxicity/membrane damage, metabolic activity, and total nitric oxide production (tNOp). While P188 enhanced cell number/viability, metabolic activity, and tNOp, an increase in cytotoxicity/membrane damage after mild-to-moderate injury was prevented. In severely injured MBEC, P188 improved metabolic activity only. P188, present during reoxygenation, influenced MBEC function directly in simulated I/R and compression-type TBI.[1] Background: Skeletal muscle injury can result in significant edema, which can in turn lead to the development of acute extremity compartment syndrome (CS). Poloxamer-188 (P-188), a multiblock copolymer surfactant, has been shown to decrease edema by sealing damaged membranes in a number of tissues after a variety of injury modalities. The objective is to determine whether the administration of P-188 significantly reduces skeletal muscle edema associated with ischemia/reperfusion injury (I-R). Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats underwent 180 minutes of tourniquet-induced ischemia. Five minutes before tourniquet release, rats received either a bolus of (1) P-188 (150 mg/kg; P-188 group) or (2) vehicle (Vehicle group) via a jugular catheter (n=10 per group). After 240 minutes reperfusion, both groups received a second bolus of either P-188 (P-188) or vehicle (Vehicle) via a tail vein catheter. Sixteen hours later, rats were killed; muscle weights were determined, infarct size (2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride method), and blinded histologic analysis (hematoxylin and eosin) were performed on the gastrocnemius and tibialis anterior muscles, as well as indices of antioxidant status. Results: P-188 resulted in significantly less edema (wet weight) and reduced an index of lipid peroxidation compared with Vehicle (p<0.05). Wet:dry weight ratios were less in the P-188 group (indicating less edema). Muscle viability as indicated by 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining or routine histology did not reveal statistically significant differences between groups. Conclusion: P-188 significantly reduced ischemia-reperfusion-related muscle edema and lipid peroxidation but did not impact muscle viability. Excess edema can lead to acute extremity CS, which is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. P-188 may provide a potential adjunctive treatment for the reduction of CS.[2] The aim of this work was to investigate the effect of triblock copolymer poloxamer 188 on nanoparticle morphology, size, cancer cell uptake, and cytotoxicity. Docetaxel-loaded nanoparticles were prepared by oil-in-water emulsion/solvent evaporation technique using biodegradable poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) with or without addition of poloxamer 188, respectively. The resulting nanoparticles were found to be spherical with a rough and porous surface. The nanoparticles had an average size of around 200 nm with a narrow size distribution. The in vitro drug-release profile of both nanoparticle formulations showed a biphasic release pattern. An increased level of uptake of PLGA/poloxamer 188 nanoparticles in the docetaxel-resistant MCF-7 TAX30 human breast cancer cell line could be found in comparison with that of PLGA nanoparticles. In addition, the docetaxel-loaded PLGA/poloxamer 188 nanoparticles achieved a significantly higher level of cytotoxicity than that of docetaxel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles and Taxotere (P < .05). In conclusion, the results showed advantages of docetaxel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles incorporated with poloxamer 188 compared with the nanoparticles without incorporation of poloxamer 188 in terms of sustainable release and efficacy in breast cancer chemotherapy. [3] |
| 分子量 |
8800 (Average)
|
|---|---|
| 精确质量 |
304.115
|
| CAS号 |
9003-11-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
691397-13-4;126925-06-2;697765-47-2;9003-11-6;106392-12-5
|
| PubChem CID |
24751
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow solid
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
370.7±37.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
60-50ºC
|
| 闪点 |
160.5±26.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.452
|
| LogP |
0
|
| tPSA |
25.06
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
0
|
| 重原子数目 |
7
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
36.7
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
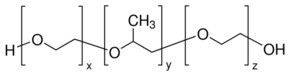
CC(COCCO)OCCO
|
| InChi Key |
OQNWUUGFAWNUME-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C7H16O4/c1-7(11-5-3-9)6-10-4-2-8/h7-9H,2-6H2,1H3
|
| 化学名 |
2-[2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)propoxy]ethanol
|
| 别名 |
Pluronic F-68; Pluronic F-127; 2-[2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)propoxy]ethanol; 721929-01-7; Therabloat (TN); ...; CAS-9003-11-6;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~100 mg/mL
Water: ~100 mg/mL Ethanol: ~100 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。